CT is 24th in U.S., 2nd in New England in International Students; Numbers Rising
/There were 15,278 international students enrolled at Connecticut collegiate institutions during the 2017-18 academic year, which represents an increase of 4 percent over the previous year and a 63 percent increase since 2012.
In academic year 2017-18, Connecticut ranked second in New England and 24th in the U.S. in international student enrollment, according to the 2018 Open Doors report released by the nonprofit Institute of International Education (IIE) and the U.S. Department of State’s Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs (ECA).
Between AY 2012-13 and AY 2017-18, Yale University and the University of Connecticut took the top spots as the universities with the largest share of international students in Connecticut.
International students represent a big economic injection for New England, the report points out. In academic year 2017-18, international students contributed $39.4 billion to the overall U.S. economy, with $4.2 billion added to the New England economy alone. Between 2012 and 2018, international students contributed a total of $21.3 billion to the New England economy. Foreign students contributed an estimated $584 million to Connecticut’s economy in the past year, according to the report, which was highlighted recently by the New England Board of Higher Education.
The number of international students in New England has increased every year since 2012 and the region’s growth on this measure now outpaces the nation. In the 2017-18 academic year, the region enrolled 6.3 percent more international students than the previous academic year (AY). This figure compares to a national increase of only 1.5 percent during the same period.
 Both public and private nonprofit institutions in New England saw a 61 percent rise in the number of foreign students over a five-year period from AY 2012-13 to AY 2017-18, which is comparable to the national growth in the international student population over the same period.
Both public and private nonprofit institutions in New England saw a 61 percent rise in the number of foreign students over a five-year period from AY 2012-13 to AY 2017-18, which is comparable to the national growth in the international student population over the same period.
International students have helped forestall a nationwide enrollment crisis. The total higher education population in the U.S. topped out in 2010 at about 21 million students and has been slowly declining since then. The decline in New England is especially acute. This has been countered to some extent by growth of the foreign student population, coupled with a rise in online enrollment, which together comprise almost a quarter of the nation’s students.
The data indicates that there were 9,350 international students enrolled in Connecticut colleges and universities in 2012; 14,711 in 2017 and 15,278 in 2018. The number of international students increased from 2017 to 2018 in every New England state with the exception of New Hampshire, which saw a slight decrease. Only Massachusetts has more international students than Connecticut, among the six New England states.




 CCAT and the University of Hartford have a long history of working together developing programs, obtaining grant funding, sharing equipment and facilities, and ensuring that students have interesting research projects as well as hands-on learning opportunities through internships and experiential education. This is the latest program collaboration.
CCAT and the University of Hartford have a long history of working together developing programs, obtaining grant funding, sharing equipment and facilities, and ensuring that students have interesting research projects as well as hands-on learning opportunities through internships and experiential education. This is the latest program collaboration.

 Bye will begin serving as the Commissioner-designate later this month. Her nomination will be sent to the General Assembly for confirmation. Earlier in her career, Bye was director of the University of Saint Joseph School for Young Children and Trinity College Community Child Center preschools, and was early childhood director at the Capitol Region Education Council (CREC), where she supervised the birth to three program for CREC, and also helped to open two early childhood magnet schools. She was later elected to the Board of Education in West Hartford, then to the State House and State Senate. Reelected last fall, she did not take the oath of office last week in order to accept Lamont’s
Bye will begin serving as the Commissioner-designate later this month. Her nomination will be sent to the General Assembly for confirmation. Earlier in her career, Bye was director of the University of Saint Joseph School for Young Children and Trinity College Community Child Center preschools, and was early childhood director at the Capitol Region Education Council (CREC), where she supervised the birth to three program for CREC, and also helped to open two early childhood magnet schools. She was later elected to the Board of Education in West Hartford, then to the State House and State Senate. Reelected last fall, she did not take the oath of office last week in order to accept Lamont’s  Unlike a previous iteration of this federal grant program – which focused on expanding preschool for four year-olds – the new grant focuses on child success from to zero to five, with an emphasis on infants and toddlers. Further, officials said, it calls on states to look beyond the classroom to broader measures of child and family success, including mental and physical health, family stability, and parental employment. Because such considerations involve multiple agencies, it calls on states to advance a cross-system data and performance infrastructure, asking them to cost-effectively implement new solutions with an emphasis on measurable outcomes.
Unlike a previous iteration of this federal grant program – which focused on expanding preschool for four year-olds – the new grant focuses on child success from to zero to five, with an emphasis on infants and toddlers. Further, officials said, it calls on states to look beyond the classroom to broader measures of child and family success, including mental and physical health, family stability, and parental employment. Because such considerations involve multiple agencies, it calls on states to advance a cross-system data and performance infrastructure, asking them to cost-effectively implement new solutions with an emphasis on measurable outcomes. DEI is a national, transparent, annual benchmarking tool that offers businesses an opportunity to receive an objective score, on a scale of zero (0) to 100, on their disability inclusion policies and practices. The
DEI is a national, transparent, annual benchmarking tool that offers businesses an opportunity to receive an objective score, on a scale of zero (0) to 100, on their disability inclusion policies and practices. The 

