The Green Book Has Hartford Debut - Documentary Tells Real Story of Guide to Freedom Through Segregated America
/Little known by most people - regardless of race - until recently, the Green Book has recently exploded into the public consciousness.
Described as "the essential travel guide for a segregated America," within just the past two days a popular movie by that name won the Academy Award for best picture, and a documentary relating the story of real people and places that inspired the popular motion picture debuted on the Smithsonian Channel.
The documentary, "The Green Book: Guide to Freedom," was shown at a special preview at the Wadsworth Atheneum in Hartford, in a showing coordinated by the Amistad Center for Art and Culture, Comcast, and the Smithsonian Channel. It marked the third year that Comcast has joined with the Amistad Center and Smithsonian Channel to bring a special presentation to Hartford during Black History month.
Nearly 100 people were on hand for the local premiere of the documentary, which was followed by a panel discussion including Kelli Herod, Vice President of Post Production at Smithsonian Channel, and Stacey Close, Associate Vice President for Equity and Diversity at Eastern Connecticut State University, moderated by Kara Sundlun of WFSB. Amistad Center Executive Director & Curator at Large Wm. Frank Mitchell, Brad Palazzo, Comcast Director of Community Impact and Hartford Mayor Luke Bronin also spoke briefly, with Bronin saluting the "resiliance, ingenuity and determination" of those who traveled through dangerous times.
 The documentary was produced by award-winning filmmaker Yoruba Richen. It premieres this week on Smithsonian Channel, telling the story of the Green Book, launched in the 1930's by Victor Green, a black postal carrier from Harlem who created a volume that was "part travel guide and part survival guide." It helped African-Americans navigate safe passage across a dangerously segregated nation, identifying towns, hotels, restaurants and businesses that would be hospitable to African-Americans, sometimes few and far between.
The documentary was produced by award-winning filmmaker Yoruba Richen. It premieres this week on Smithsonian Channel, telling the story of the Green Book, launched in the 1930's by Victor Green, a black postal carrier from Harlem who created a volume that was "part travel guide and part survival guide." It helped African-Americans navigate safe passage across a dangerously segregated nation, identifying towns, hotels, restaurants and businesses that would be hospitable to African-Americans, sometimes few and far between.
The challenges were not only in the South. In fact, a page in the 1948 Green Book, lists locations in Connecticut - and the list does not fill the page. The locations were in Bridgeport, Hartford, New Haven, New London, Stamford, Waterbury and West Haven. Included are restaurants, hotels, tourist homes, beauty parlors, barber shops, and night clubs. The 1967 edition also includes five Hartford locations, including one - the former Bond Hotel - that is still standing to this day.
"We are proud to tell the true story behind this remarkable guide and to shine new light on this disturbing yet important period in Amerian history," said David Royle, Smithsonian Channel's Chief Programming officer.
The documentary tells the story of the rise of the African American middle class in Detroit, and the iconic A.G. Gaston Motel in Birmingham, Alabama - a pivotal location in the civil rights movement. It also recalls that during its 1950s heyday, the Idlewild Resort in Michigan was a magnet for black culture and entertainment, with a booming nightlife featuring famous performers like Louis Armstrong, Sarah Vaughan and Dinah Washington. In the Q&A in Hartford following the advance showing, one audience member recalled her family owning property at the Idlewild - a local connection that the panel did not expect, but was clearly pleased to learn.
"At Comcast NBC Universal diversity and inclusion is a fundamental part of our company culture and are crucial components to all of our efforts to create and deliver the best and boldest technology and entertainment for our customers," noted Palazzo. "The Green Book: Guide to Freedom screening is another way for us to bring diverse entertainment and story-telling locally to Hartford-area residents." Comcast, with Connecticut offices in Berlin, has partnered with the Amistad on a number of initiatives over the years and "are proud to play a small role in helping them to tell their cultural story."
The Amistad Center for Art & Culture, located in the Wadsworth Atheneum, celebrates art and culture influenced by people of African descent through education, scholarship and social experiences.
