Credit Union Branch Inside High School Encourages Financial Literacy
/Getting banking business done – or being introduced to an array of personal financial services for the first time – has become easier than ever for students attending Rocky Hill High School. That’s because they don’t even need to leave the confines of high school to visit a Nutmeg State Financial Credit Union branch – it’s just steps away from their school cafeteria.
Credit union branches located inside high schools are not common. In fact, this might be the first of its kind in Connecticut. The branch is a new step for the credit union and focuses on preparing students for their financial future. It features tablets, an ATM, and (coming soon) a self-service kiosk to be used by students and faculty for transactions such as account transfers, loan payments, and check and cash deposits or withdrawals.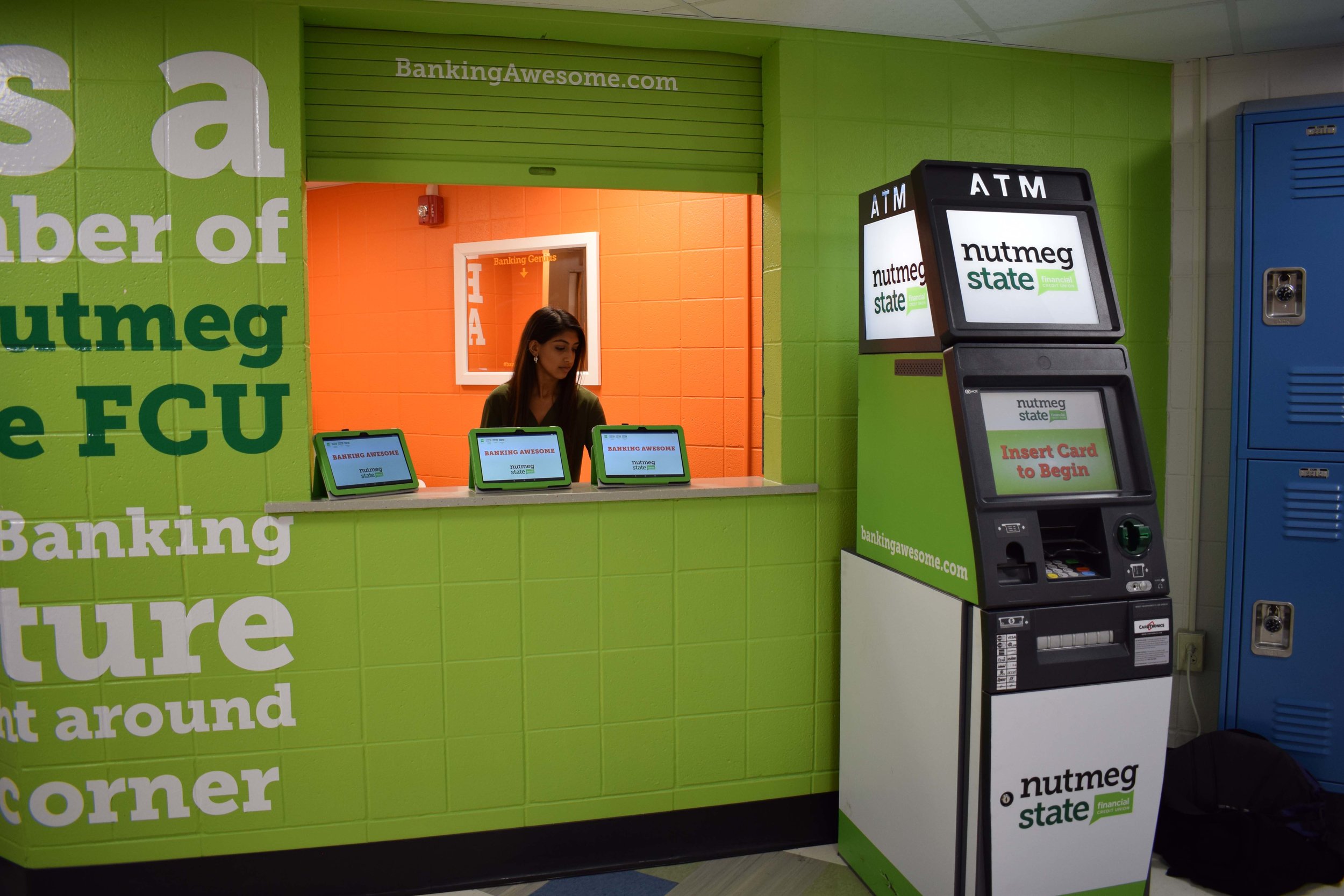
Nutmeg State FCU President and CEO John Holt says his enthusiasm and the support from Rocky Hill High Schools administrators and teachers is matched by the student response.
“We want to give students first-hand knowledge and experience,” Holt explains, “to help them better understand banking and prepare them for smart decision-making in the future.”
The staff includes three Rocky Hill High School students who are specially trained not only in technology but in terminology, so they can pass along that combination of know-how and understanding to their peers. For many, understanding the differences between a credit union and a bank is an unexpected first lesson. And students are often intrigued by the credit union structure, including that it is a non-profit institution which allows them to become members (and therefore part owners of the credit union).
If the initial weeks are any indication, there is a receptive audience of students, very supportive teachers and administrators, and parents looking on approvingly from the sidelines. More than 100 accounts have been opened at the branch in the first few months of operation, and there have been many more conversations providing insight for high school students into the products and services a financial institution offers – plus some tips on how to manage money effectively.
“The need for financial literacy education has never been greater,” said Jeremy Race, President and CEO of Junior Achievement of Southwest New England, an organization with a strong classroom presence focused on financial education and entrepreneurship. “According to a recent Forbes article, 44% of Americans don’t have enough cash to cover a $400 emergency and 33% of adults have $0 saved for retirement. This is staggering evidence that clearly demonstrates the critical need for young people to learn financial responsibility and financial ‘smarts’ at a young age.”
 Because the technology is intuitive for most students, their transaction time can be used to talk about subjects they may be less familiar with – such as balancing a checkbook, how debit cards and account balances relate to each other, loans and interest rates, and what a credit score is all about. Not the typical teen conversation, but Holt indicates that students have been quite interested in learning more.
Because the technology is intuitive for most students, their transaction time can be used to talk about subjects they may be less familiar with – such as balancing a checkbook, how debit cards and account balances relate to each other, loans and interest rates, and what a credit score is all about. Not the typical teen conversation, but Holt indicates that students have been quite interested in learning more.
“The younger generation has a passion for community,” Holt has observed, “and they see the practical value. This has really opened their eyes.”
Some of the lessons are already being integrated into the school’s business classes – which seem “real” with a financial institution’s branch office just down the hall. The branch is open during lunch periods, study halls, and other times convenient to students, teachers and staff, without being a distraction from more traditional school curricula.
Outgoing Connecticut State Treasurer Denise L. Nappier, a longstanding proponent of financial literacy, has stressed that “Financial education is important during all stages of life, because economic opportunity can be a catalyst for change and enduring success,” adding that “information and training can help them build a better future.”
With the program off to a solid start, Holt said that Nutmeg State FCU would be interested in a similar initiative in another high school near one of their 11 credit union branches in Connecticut. They are headquartered in Rocky Hill, having been chartered in 1936. In addition to Rocky Hill, they’re located in Manchester, New Britain, Hartford, Glastonbury, West Hartford, Cromwell, Orange, Stratford, Milford and North Haven.
The Connecticut-based credit union also reaches out to local communities in other distinctive ways. In Milford and North Haven, they have added “DMV Express” services in conjunction with the state Department of Motor Vehicles, and three locations are within retail stores – the Walmart in Cromwell, and the ShopRite supermarkets in Stratford and Orange. To learn more about Nutmeg State Financial Credit Union, visit www.nutmegstatefcu.org.
Photos: (Top right) - Rocky Hill High School Student Alisha Chhabra conveniently accesses the new Nutmeg State Financial Credit Union branch at her school. (Midde left) - Rocky Hill High School recently celebrated the opening of its first on-site Nutmeg State Financial Credit Union branch. From left: Chuck Zettergren Assistant Superintendent, Dr. Mark Zito Superintendent, Mike Petti Vice Chairman, John Holt President & CEO, Ben Lukens Student, Alisha Chhabra Student, Michael Patano Student, Muhammed Bilal Student, Cynthia Latina Business Education Teacher, Timothy Bifolck Business Education Teacher, Mario Almeida Principal. (Bottom right) Nutmeg State FCU President and CEO John Holt.






