It was established in the final hours of the 2018 legislative session, and held its first meeting the following month, back in June. Special Act 18-8 created Connecticut’s Blockchain Working Group, with little fanfare and less notice. The objective: make recommendations to the incoming 2019 legislature that will “help promote innovation and economic growth by reducing barriers to and expediting the expansion of the state's blockchain industry.”
While the Task Force was getting started, another blockchain initiative was grabbing headlines. Seven Stars Cloud announced in early July that it was planning to purchase the former University of Connecticut campus in West Hartford to develop a $283 million financial technology hub that would attract more than 50 companies, along with a research institute and training center, with blockchain technology being the centerpiece.
Local zoning approvals are pending, and the state has agreed to loan the company $10 million for renovations to the 58-acre property, and to forgive the loan if the company employs 330 people there over five years. In late August, the company changed its name to Ideanomics.
The legislation calls for the leaders of the legislature’s Commerce Committee – Republicans and Democrats – to jointly appoint and convene a working group to develop a master plan for fostering the expansion of the blockchain industry in the state and recommend policies and state investments to make Connecticut a leader in blockchain technology. It calls for the “master plan” to:
- Identify the economic growth and development opportunities presented by blockchain technology;
- assess the existing blockchain industry in the state;
- review workforce needs and academic programs required to build blockchain expertise across all relevant industries; and
- make legislative recommendations that will help promote innovation and economic growth by reducing barriers to and expediting the expansion of the state's blockchain industry.
A final report and recommendations is due on January 1, 2019.
The Working Group, which met initially on June 28 in Stamford, is chaired by Nick Kammerman of Westport-based Chateaux. Members include David Noble (UConn Business School), Don Tirea (Checkmate Inc.), Jamil Hasan (Blockchain Consultant), Kevin Hart (Green Check Verified), Emily Goodman Binick (Blockchain Consultant), Margaret Feeney (Nat West Markets), Bryant Eisenbach (DappDevs), Spencer Curry (Trifecta Ecosystems), Philip Bradford (UConn Engineering School) and Stephen Ehrlich (Crypto Trading Technologies). Legislators participating in the Working Group are Senators Joan Hartley and L. Scott Frantz and Representatives Caroline Simmons and Dave Yaccarino. State Economic and Community Development Commissioner Catherine Smith serves as an ex-officio member.
Among the tax treatments the Working Group discussed preliminarily at the meeting, according to the official Minutes, were creating “tax incentives for companies that create blockchain products or use them who are currently in the state or coming to the state,” “changing laws to give blockchain industries access to banks in order to pay taxes,” and “figuring out how the state of Connecticut can implement a system to help blockchain/cryptocurrency companies and individuals pay taxes and fees.”
Testifying in support of the legislature this spring, Spencer Curry, CEO and co-founder of Trifecta Ecosystems, explained that “blockchain stands to revolutionize global industries by creating new revenue models and driving costs down on existing revenue models, automating processes with smart contracts, increasing traceability/visibility, and hardening security to malicious attackers.”
Supriyo B. Chatterjee of West Hartford noted that “blockchain has arrived in the Connecticut industries andwith it brings high-vbalue jobs that will contribute significantly to the Connecticut economy.” He pointed out that blockchain will have a “profound effect on the health sciences industry,” as well as the insurance industry and STEM jobs, and will “fundamentally change the distribution of goods and services worldwide.”
Curry went on to suggest that “supporting this technology will benefit Connecticut’s workforce through an infusion of excellent talent from around the world. If the State does not embrace blockchain technology, it … will only hasten the corporate flight from our state.” He said that “if the State chooses to empower companies exploring blockchain technologies, then a new wave of prosperity and success awaits these tried and true Connecticut industries,” such as insurance, advanced manufacturing, healthcare, financial, agriculture and military supply chain.
Commissioner Smith, one of the seven people to submit testimony on the bill, told the Commerce Committee at the March public hearing that the department lacks “the in-house expertise to conduct an informed analysis” of “all facets of blockchain technology.” The original version of the bill included $200,000 allocation for the Department of Economic and Community Development to conduct the study. The Senate amendment eliminated the funding allocation.
Don Tirea of DappDevs indicated that a blockchain initiative that “incentivizes research and development for enterprises and startups, coupled with a highly skilled tech talent pipeline is a recipe for economic revitalization across Connecticut’s historic industries. He added that embracing blockchain technology would create a “shift in our nation’s perspective of Connecticut’s ability to innovate”
Co-sponsors of the original legislation (Senate Bill 443), which was later amended in the Senate, included Senators Michael McLachlan, Heather Somers, Scott Frantz, and George Logan. House co-sponsors included Caroline Simons, Michael Winkler, Livvy Floren, Laura Devlin and Linda Orange.

