National Leader, Connecticut Green Bank Reaches Milestone in Project Financing
/The Connecticut Green Bank’s C-PACE program recently surpassed $100 million in closed project financing. Out of the 19 states with C-PACE (Commercial Property Assessed Clean Energy) programs, this project financing level is second only to California, according to officials.
The Connecticut Green Bank’s C-PACE program reached the milestone of $100 million in total closed project financing. The solar photovoltaic (PV) and energy efficiency projects, which vary in size and scope, are saving more than $9.29 million annually in energy costs for nearly 170 building owners across multiple sectors. 
The Green Bank, which administers the C-PACE program, seeks to make green energy more accessible and affordable to commercial and industrial property owners by providing no money down long-term financing for meaningful energy upgrades to their buildings.
C-PACE enables building owners to finance qualifying energy efficiency and renewable energy improvements through a voluntary assessment on their property tax bill. As the program grows, more Connecticut businesses can achieve lower energy costs. Reaching $100 million in closed project financing reaffirms Connecticut’s program as a national leader, officials indicated.
Since its inception in 2011, 166 C-PACE projects have been closed in 69 of the 128 municipalities that have opted into the program. C-PACE funds have been used in manufacturing facilities, non-profits, houses of worship, retail establishments, office buildings, and other business entities. The projects consist of solar installations, new 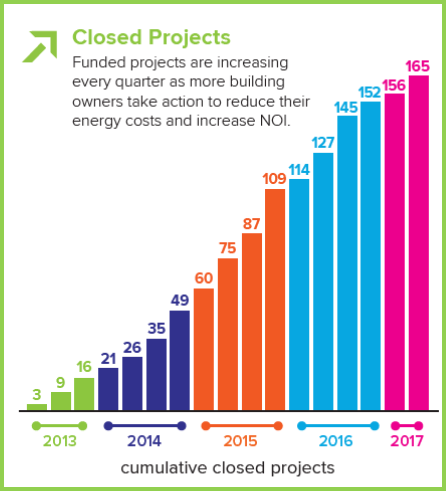 boilers, energy efficiency lighting measures, HVAC systems, and other energy improvements that help building owners to take control of their energy costs.
boilers, energy efficiency lighting measures, HVAC systems, and other energy improvements that help building owners to take control of their energy costs.
“Connecticut’s Green Bank has really been the national leader for C-PACE,” said David Gabrielson, the Executive Director of PACENation, the national non-profit that supports development of PACE programs nationwide. “The way they administer their program has really served as a great example for other program administrators throughout the U.S., and we congratulate the entire Green Bank team on this impressive milestone.”
The project that propelled the Green Bank over this milestone will be installed at Farmington Sports Arena (FSA). FSA is a 130,000-square foot modern indoor sports facility that is home to four indoor and three outdoor artificial turf fields as well as four natural grass outdoor fields. The project, which will be installed by 64 Solar, consists of two solar PV systems (170 kW total).
Connecticut’s C-PACE program maintains an open market approach, allowing private capital providers to finance projects for building owners, and, in 2015, the Green Bank reached an agreement that provided it access to up to $100 million in private funding for C-PACE projects. Today, nearly 70% of the funding in the program consists of private capital.
“The Connecticut Green Bank is a leader in the green energy movement, but the rapid growth of C-PACE wouldn’t be possible 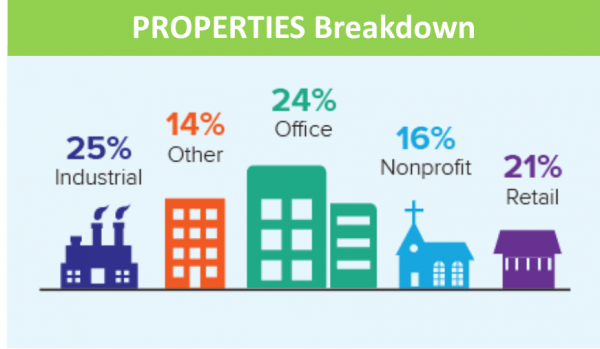 without the support of our contractors, capital providers, municipal officials, and other stakeholders who have contributed to the C-PACE movement,” said Mackey Dykes, Vice President of Commercial, Industrial and Institutional programs at the Connecticut Green Bank. “There is still significant potential for energy improvements for Connecticut businesses and non-profits, and we look forward to bringing cleaner and cheaper energy to more building owners across the state.”
without the support of our contractors, capital providers, municipal officials, and other stakeholders who have contributed to the C-PACE movement,” said Mackey Dykes, Vice President of Commercial, Industrial and Institutional programs at the Connecticut Green Bank. “There is still significant potential for energy improvements for Connecticut businesses and non-profits, and we look forward to bringing cleaner and cheaper energy to more building owners across the state.”
The website Energy Collective noted recently that “states have and will continue to play a key role in leading the clean energy transition,” highlighting the work in Connecticut as among the national models.
“Connecticut has found a way to make the financing of clean energy deployment more accessible and affordable for consumers and businesses. In 2011 the state legislature created the Connecticut Green Bank, the nation’s first green bank. It uses public funds to attract private capital investment in green energy projects. By leveraging private investment, the Green Bank significantly increases the total amount of financing available for clean energy projects.
make the financing of clean energy deployment more accessible and affordable for consumers and businesses. In 2011 the state legislature created the Connecticut Green Bank, the nation’s first green bank. It uses public funds to attract private capital investment in green energy projects. By leveraging private investment, the Green Bank significantly increases the total amount of financing available for clean energy projects.
The site highlighted that “Among the Green Bank’s most successful initiatives is the Commercial Property Assessed Clean Energy (C-PACE) program, which allows commercial property owners to pay for clean energy or efficiency upgrades over time through their property taxes.
The Connecticut Green Bank is the nation’s first green bank. Established by the Connecticut General Assembly on July 1, 2011 as a part of Public Act 11-80, the Connecticut Green Bank evolved from the Connecticut Clean Energy Fund (CCEF) and the Clean Energy Finance and Investment Authority (CEFIA), which was given a broader mandate in 2011 to become the Connecticut Green Bank.
https://youtu.be/kPqO4QlTkDU




