US DOT Looks to Future of Transportation Infrastructure, Taps College Consortium Including UConn for $14.2 Million Initiative
/Connecticut’s deteriorating transportation infrastructure, and the lack of sufficient funding to make needed improvements, have been in the news often in recent months. While not an immediate solution to pressing challenges, an announcement from the U.S. Department of Transportation may provide encouragement for those seeking longer-term remedies. The U.S. DOT has selected the University of Maine to lead the creation of a highly competitive University Transportation Center (UTC), to focus on “improving the curability and extending the life of transportation infrastructure.”
The initiative, to include the University of Connecticut and the Connecticut Department of Transportation, will be called the Transportation Infrastructure Durability Center (TIDC). TIDC aims to help save taxpayer dollars by extending the life of transportation assets, including bridges, roads and rail.
The U.S. DOT will provide as much as $14.2 million over five years for the UMaine-led coalition including UConn, University of Rhode Island, University of Massachusetts Lowell, University of Vermont, and Western New England University.
Additional partners include representatives from the Maine Department of Transportation (MDOT), Vermont Agency of Transportation, Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT), Connecticut Department of Transportation (ConnDOT), Rhode Island Department of Transportation (RIDOT), and the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) Transportation and Development Institute.
“Along with our partners from all New England states, we look forward to leading research to extend the life of existing bridges, construct longer-lasting assets, and reduce costs for the DOT and the public,” said Dr. Habib Dagher, founding executive director of the UMaine Advanced Structures and Composites Center, and center director of the newly formed TIDC Center.
Officials explain that working with state DOTs, the new TIDC will seek to identify new materials and technologies that maximize the impact of transportation infrastructure investments. The center will work along four pathways:
- develop improved road and bridge monitoring and assessment tools;
- develop better ways to strengthen existing bridges to extend their life;
- use new materials and systems to build longer-lasting new bridges and accelerate construction; and
- use new connectivity tools to enhance asset and performance management while promoting workforce development, the release said.
According to the U.S. DOT, each University Transportation Center is a consortium of two- and four-year colleges and universities that come together to form a unique center of transportation excellence on a specific research topic.
“Together, they advance U.S. technology and expertise in the many disciplines comprising transportation through education, solutions-oriented research and technology transfer, and the exploration and sharing of cutting-edge ideas and approaches,” USDOT explains.
 The U.S. DOT invests in the future of transportation through its University Transportation Centers (UTC) Program, which awards and administers grants to consortia of colleges and universities across the United States. In the Northeast, other consortia with the same policy focus include a 9-institution UTC led by Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey and a 6-institution group led by Pennsylvania State University.
The U.S. DOT invests in the future of transportation through its University Transportation Centers (UTC) Program, which awards and administers grants to consortia of colleges and universities across the United States. In the Northeast, other consortia with the same policy focus include a 9-institution UTC led by Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey and a 6-institution group led by Pennsylvania State University.
Other groupings include a 10-institution consortium led by the University of Florida devoted to reducing congestion; a 6-institution effort to promote safety led by the University of Michigan and a 8-institution initiative to improve mobility of people and goods coordinated by the University of Southern California.
The newly announced TIDC will harness the experience of 28 faculty researchers, including a team of five engineering faculty members from UConn, led by Civil and Environmental Engineering Department Professor Ramesh B. Malla, and will train 280 student researchers from all New England states. It will focus on real infrastructure needs identified by DOT partners, and prioritize extending the life of existing transportation assets to ensure cost-effectiveness.
“As a regional and national leader in transportation-related research, UMaine is prepared and ready to take on this work,” said U.S. Sen. Angus King of Maine. “The creation of this new center will allow the university to expand its efforts to tackle the infrastructure problems facing communities not just in Maine, but across the country. This project has the potential to save taxpayer money and improve quality of life.”
“We are eager to partner with this program to support research that will offer new technologies and techniques that ensure taxpayer investments continue to be maximized while also extending the lifespan of our investments,” said Maine DOT Commissioner David Bernhardt. Officials noted that member universities of the new TIDC have an extensive record of accomplishments in transportation infrastructure research, education and technology transfer.
New England’s transportation infrastructure faces unique challenges due to harsh winter weather and short construction seasons. According to ASCE, Nearly 30 percent of New England roads are rated in poor condition which, on average, costs each motorist $584 annually in extra vehicle repairs and operating costs. Nationally, driving on roads in need of repair costs U.S. motorists $120.5 billion.
Since 1987, the UTC program has advanced transportation research and technology at colleges and universities across the country. Every five years, academic institutions nationwide compete to form their region’s UTC.



