Ratepayers, Businesses, and Environmental Advocates Seek to Reverse Decision on Ratepayer Fund Raids
/Attorneys for ratepayers, efficiency businesses and environmental organizations have filed an appeal in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit in New York , asking the appellate court to reverse an October 25 U.S. District Court decision that denied plaintiffs a remedy in their lawsuit to force the State of Connecticut to restore $145 million in ratepayer dollars intended to save families money on energy bills and reduce climate pollution.
The original lawsuit, filed in May, was filed to stop the state legislature’s 2017 sweep of Connecticut’s energy efficiency and clean energy funds, and to prevent future diversions of ratepayer funds. The original complaint argued that diverting ratepayer funding to plug a budget deficit instead of using the dedicated funds for its intended purpose violates the Contract Clause and Equal Protection Clause of the United States Constitution and functions as an illegal tax on tax-exempt organizations like churches and nonprofits.
“We are pursuing the case to fix the damage the raids have done to Connecticut families and businesses,” said Roger Reynolds, chief legal director at Connecticut Fund for the Environment. “Residents trusted that their ratepayer dollars would go where their electric bills said they would—towards energy efficiency and clean energy programs that save money and cut climate pollution. Instead those hard-earned dollars were used to plug a hole in the state budget. We believe the appellate court will see that the state’s action violated federal contract and tax law, and ask them to correct that mistake to put Connecticut back on the path to a healthier energy future and a stronger economy.”
Judge Janet C. Hall at the U.S. District Court in New Haven ruled in October that the state’s 2017 budget that swept ratepayer funds did not impair contracts between ratepayers and their electric distribution companies because neither utility tariffs nor state law ever promised ratepayers that their dollars would not be transferred to the General Fund for unrelated purposes.
The organizations filing the suit pointed out that when the General Assembly found itself facing a deficit in fall 2017, they passed a budget instructing the state to “sweep” and divert the energy efficiency and clean energy funds to the general fund. However, these funds are not government property, they stressed, and were not raised through state taxes but were paid by ratepayers to utilities for specific services. Therefore, "seizing these funds amounts to taking ratepayer funds that were paid for another purpose."
As a result of the "raids", the filers of the lawsuit pointed out that "12,900 homes will not receive energy assessments, weatherization upgrades, reduced pricing on insulation, or associated energy bill savings. Furthermore, 5,600 of these are low income households that often require additional financial assistance to close the energy affordability gap. The award-winning Connecticut Green Bank leverages $6 in private investment for every $1 of renewable energy funding. Yet these sweeps resulted in a 53% reduction in this program’s budget, requiring layoffs and project cancellations."
This case raises an important legal issue relevant beyond Connecticut, according to environment groups, because it is the first time ratepayers argued in court that when they pay their utility bills with surcharges dedicated for specific programs or services—such as energy efficiency and renewable energy—enforceable contracts arise that cannot be invaded by any state.
"Connecticut’s leaders broke the trust of their constituents when they turned electric ratepayer dollars into an illegal tax,” said lead plaintiff Leticia Colon de Mejias, chair of Efficiency For All (EFA) and founder. “Even in these difficult times, it is obvious that stealing ratepayer funds intended to help Connecticut residents and businesses reduce energy waste, save money on energy bills, and access clean resources is a bad choice."
“Sierra Club Connecticut supports this legal appeal by Connecticut Fund for the Environment and allies, and the advocacy of groups including Efficiency for All, to restore the misappropriated energy efficiency monies that our General Assembly voted to take away and use as a stop gap for our budget woes" said Martha Klein, chair, Sierra Club Connecticut. "It was a myopic mistake, as these funds have been proven to create jobs, make revenue for the state, and reduce climate-destroying greenhouse gas emissions. This type of fund raiding hurts all of us in the long run. That money was taken from ratepayers specifically to improve the efficiency of our whole state, which would save all of us money on energy costs, and improve our health and climate.”
When the initial suit was filed against the state back in May, Governor Malloy issued a statement that, rather than defending the state action, seemed to take the opposite view:
"This should come as a surprise to no one. I have long maintained that these shortsighted sweeps would increase energy costs for consumers and businesses and cause untold harm to our green energy economy. [W]e should be cementing our role as a national leader in our efforts to combat climate change and protect our communities. The energy sweeps . . . represented a massive step backwards, and I continue to strongly oppose them," Malloy said.


 “I am delighted the city has joined Sustainable CT in our latest efforts to develop and implement sustainability and renewable energy initiatives in Norwalk,” said Mayor Harry Rilling. “Being energy conscience is the right thing to do as we all have a moral obligation to lessen our environmental impact. I am glad the city has taken a leadership role and joined this important sustainability initiative.” Norwalk’s Council approved the resolution to join Sustainable CT in mid-August and designated the Common Council Planning Committee as the “Sustainability Team” for the program. Norwalk was officially registered with Sustainable CT on August 24.
“I am delighted the city has joined Sustainable CT in our latest efforts to develop and implement sustainability and renewable energy initiatives in Norwalk,” said Mayor Harry Rilling. “Being energy conscience is the right thing to do as we all have a moral obligation to lessen our environmental impact. I am glad the city has taken a leadership role and joined this important sustainability initiative.” Norwalk’s Council approved the resolution to join Sustainable CT in mid-August and designated the Common Council Planning Committee as the “Sustainability Team” for the program. Norwalk was officially registered with Sustainable CT on August 24.
 Her work at C-CHANGE is designed to accelerate and strengthen public education on climate change and pollution issues, bringing the science down to the individual level, highlighting the impacts on people, rather than the planet.
Her work at C-CHANGE is designed to accelerate and strengthen public education on climate change and pollution issues, bringing the science down to the individual level, highlighting the impacts on people, rather than the planet.