Victor Green looked forward to the day people wouldn't need the Green Book. In the 1949 edition he wrote,
There will be a day sometime in the near future when this guide will not have to be published. That is when we as a race will have equal opportunities and privileges in the United States. It will be a great day for us to suspend this publication for then we can go wherever we please, and without embarrassment. But until that time comes we shall continue to publish this information for your convenience each year.
The year the Civil Rights Act passed, in 1964, was the Green Book’s last. As the panelists in Hartford noted, more than 50 years later, the struggle for equality continues.



 Current pricing for roundtrip flights in May: from $78 to Raleigh/Durham and Orlando, from $118 to Denver, depending upon length of stay and day of the week of selected flights.
Current pricing for roundtrip flights in May: from $78 to Raleigh/Durham and Orlando, from $118 to Denver, depending upon length of stay and day of the week of selected flights.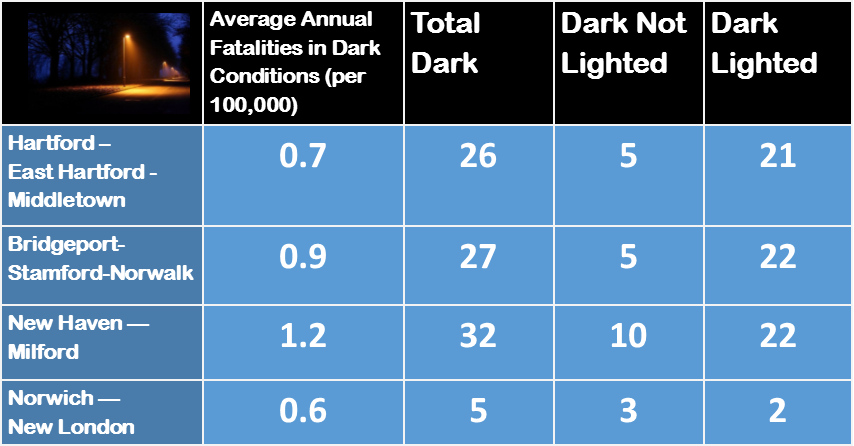

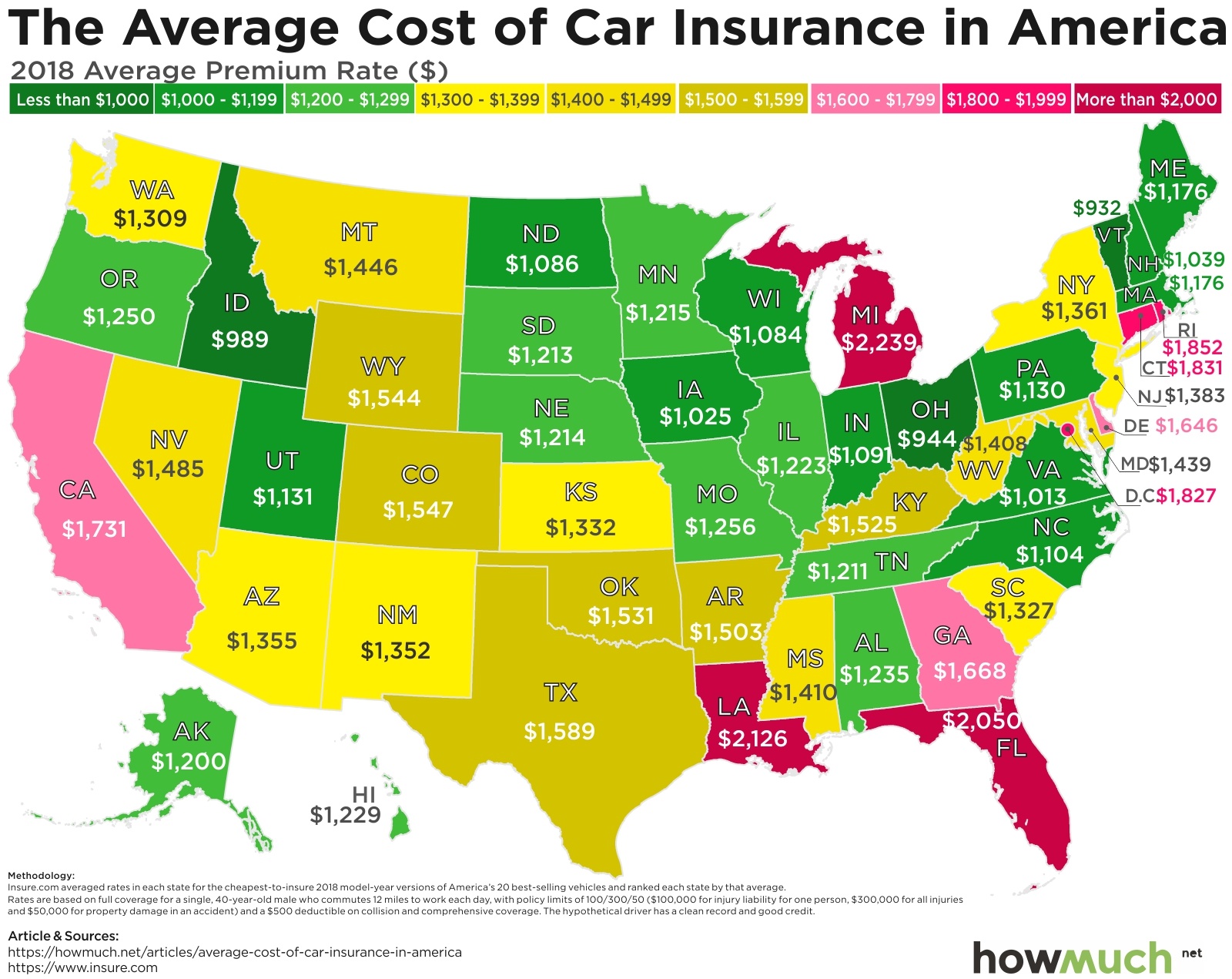
 The characterization of two of the state’s largest cities as potential “suburbs” of New York and Boston, seemingly overlooking Bradley International Airport and Tweed-New Haven in the process, has raised questions from officials.
The characterization of two of the state’s largest cities as potential “suburbs” of New York and Boston, seemingly overlooking Bradley International Airport and Tweed-New Haven in the process, has raised questions from officials.
 Cohen, who has received national recognition in his field, praised the CTrail Hartford line - which connects New Haven, Hartford, and Springfield, MA - and CTfasttrak bus line – which links Hartford and New Britain - noting that “we are starting to see residential and business development near the stations, and this is one of the big benefits of transit.”
Cohen, who has received national recognition in his field, praised the CTrail Hartford line - which connects New Haven, Hartford, and Springfield, MA - and CTfasttrak bus line – which links Hartford and New Britain - noting that “we are starting to see residential and business development near the stations, and this is one of the big benefits of transit.” The accelerated change in attitude at DOT since Redeker took the helm in 2011 was evident in his being warmly introduced as a friend prior to his keynote address – not the adversary that previous vehicle-centric commissioners may have been. He went on to highlight the department’s work on state projects, and in concert with municipalities, that is steadily transforming Connecticut into a more pedestrian and bike-friendly state.
The accelerated change in attitude at DOT since Redeker took the helm in 2011 was evident in his being warmly introduced as a friend prior to his keynote address – not the adversary that previous vehicle-centric commissioners may have been. He went on to highlight the department’s work on state projects, and in concert with municipalities, that is steadily transforming Connecticut into a more pedestrian and bike-friendly state.