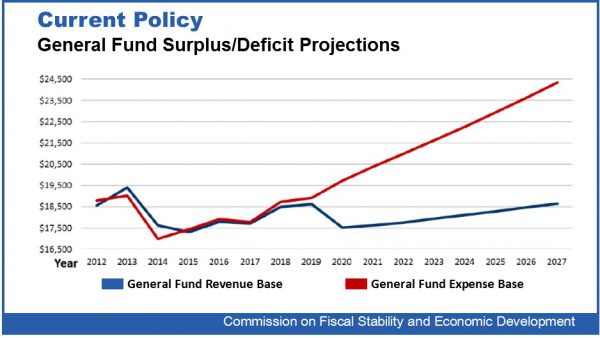 Smith and Robert Patricelli, former CEO & Founder of Women's Health USA, who co-chaired the panel, were featured along with Commission member Cindi Bigelow, CEO of Bigelow Tea, at an event coordinated by the Hartford Business Journal last week. It was one of nearly 100 forums, discussions and one-on-one meetings that the co-chairs and other commission members have had since their findings and recommendations were issued.
Smith and Robert Patricelli, former CEO & Founder of Women's Health USA, who co-chaired the panel, were featured along with Commission member Cindi Bigelow, CEO of Bigelow Tea, at an event coordinated by the Hartford Business Journal last week. It was one of nearly 100 forums, discussions and one-on-one meetings that the co-chairs and other commission members have had since their findings and recommendations were issued.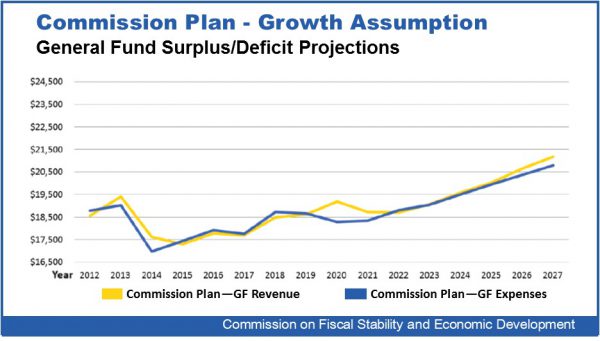
 The co-chairs say it is understandable that more was not done with the Commission’s recommendations during the short 2018 legislative session, largely because an election was just around the corner. Instead, the legislature opted to have the Office of Policy and Management (OPM) coordinate two studies, soon to get underway. One would look at the Commission’s recommendations that involve “rebalancing of state taxes to better stimulate economic growth without raising net new taxes”; the other would conduct a study of the proposal for reform of the Teachers' Retirement System.
The co-chairs say it is understandable that more was not done with the Commission’s recommendations during the short 2018 legislative session, largely because an election was just around the corner. Instead, the legislature opted to have the Office of Policy and Management (OPM) coordinate two studies, soon to get underway. One would look at the Commission’s recommendations that involve “rebalancing of state taxes to better stimulate economic growth without raising net new taxes”; the other would conduct a study of the proposal for reform of the Teachers' Retirement System.
 The survey found that 38 percent of students whose grades were mostly A’s texted or e-mailed while driving a car on at least one occasion in the 30 days prior to the survey. The percentage was slightly less among students with lower grades: 31% of students with mostly B’s, 30% of students with mostly C’s and 23% of students with mostly D’s and F’s.
The survey found that 38 percent of students whose grades were mostly A’s texted or e-mailed while driving a car on at least one occasion in the 30 days prior to the survey. The percentage was slightly less among students with lower grades: 31% of students with mostly B’s, 30% of students with mostly C’s and 23% of students with mostly D’s and F’s. More than a dozen Connecticut companies had a presence in the state’s pavilion at the event: Jackson Laboratory, Sema4, Genotech Matrix, AlvaHealth, RallyBio, Cantor Colburn, Pfizer, e-Path Learning, Thetis Pharmaceuticals, XViVO, Clarity Quest, Lucerna, Wyant Simboli, Boehringer Ingelheim, Aeromics, LambdaVision, Pattern Genomics.
More than a dozen Connecticut companies had a presence in the state’s pavilion at the event: Jackson Laboratory, Sema4, Genotech Matrix, AlvaHealth, RallyBio, Cantor Colburn, Pfizer, e-Path Learning, Thetis Pharmaceuticals, XViVO, Clarity Quest, Lucerna, Wyant Simboli, Boehringer Ingelheim, Aeromics, LambdaVision, Pattern Genomics. All told, there were more than 1,000 companies from dozens of nations represented at the 25th anniversary conference. The organizations
All told, there were more than 1,000 companies from dozens of nations represented at the 25th anniversary conference. The organizations 

 by the Common Core Standards and provides a pathway for 21st Century Skills.
by the Common Core Standards and provides a pathway for 21st Century Skills. Globally-Focused Coursework would require at least 7.0 credits or demonstration of mastery and Globally-focused Student Activities would require competency in global citizenship through active participation in “at least one or more co-curricular and other school-sponsored or endorsed activities over at least 3 years of their high school experience with suggested involvement of a total of at least 15 hours.”
Globally-Focused Coursework would require at least 7.0 credits or demonstration of mastery and Globally-focused Student Activities would require competency in global citizenship through active participation in “at least one or more co-curricular and other school-sponsored or endorsed activities over at least 3 years of their high school experience with suggested involvement of a total of at least 15 hours.”
 As he further established his career, Church traveled to remote places to sketch majestic scenes unfamiliar to his American audience, turning them into dramatic, large-scale paintings. These travels provided Church with ideas and material to produce major paintings for his wealthy patrons, including prominent American industrialists and financiers such as Hartford’s Timothy Mather Allyn, J. Pierpont Morgan and firearms manufacturer Elizabeth Hart Jarvis Colt.
As he further established his career, Church traveled to remote places to sketch majestic scenes unfamiliar to his American audience, turning them into dramatic, large-scale paintings. These travels provided Church with ideas and material to produce major paintings for his wealthy patrons, including prominent American industrialists and financiers such as Hartford’s Timothy Mather Allyn, J. Pierpont Morgan and firearms manufacturer Elizabeth Hart Jarvis Colt.






 Honored at the event, and participating in a conversation moderated by CBS News medical correspondent Dr. Max Gomez, highlighting their work in the field, were:
Honored at the event, and participating in a conversation moderated by CBS News medical correspondent Dr. Max Gomez, highlighting their work in the field, were:





