 Tesla is prohibited from selling directly in Connecticut, Michigan, Texas, and West Virginia, according to the company. There are about 1,300 Teslas registered in Connecticut, nearly two-thirds of the electric vehicles in the state, according to the state Department of Motor Vehicles.
Tesla is prohibited from selling directly in Connecticut, Michigan, Texas, and West Virginia, according to the company. There are about 1,300 Teslas registered in Connecticut, nearly two-thirds of the electric vehicles in the state, according to the state Department of Motor Vehicles.
 rding to the Treasurer’s Office. Representing the Connecticut Treasurer’s Office at the annual meeting, and presenting the proposal, was Aeisha Mastagni, a Portfolio Manager in the Corporate Governance Unit of the California State Teachers’ Retirement System. Overall, according to a U.S. Securities & Exchange Commission filing, 74.7 million shareholders voted against the proposal, with 32.7 million voting in favor.
rding to the Treasurer’s Office. Representing the Connecticut Treasurer’s Office at the annual meeting, and presenting the proposal, was Aeisha Mastagni, a Portfolio Manager in the Corporate Governance Unit of the California State Teachers’ Retirement System. Overall, according to a U.S. Securities & Exchange Commission filing, 74.7 million shareholders voted against the proposal, with 32.7 million voting in favor.
 ess to the issue of childhood drownings. Steven Hernández,, Executive Director of the Commission on Women,
ess to the issue of childhood drownings. Steven Hernández,, Executive Director of the Commission on Women,  The statistics about children’s drowning deaths have not changed over time, implying that current strategies for prevention are not enough, officials said. Increasing children’s access to swim lessons, encouraging schools to teach water safety skills to students and giving parents easy-to-use and engaging tools to talk to their children about how to be safe around water are just a few actions that can have a big effect in reducing drowning rates, officials stressed.
The statistics about children’s drowning deaths have not changed over time, implying that current strategies for prevention are not enough, officials said. Increasing children’s access to swim lessons, encouraging schools to teach water safety skills to students and giving parents easy-to-use and engaging tools to talk to their children about how to be safe around water are just a few actions that can have a big effect in reducing drowning rates, officials stressed. nts have been selected to receive the prestigious awards, including organizations and initiatives from
nts have been selected to receive the prestigious awards, including organizations and initiatives from 




 The Mattress Recycling Council (MRC), a non-profit organization established by the mattress industry that created and manages the program in Connecticut, California and Rhode Island, presented its inaugural
The Mattress Recycling Council (MRC), a non-profit organization established by the mattress industry that created and manages the program in Connecticut, California and Rhode Island, presented its inaugural  “We are pleased with the program’s productive start and will continue to work with city leaders, businesses and the state to improve the program, expand the number of communities served, and increase the volume of mattresses recycled,” said Ryan Trainer, President of MRC and the International Sleep Products Association.
“We are pleased with the program’s productive start and will continue to work with city leaders, businesses and the state to improve the program, expand the number of communities served, and increase the volume of mattresses recycled,” said Ryan Trainer, President of MRC and the International Sleep Products Association.


 Studies show that there is no unmet demand for natural gas in Connecticut, opponents of the planned pipeline said, stressing that gas pipelines are routinely only half full now and electricity demand in New England has remained virtually flat over more than 10 years. Proponents have
Studies show that there is no unmet demand for natural gas in Connecticut, opponents of the planned pipeline said, stressing that gas pipelines are routinely only half full now and electricity demand in New England has remained virtually flat over more than 10 years. Proponents have 


 for a proposed mixed use development project at 161-177 State Street, which is phase one of a multi-phase project that includes demolition of the Mills public housing project and implementation of the Harbor Brook Flood Control project north of the Hub site. The new building will be within walking distance of Meriden`s new Transit center.
for a proposed mixed use development project at 161-177 State Street, which is phase one of a multi-phase project that includes demolition of the Mills public housing project and implementation of the Harbor Brook Flood Control project north of the Hub site. The new building will be within walking distance of Meriden`s new Transit center. In February, the Connecticut Small Business Development Center (CTSBDC), the City of Meriden and The Midstate Chamber of Commerce announced the opening of the newest CTSBDC office, to be located at Meriden City Hall.
In February, the Connecticut Small Business Development Center (CTSBDC), the City of Meriden and The Midstate Chamber of Commerce announced the opening of the newest CTSBDC office, to be located at Meriden City Hall.



























