Disconnected Youth: Fewer in Connecticut Than Nationally; Disparities Reduced But Continue
/Fewer young people across the country are disconnected from school and work today than were before the Great Recession, according to new national data. The 2015 youth disconnection rate, 12.3 percent, is below the 2008 rate of 12.6 and well below the 2010 youth disconnection peak, 14.7 percent.
All of Connecticut’s five Congressional Districts show lower rates of disconnected youth than the national average.
That’s a 16 percent drop over five years translates to roughly 900,000 fewer young people cut off from pathways that lead to independent, rewarding adulthoods, according to data compiled by the Social Science Research Council.
The report, “Promising Gains, Persistent Gaps,” compares the degree of youth disconnectedness in Congressional Districts across the country.
Disconnected youth are teenagers and young adults between the ages of 16 and 24 who are neither in school nor working. Being detached from both the educational system and the labor market during the pivotal years of emerging adulthood can be dispiriting and damaging to a young person, and the effects of youth disconnection have been shown to follow individuals for the rest of their lives, resulting in lower incomes, higher unemployment rates, and negative physical and mental health outcomes. The harms accrue not only to young people themselves, but reverberate across time and place, making youth disconnection a national concern that must be addressed by society at large.
Youth disconnection rates vary enormously by congressional district—from an impressively low rate of 4.4 percent in Wisconsin District 2, the mostly urban Madison area, to an alarmingly high rate of 23.1 percent—or nearly one in every four young people—in Kentucky District 5 in rural Appalachia.
Connecticut fares relatively well. Northeastern and Midwestern congressional districts have lowest rates of youth disconnection, 11.1 percent on average.
 Connecticut’s best ranked Congressional district is the 2nd, in Eastern Connecticut, with an 8.7 percent of youth ages 16-24 disconnected, ranking 60th among the nation’s 435 Congressional districts. Next best if Connecticut’s 5th district, in Western Connecticut, ranked 116th with 9.9 percent disconnected youth. The 3rd C.D. ranks 134th, at 10.1 percent; the 4th C.D ranks 104th with 10.3 percent; and the 1st C.D. ranks 167th at 10.9 percent.
Connecticut’s best ranked Congressional district is the 2nd, in Eastern Connecticut, with an 8.7 percent of youth ages 16-24 disconnected, ranking 60th among the nation’s 435 Congressional districts. Next best if Connecticut’s 5th district, in Western Connecticut, ranked 116th with 9.9 percent disconnected youth. The 3rd C.D. ranks 134th, at 10.1 percent; the 4th C.D ranks 104th with 10.3 percent; and the 1st C.D. ranks 167th at 10.9 percent.
On average, a gap of 7.4 percentage points separates the best and worst districts within a state. Connecticut’s gap is only 2.2 percentage points.
The greatest disparity is found in New York State; a worrisome 15.2 percentage points separate New York’s District 20 in the Albany area (7.1 percent) and District 15 in New York City’s South Bronx (22.3 percent).
The most equitable state in terms of youth disconnection is also found in the Northeast; a nearly negligible 0.1 point separates Maine’s District 1, which hugs the southern coast and includes the capital, Augusta (9.8 percent), and District 2, a more rural district that encompasses most of the state (9.7 percent).
The analysis found that nationally, young women are slightly less likely to be disconnected than young men. And there is “astonishing variation in disconnection rates by race and ethnicity.” The share of young people cut off from workforce and educational opportunities, the report found, ranges from only one in fourteen Asian American youth to more than one in four Native American youth. The Asian American youth disconnection rate is 7.2 percent; the white rate is 10.1 percent; the Latino rate is 14.3 percent; the black rate is 18.9 percent; and the Native American rate is 25.4 percent.
The report concludes that “at-risk youth need the kind of support from communities and institutions that other young people take for granted: safe places to live and food on the table; caring adults to help them navigate the often-bewildering transition from child to adult; opportunities to try new things, to fail, and to try again; and experiences that build not just hard and soft skills for the marketplace, but also self-knowledge, agency, and confidence.”



 The Office “actively assists local, national and international motion picture, TV and media production entities with finding locations in Connecticut, rules and procedures, securing permits, hiring local cast and crew and other services,” according to the agency’s website. In addition, the Office “represents the state and its agencies, municipalities and resident media professionals in interactions with media production entities and the industry at large.”
The Office “actively assists local, national and international motion picture, TV and media production entities with finding locations in Connecticut, rules and procedures, securing permits, hiring local cast and crew and other services,” according to the agency’s website. In addition, the Office “represents the state and its agencies, municipalities and resident media professionals in interactions with media production entities and the industry at large.” venue in the city. Ralph Edwards/Stu Billett Productions received nearly $4 million in tax credits in fiscal year 2016, spending just over $13 million in the state on a number of prominent program productions.
venue in the city. Ralph Edwards/Stu Billett Productions received nearly $4 million in tax credits in fiscal year 2016, spending just over $13 million in the state on a number of prominent program productions.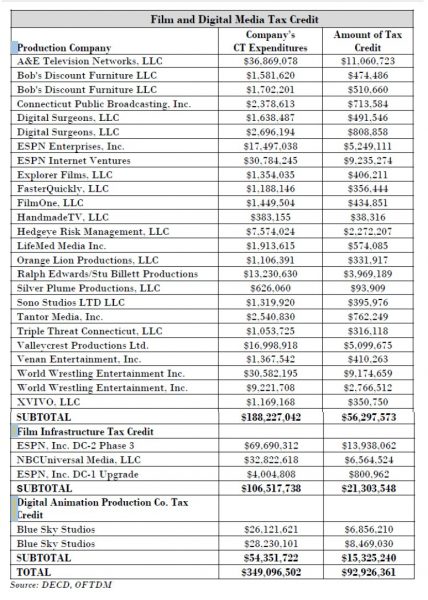