 Rounding out the top ten are Virginia ($7,161), New Jersey ($7,151), Maryland ($7,043), Hawaii ($6,981), D.C. ($6,963), Texas ($6,902), Colorado ($6,718), and Georgia (6,675). New York is next at $6,671.
Rounding out the top ten are Virginia ($7,161), New Jersey ($7,151), Maryland ($7,043), Hawaii ($6,981), D.C. ($6,963), Texas ($6,902), Colorado ($6,718), and Georgia (6,675). New York is next at $6,671.
 The analysis, by the financial services website WalletHub, was based on 40 key indicators of livability, ranging from housing costs to school-system quality to restaurants per capita. The indicators were grouped into five categories – affordability, economic health, education & health, safety, and quality of life.
The analysis, by the financial services website WalletHub, was based on 40 key indicators of livability, ranging from housing costs to school-system quality to restaurants per capita. The indicators were grouped into five categories – affordability, economic health, education & health, safety, and quality of life.


 The comprehensive assessment of Hartford’s ecosystem also noted that “Hartford’s [startup] founders claim to have the right ambition to go global,” concluding that “Hartford’s startups have more potential to strengthen Global Market Reach and Global Connectedness.” In a number of areas analyzed in the assessment, Hartford is seen as having potential to strengthen the local startup community, its reach beyond Hartford, and the demographic of startup teams.
The comprehensive assessment of Hartford’s ecosystem also noted that “Hartford’s [startup] founders claim to have the right ambition to go global,” concluding that “Hartford’s startups have more potential to strengthen Global Market Reach and Global Connectedness.” In a number of areas analyzed in the assessment, Hartford is seen as having potential to strengthen the local startup community, its reach beyond Hartford, and the demographic of startup teams.




 “I am delighted the city has joined Sustainable CT in our latest efforts to develop and implement sustainability and renewable energy initiatives in Norwalk,” said Mayor Harry Rilling. “Being energy conscience is the right thing to do as we all have a moral obligation to lessen our environmental impact. I am glad the city has taken a leadership role and joined this important sustainability initiative.” Norwalk’s Council approved the resolution to join Sustainable CT in mid-August and designated the Common Council Planning Committee as the “Sustainability Team” for the program. Norwalk was officially registered with Sustainable CT on August 24.
“I am delighted the city has joined Sustainable CT in our latest efforts to develop and implement sustainability and renewable energy initiatives in Norwalk,” said Mayor Harry Rilling. “Being energy conscience is the right thing to do as we all have a moral obligation to lessen our environmental impact. I am glad the city has taken a leadership role and joined this important sustainability initiative.” Norwalk’s Council approved the resolution to join Sustainable CT in mid-August and designated the Common Council Planning Committee as the “Sustainability Team” for the program. Norwalk was officially registered with Sustainable CT on August 24.






