 NACE is the leading source of information nationwide on the employment of the college educated, and forecasts hiring and trends in the job market; tracks starting salaries, recruiting and hiring practices, and student attitudes and outcomes; and identifies best practices and benchmarks.
NACE is the leading source of information nationwide on the employment of the college educated, and forecasts hiring and trends in the job market; tracks starting salaries, recruiting and hiring practices, and student attitudes and outcomes; and identifies best practices and benchmarks.
 In addition, “the unemployment rate in [metro] Hartford for adults with at least a bachelor's degree is the lowest in all the metropolitan areas analyzed, whereas last year, it was in the middle of the pack.”
In addition, “the unemployment rate in [metro] Hartford for adults with at least a bachelor's degree is the lowest in all the metropolitan areas analyzed, whereas last year, it was in the middle of the pack.”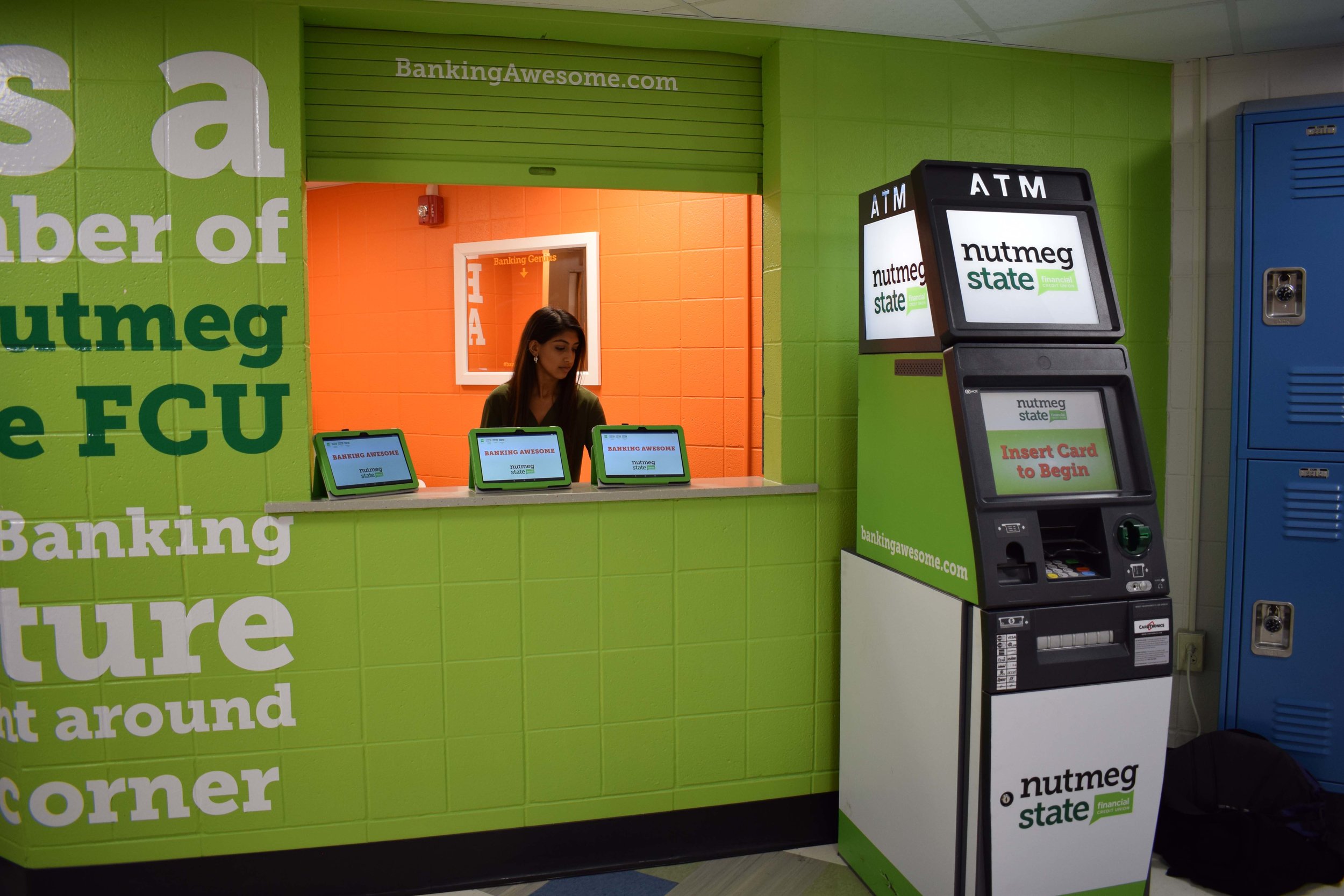
 Because the technology is intuitive for most students, their transaction time can be used to talk about subjects they may be less familiar with – such as balancing a checkbook, how debit cards and account balances relate to each other, loans and interest rates, and what a credit score is all about. Not the typical teen conversation, but Holt indicates that students have been quite interested in learning more.
Because the technology is intuitive for most students, their transaction time can be used to talk about subjects they may be less familiar with – such as balancing a checkbook, how debit cards and account balances relate to each other, loans and interest rates, and what a credit score is all about. Not the typical teen conversation, but Holt indicates that students have been quite interested in learning more.



