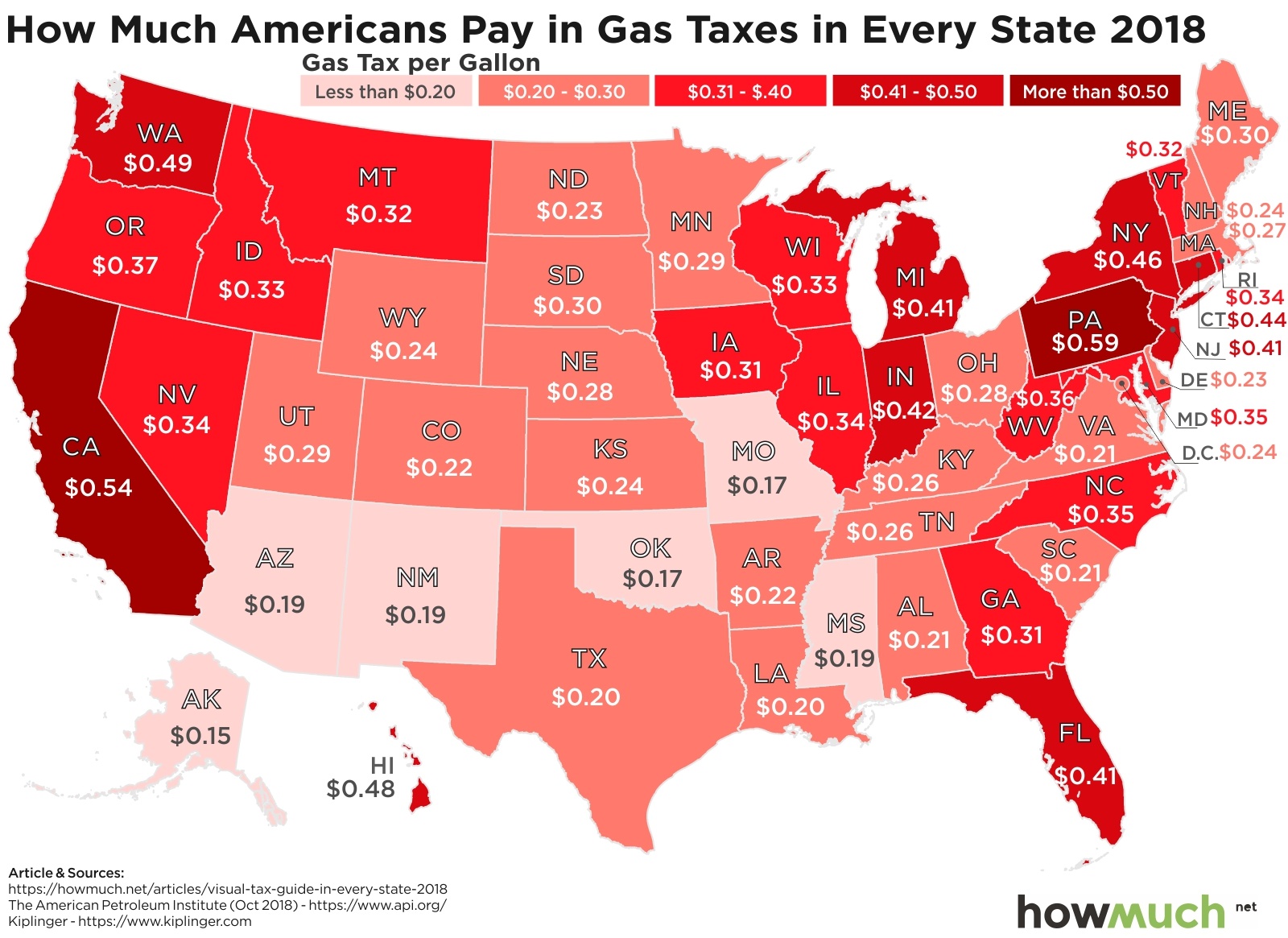
 In total, 27 states have raised or reformed their gas taxes since 2013. Indiana instituted a 10-cent increase in 2017; Oregon approved a 10-cent phase-in that began this year. The South Carolina legislature overrode a Governor’s veto to enact a 12-cent-per- gallon increase in the tax rate to be phased in over 6 years, according to data compiled by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Oklahoma’s legislature approved a 3 cent increase this year - that state’s first since 1987.