 Leading the way in the five-year analysis, released this month, are Barnstable in Massachusetts, at 13.7 percent employment growth; in New Hampshire it is Portsmouth at 10.1 percent, in Rhode Island, Providence/Warwick at 7.7 percent; Maine the greatest job growth has been in Portland/South Portland at 7.1 percent. Vermont is the only New England state with a leading city growing jobs at lower rate than Connecticut’s – Burlington/South Burlington at .8 percent. Only Alaska and Wyoming are lower, rounding out the 50 states.
Leading the way in the five-year analysis, released this month, are Barnstable in Massachusetts, at 13.7 percent employment growth; in New Hampshire it is Portsmouth at 10.1 percent, in Rhode Island, Providence/Warwick at 7.7 percent; Maine the greatest job growth has been in Portland/South Portland at 7.1 percent. Vermont is the only New England state with a leading city growing jobs at lower rate than Connecticut’s – Burlington/South Burlington at .8 percent. Only Alaska and Wyoming are lower, rounding out the 50 states.


 The analysis, by the financial services website WalletHub, was based on 40 key indicators of livability, ranging from housing costs to school-system quality to restaurants per capita. The indicators were grouped into five categories – affordability, economic health, education & health, safety, and quality of life.
The analysis, by the financial services website WalletHub, was based on 40 key indicators of livability, ranging from housing costs to school-system quality to restaurants per capita. The indicators were grouped into five categories – affordability, economic health, education & health, safety, and quality of life.
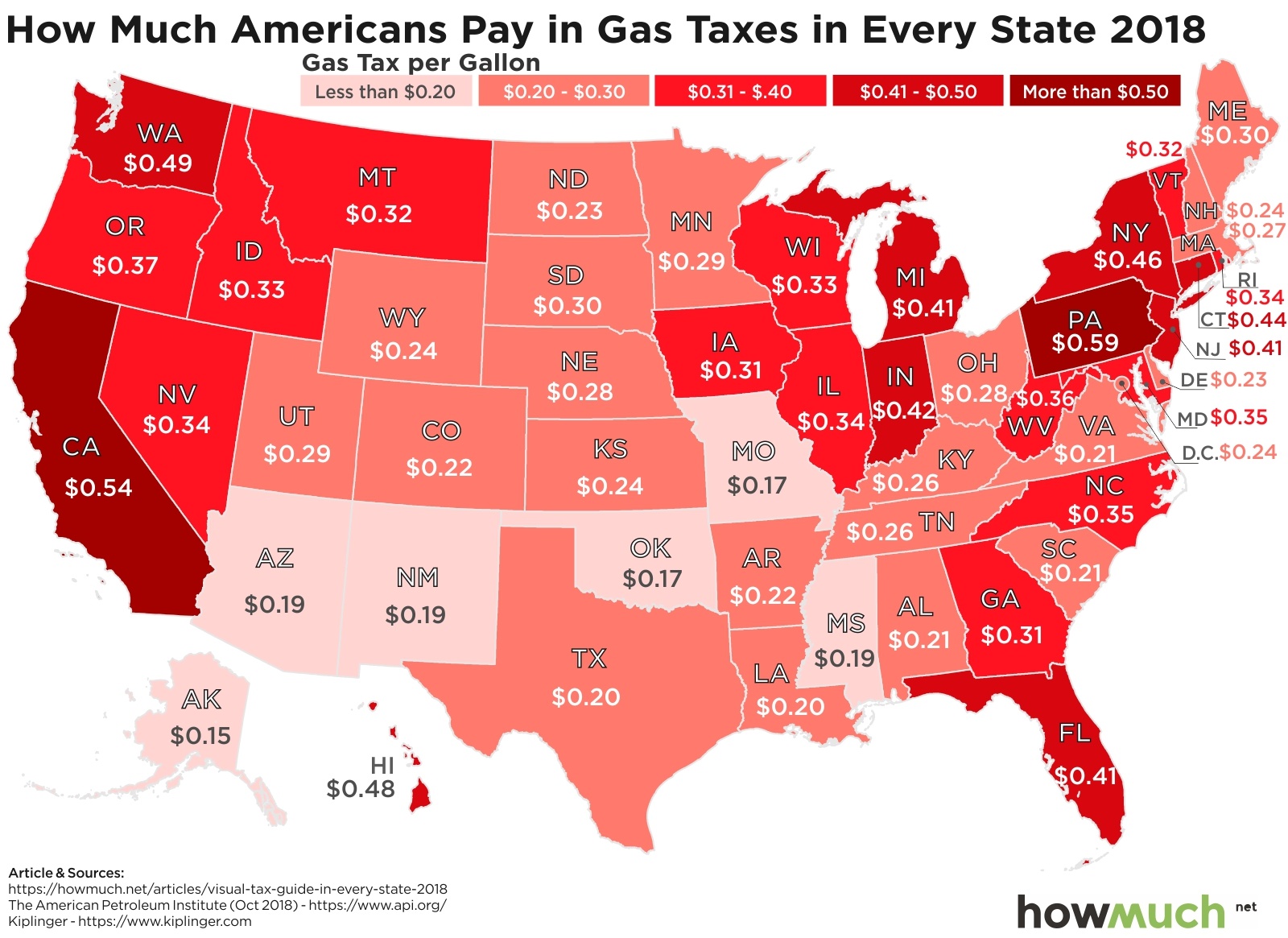
 In total, 27 states have raised or reformed their gas taxes since 2013. Indiana instituted a 10-cent increase in 2017; Oregon approved a 10-cent phase-in that began this year. The South Carolina legislature overrode a Governor’s veto to enact a 12-cent-per- gallon increase in the tax rate to be phased in over 6 years, according to data compiled by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Oklahoma’s legislature approved a 3 cent increase this year - that state’s first since 1987.
In total, 27 states have raised or reformed their gas taxes since 2013. Indiana instituted a 10-cent increase in 2017; Oregon approved a 10-cent phase-in that began this year. The South Carolina legislature overrode a Governor’s veto to enact a 12-cent-per- gallon increase in the tax rate to be phased in over 6 years, according to data compiled by the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Oklahoma’s legislature approved a 3 cent increase this year - that state’s first since 1987. The survey revealed that residents are not satisfied with the current health care system: 80 percent agree or strongly agree that “the system needs to change.” When given more than 20 options, they focused on the high prices charged by industry players, citing most frequently as a “major reason” for high health care costs:
The survey revealed that residents are not satisfied with the current health care system: 80 percent agree or strongly agree that “the system needs to change.” When given more than 20 options, they focused on the high prices charged by industry players, citing most frequently as a “major reason” for high health care costs:


 The comprehensive assessment of Hartford’s ecosystem also noted that “Hartford’s [startup] founders claim to have the right ambition to go global,” concluding that “Hartford’s startups have more potential to strengthen Global Market Reach and Global Connectedness.” In a number of areas analyzed in the assessment, Hartford is seen as having potential to strengthen the local startup community, its reach beyond Hartford, and the demographic of startup teams.
The comprehensive assessment of Hartford’s ecosystem also noted that “Hartford’s [startup] founders claim to have the right ambition to go global,” concluding that “Hartford’s startups have more potential to strengthen Global Market Reach and Global Connectedness.” In a number of areas analyzed in the assessment, Hartford is seen as having potential to strengthen the local startup community, its reach beyond Hartford, and the demographic of startup teams.




 The VentureClash competition started with applications from 300 companies from more than 15 countries. After two rounds of judging, nine finalists were named, and they then went on to compete at the live pitch event. The judges included investors and subject-matter experts from Greycroft Partners, Oak HC/FT, Real Ventures, Stanley Ventures, Teamworthy Ventures, Travelers and the Royal Bank of Scotland.
The VentureClash competition started with applications from 300 companies from more than 15 countries. After two rounds of judging, nine finalists were named, and they then went on to compete at the live pitch event. The judges included investors and subject-matter experts from Greycroft Partners, Oak HC/FT, Real Ventures, Stanley Ventures, Teamworthy Ventures, Travelers and the Royal Bank of Scotland.


 “This aging population has contributed to diminished economic growth, with Connecticut being one of only four states in the country with contracting output. This occurred while its population growth was nearly at the bottom for all states, along with having one of the largest contractions of prime working-age adults,” S&P noted in their analysis. “The outlook is equally dim. We expect the state's higher concentration of middle-aged and elderly residents compared with young adults and children to worsen.”
“This aging population has contributed to diminished economic growth, with Connecticut being one of only four states in the country with contracting output. This occurred while its population growth was nearly at the bottom for all states, along with having one of the largest contractions of prime working-age adults,” S&P noted in their analysis. “The outlook is equally dim. We expect the state's higher concentration of middle-aged and elderly residents compared with young adults and children to worsen.” It went on to explain that “upon further look, there is a profound distinction among the projected population shift when broken down by age. Between 2010 and 2040, Connecticut’s age 65 years and over population is on pace to increase by 57%. However, its population between the ages of 20-64 is projected to grow less than 2% and the population age 18 and under is projected to decline by 7%.”
It went on to explain that “upon further look, there is a profound distinction among the projected population shift when broken down by age. Between 2010 and 2040, Connecticut’s age 65 years and over population is on pace to increase by 57%. However, its population between the ages of 20-64 is projected to grow less than 2% and the population age 18 and under is projected to decline by 7%.”



