 According to the Nature Conservancy, Bridgeport currently has a 19% tree canopy cover, for example. If all open spaces, vacant lots and parking lots could be planted, the city would have a 62% tree canopy cover. The ramifications would be substantial, impacting various health and quality of life factors.
According to the Nature Conservancy, Bridgeport currently has a 19% tree canopy cover, for example. If all open spaces, vacant lots and parking lots could be planted, the city would have a 62% tree canopy cover. The ramifications would be substantial, impacting various health and quality of life factors.

 The article points out that “the connection between climate change and hurricanes has become hard for anyone to ignore.”
The article points out that “the connection between climate change and hurricanes has become hard for anyone to ignore.”


 Memo of Understanding to get have 150,000 EVs on Connecticut roads by 2025.
Memo of Understanding to get have 150,000 EVs on Connecticut roads by 2025.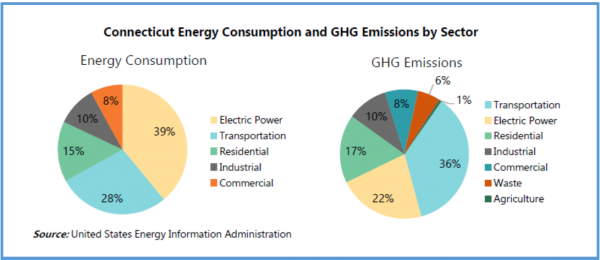
 The company - FreshBev LLC - produces two primary lines of beverages - RIPE Craft Juice and RIPE Craft Bar Juices, bringing real fresh juice to the market, and connecting local farmers to consumers by using only ingredients that could be traced back to the grower and region.
The company - FreshBev LLC - produces two primary lines of beverages - RIPE Craft Juice and RIPE Craft Bar Juices, bringing real fresh juice to the market, and connecting local farmers to consumers by using only ingredients that could be traced back to the grower and region. The results are making local history, and spreading. RIPE Craft Juices are available nationally through Whole Foods and select regional grocery chains.
The results are making local history, and spreading. RIPE Craft Juices are available nationally through Whole Foods and select regional grocery chains.
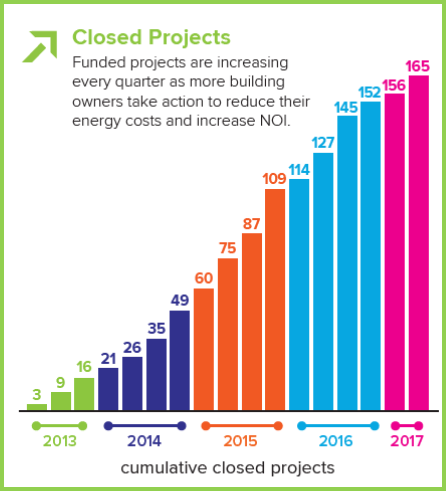 boilers, energy efficiency lighting measures, HVAC systems, and other energy improvements that help building owners to take control of their energy costs.
boilers, energy efficiency lighting measures, HVAC systems, and other energy improvements that help building owners to take control of their energy costs.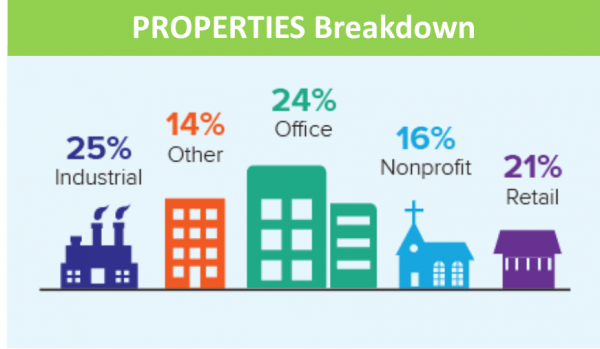 without the support of our contractors, capital providers, municipal officials, and other stakeholders who have contributed to the C-PACE movement,” said Mackey Dykes, Vice President of Commercial, Industrial and Institutional programs at the Connecticut Green Bank. “There is still significant potential for energy improvements for Connecticut businesses and non-profits, and we look forward to bringing cleaner and cheaper energy to more building owners across the state.”
without the support of our contractors, capital providers, municipal officials, and other stakeholders who have contributed to the C-PACE movement,” said Mackey Dykes, Vice President of Commercial, Industrial and Institutional programs at the Connecticut Green Bank. “There is still significant potential for energy improvements for Connecticut businesses and non-profits, and we look forward to bringing cleaner and cheaper energy to more building owners across the state.” make the financing of clean energy deployment more accessible and affordable for consumers and businesses. In 2011 the state legislature created the Connecticut Green Bank, the nation’s first green bank. It uses public funds to attract private capital investment in green energy projects. By leveraging private investment, the Green Bank significantly increases the total amount of financing available for clean energy projects.
make the financing of clean energy deployment more accessible and affordable for consumers and businesses. In 2011 the state legislature created the Connecticut Green Bank, the nation’s first green bank. It uses public funds to attract private capital investment in green energy projects. By leveraging private investment, the Green Bank significantly increases the total amount of financing available for clean energy projects.

 Tesla is prohibited from selling directly in Connecticut, Michigan, Texas, and West Virginia, according to the company. There are about 1,300 Teslas registered in Connecticut, nearly two-thirds of the electric vehicles in the state, according to the state Department of Motor Vehicles.
Tesla is prohibited from selling directly in Connecticut, Michigan, Texas, and West Virginia, according to the company. There are about 1,300 Teslas registered in Connecticut, nearly two-thirds of the electric vehicles in the state, according to the state Department of Motor Vehicles.






