In total, 27 states have raised or reformed their gas taxes since 2013. Indiana instituted a 10-cent increase in 2017; Oregon approved a 10-cent phase-in that began this year. The South Carolina legislature overrode a Governor’s veto to enact a 12-cent-per- gallon increase in the tax rate to be phased in over 6 years, according to data compiled by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Oklahoma’s legislature approved a 3 cent increase this year - that state’s first since 1987.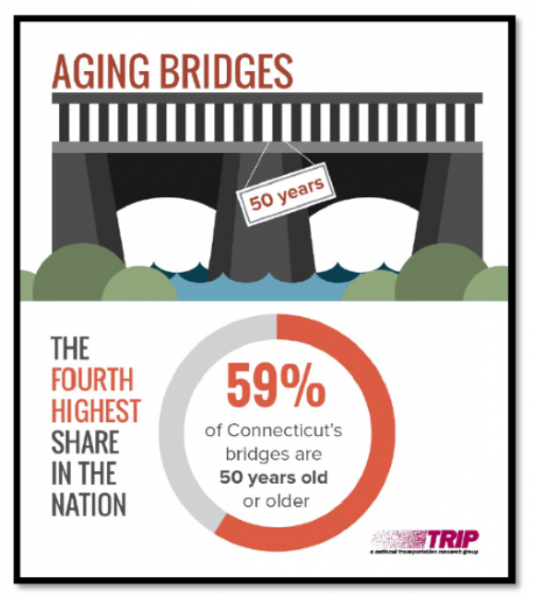 Yesterday, it was announced that 59 percent of Connecticut’s more than 4,000 bridges are 50 years or older, the fourth highest rate in the nation. The average age of all Connecticut’s bridges is 53 years, while the average age of the state’s 308 structurally deficient bridges – seven percent of the total - is 69 years. Structurally deficient bridges in Connecticut are crossed daily by 4.3 million vehicles.
Yesterday, it was announced that 59 percent of Connecticut’s more than 4,000 bridges are 50 years or older, the fourth highest rate in the nation. The average age of all Connecticut’s bridges is 53 years, while the average age of the state’s 308 structurally deficient bridges – seven percent of the total - is 69 years. Structurally deficient bridges in Connecticut are crossed daily by 4.3 million vehicles.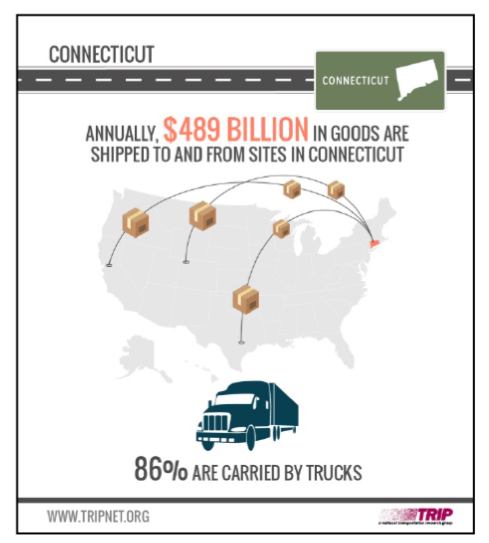 The report also noted that “annually, $489 billion in goods are shipped to and from sites in Connecticut, largely by truck,” adding that “approximately 731,000 full-time jobs in Connecticut in key industries like tourism, retail sales, agriculture and manufacturing are completely dependent on the state’s transportation network.”
The report also noted that “annually, $489 billion in goods are shipped to and from sites in Connecticut, largely by truck,” adding that “approximately 731,000 full-time jobs in Connecticut in key industries like tourism, retail sales, agriculture and manufacturing are completely dependent on the state’s transportation network.” Overall, data for Connecticut compiled by the American Hotel & Lodging Association indicate that the state’s 400 properties in the hotel industry generate 55,000 hospitality jobs and 27,00 hotel hobs, which result in $4.4 billion guest spending at hotels, local businesses and on transportation. The industry contributes $5.1 billion to GDP.
Overall, data for Connecticut compiled by the American Hotel & Lodging Association indicate that the state’s 400 properties in the hotel industry generate 55,000 hospitality jobs and 27,00 hotel hobs, which result in $4.4 billion guest spending at hotels, local businesses and on transportation. The industry contributes $5.1 billion to GDP.