 The five-story building will see researchers will move in to the new space this summer, beginning in July. It will be the first structure on the Storrs campus to utilize an “open lab” concept for research. The shared research space and open floor plan is intended to make it easier for scientists from different disciplines to collaborate, fostering innovation,
The five-story building will see researchers will move in to the new space this summer, beginning in July. It will be the first structure on the Storrs campus to utilize an “open lab” concept for research. The shared research space and open floor plan is intended to make it easier for scientists from different disciplines to collaborate, fostering innovation, 

 “More than Food focuses on promoting healthy food in pantries and helping people access other resources to find a job. We’re proud to support a partnership that is trying to find a solution to the hunger problem,” said Chris Traczyk, executive director of the Farmington Bank Community Foundation. “It’s a comprehensive, collective-impact project.” Dr. Katie Martin, assistant professor and director of the Public Health Program at USJ, and her research team developed a nutrition stoplight system called Supporting Wellness at Pantries, or “SWAP”, which helps food pantry clients choose healthier foods.
“More than Food focuses on promoting healthy food in pantries and helping people access other resources to find a job. We’re proud to support a partnership that is trying to find a solution to the hunger problem,” said Chris Traczyk, executive director of the Farmington Bank Community Foundation. “It’s a comprehensive, collective-impact project.” Dr. Katie Martin, assistant professor and director of the Public Health Program at USJ, and her research team developed a nutrition stoplight system called Supporting Wellness at Pantries, or “SWAP”, which helps food pantry clients choose healthier foods.

 The Connecticut Technology Council's annual
The Connecticut Technology Council's annual  Data used to create the ranking were collected from U.S. Census Bureau, Bureau of Labor Statistics, National Science Foundation, National Center for Education Statistics, Georgetown University’s Center on Education and the Workforce, United States Patent and Trademark Office, Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation, Tax Foundation, Consumer Technology Association, Akamai Technologies, U.S. Cluster Mapping Project and National Venture Capital Association.
Data used to create the ranking were collected from U.S. Census Bureau, Bureau of Labor Statistics, National Science Foundation, National Center for Education Statistics, Georgetown University’s Center on Education and the Workforce, United States Patent and Trademark Office, Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation, Tax Foundation, Consumer Technology Association, Akamai Technologies, U.S. Cluster Mapping Project and National Venture Capital Association.

 Sung Soon Gavel won a CLS to study Korean at Chonnam National University in Gwangju, South Korea. The CLS Korean Program in Gwangju, Korea provides students opportunities to learn Korean both inside the classroom and in an immersive cultural setting during an intensive 8-week language program set in Korea’s sixth-largest city located just south of Seoul. Students receive a minimum of 20 hours per week of classroom instruction where they learn the four major skills of speaking, listening, reading and writing in Korean.
Sung Soon Gavel won a CLS to study Korean at Chonnam National University in Gwangju, South Korea. The CLS Korean Program in Gwangju, Korea provides students opportunities to learn Korean both inside the classroom and in an immersive cultural setting during an intensive 8-week language program set in Korea’s sixth-largest city located just south of Seoul. Students receive a minimum of 20 hours per week of classroom instruction where they learn the four major skills of speaking, listening, reading and writing in Korean.

 In terms of average student debt, among the states with the highest levels, after Connecticut, are New Hampshire (#49), Pennsylvania (#48), Rhode Island (#47), Delaware (#46), Massachusetts (#45), New Jersey (#44), Minnesota (#43), Iowa (#42), South Carolina (#41), and New York (#40).
In terms of average student debt, among the states with the highest levels, after Connecticut, are New Hampshire (#49), Pennsylvania (#48), Rhode Island (#47), Delaware (#46), Massachusetts (#45), New Jersey (#44), Minnesota (#43), Iowa (#42), South Carolina (#41), and New York (#40). 46,440 students, according to the website. The 4th Congressional District has a total college enrollment of 21,537, just behind the 3rd District (46,440) and 5th District (22,451). The 2nd Congressional District has the smallest enrollment total in the state, at 11,605.
46,440 students, according to the website. The 4th Congressional District has a total college enrollment of 21,537, just behind the 3rd District (46,440) and 5th District (22,451). The 2nd Congressional District has the smallest enrollment total in the state, at 11,605.

 During the working group’s December meeting, which ran just over an hour, participants from 27 colleges and universities, including the presidents of most of the institutions, discussed the challenges and opportunities to advance innovation and entrepreneurship on their campuses and in the state.
During the working group’s December meeting, which ran just over an hour, participants from 27 colleges and universities, including the presidents of most of the institutions, discussed the challenges and opportunities to advance innovation and entrepreneurship on their campuses and in the state.



























