A public hearing this month on a proposal to “eliminate the restriction on the length of Runway 2-20 at Tweed-New Haven Airport, was, in some ways, deju vu all over again, as advocates for ramping up flights in and out of Tweed came to the State Capitol to urge action.
A decade ago, in 2009, supporters of the regional airport came to the Capitol seeking state funds to fuel growth. This year, the focus is on runway expansion to do the same. The common thread: economic development.
“To realize the region’s full potential as a destination, the airport must improve its infrastructure to support an expanded schedule of flights to additional destinations,” said Ginny Kozlowsi, then president and CEO of the Greater New Haven Convention & visitors Bureau, in 2009.
This month, she was back at the Capitol, as executive director of REX Development: “The retention and recruitment of businesses are essential for the economic success of Connecticut. With the limited flights currently available at Tweed new Haven Regional Airport, it is difficult for companies in Southern Connecticut to access current clients, attract talent and secure more business.”
In testimony this month, Garrett Sheehan, the president and CEO of the Greater New Haven Chamber of Commerce, pointed out that “The ability to bring people to New Haven and efficiently travel to other locations would greatly improve if Tweed New Haven Airport had additional flights and destinations. It is our expectation that expanding the runway from 5600 feet to 6600 feet, within the airport’s existing footprint, will open the door for new commercial service at Tweed.”
Sheehan noted that today “business is conducted on a global scale. The New Haven region is home to thriving manufacturers, biotech companies, tech startups, and other important businesses. These companies have employees that travel regularly and customers and suppliers who need to visit.”
He named the local organizations and businesses supporting what he described as “a better Tweed”: Avangrid, Alexion, Arts Council of Greater New Haven, Arvinas, ASSA ABLOY, Biorez, CA White, CT Bio, CT Tourism Coalition, DISTRICT New Haven, Ferguson & McGuire Insurance, Fitstyle by Shana, Marcum, My Language Link, New Haven Manufacturing Association, Prometheus Research, Radiall USA, Inc., Regional Water Authority, Technolutions, The Outtrim Group, Ulbrich Stainless Steels and Special Metals, and Yale New Haven Health.
One of them, ASSA ABLOY, testified ten years ago, when vice president Jack Dwyer stated: “A clear function of business travel efficiency is proximity to an airport…and having Tweed as a viable alternative is viewed by our management team and owners as being a factor in our ongoing and future success.”
In its testimony this month, Yale New Haven Health senior vice president Vin Petrini, chief policy and communications officer, pointed out that “Yale New Haven Health is currently the largest private employer in Connecticut with more than 25,000 employees located in nearly every town, city and legislative district in the State. We also have the distinction of being the State’s largest taxpayer having paid more than $300 million in provider taxes last year alone.”
Petrini said “Tweed represents the second most underserved region in the nation,” stating that action on the legislation would unleash a “key linchpin in the economic future of the region and the state of Connecticut.”
Ryan Duques, chairman of Madison’s Economic Development Commission, a tech startup managing partner and the former publisher of 15 Connecticut newspapers, and told lawmakers that “Tweed is vital to the economic sustainability of south-central Connecticut,” adding that “it is our expectation that this change will open the door for new commercial service at Tweed with additional destinations and flights.”
The words of former Southern Connecticut State University president Cheryl Norton a decade ago could easily have been said this month: “a robust regional airport would provide another travel option to our crowded roadways and trains.”
https://youtu.be/M1i8brlb16I












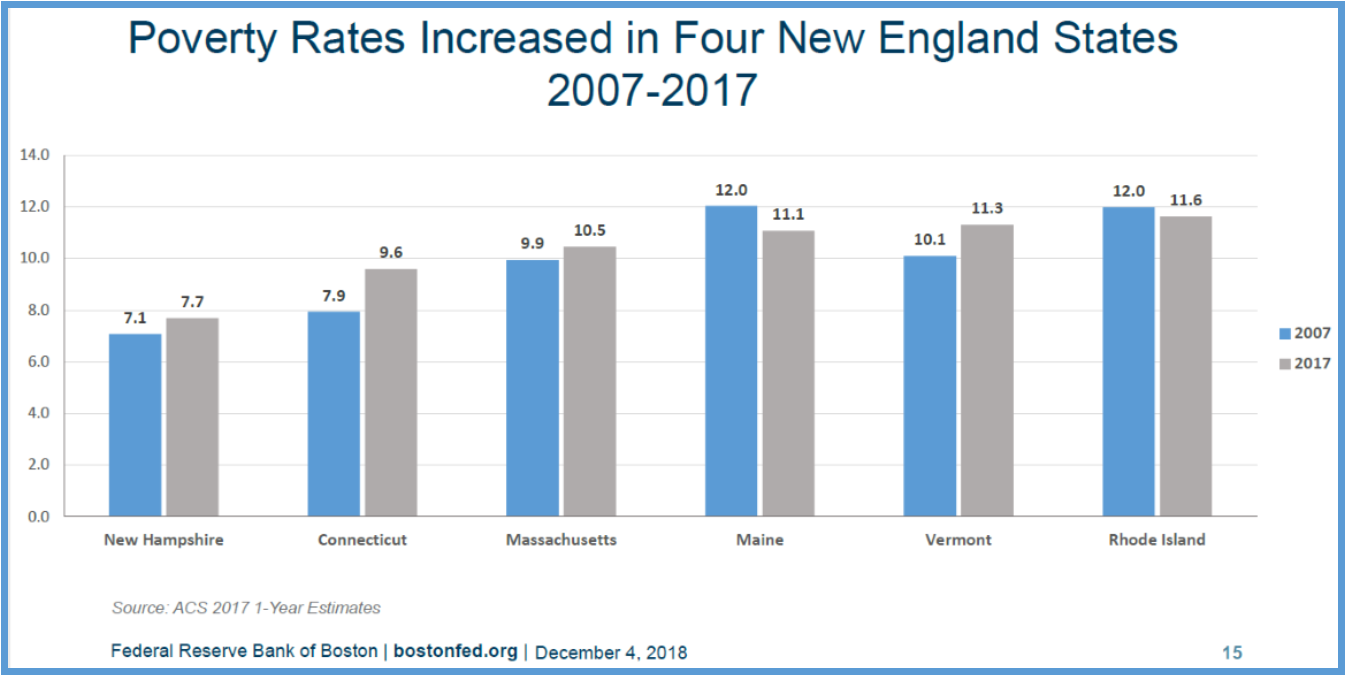
 Although poverty rates declined in all New England states between 2014 and 2017, as of 2017 four out of the six states exhibit higher poverty rates than they did in 2007. Among the region’s unemployed workers, the poverty rate as of 2017 is higher than it was in 2007, and it’s also higher than it was in 2010, after the recession had officially ended, the Boston Fed
Although poverty rates declined in all New England states between 2014 and 2017, as of 2017 four out of the six states exhibit higher poverty rates than they did in 2007. Among the region’s unemployed workers, the poverty rate as of 2017 is higher than it was in 2007, and it’s also higher than it was in 2010, after the recession had officially ended, the Boston Fed 



























