As progress is being made in Connecticut and across the country to end homelessness among veterans, greater attention appears to be turning next to homelessness among families with children.
Families with children under age 6 are the fastest growing segment of the homeless population in the United States, Myra Jones-Taylor, Commissioner of Connecticut’s Office of Early Childhood, told state legislators recently.
In Connecticut, an estimated 3,000 to 9,000 families with young children are homeless, Jones-Taylor said. Of that estimate, approximately 1,125 families experienced homelessness in 2015 with 2,022 children impacted. Of those children, 43 percent were under the age of 5 and 42 percent were between the ages of 5 and 12.
Governor Malloy announced last month that the federal government has certified Connecticut as having effectively ended homelessness among veterans. Just the second state in the nation to accomplish the milestone, Connecticut has implemented a comprehensive, unprecedented system to target homelessness among veterans. Connecticut was one of the first states to join a national initiative that sought to secure commitments from communities across the country to end veteran homelessness by the end of 2015.
Nationally, between 2009 and 2015, there has been a 35 percent reduction in the number of homeless veterans, according to a Governing magazine’s review of data from the Department of Housing and Urban Development, published this month. In addition to Connecticut, major cities including New Orleans, Houston and Las Vegas have indicated that “they’ve effectively eliminated homelessness among veterans.”
“But most people who are homeless are not veterans. And in many of the nation’s large cities, homelessness among the general population appears to be getting worse,” the magazine points out. Between 2014 and 2015, overall homelessness in the nation’s 50 largest urban areas increased by 3 percent. The numbe r of unsheltered individuals in those cities went up 10.5 percent and the number of unsheltered people in homeless families grew by 18.8 percent, Governing revealed.
r of unsheltered individuals in those cities went up 10.5 percent and the number of unsheltered people in homeless families grew by 18.8 percent, Governing revealed.
Many attribute the success in reducing the veteran homeless population to an aggressive well-planned effort initiated at the federal level, and are looking for similar efforts focused on homeless youth.
In President Obama’s budget plan submitted to Congress this year, he requested $10.967 billion for the purpose of reaching and maintaining the goal of ending family homelessness by 2020. The National Alliance to End Homelessness emphasizes that “should this request be enacted by Congress, it would give communities what they need to end homelessness for families with children.”
Connecticut Child Advocate Sarah Healy Eagan has said that “research has shown that homelessness puts children at increased risk of health problems, developmental delays, academic underachievement, and mental health problems.”
According to the National Low Income Housing Coalition (NLIHC), the federal Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) is asking Congress to provide sufficient funding for 10,000 new housing choice vouchers for homeless families with children, funding for 25,000 new permanent supportive housing units, and funds to provide 8,000 families with rapid rehousing assistance.
In addition, HUD announced a legislative proposal where it will seek $11 billion in mandatory spending over the next 10 years to serve a total of 550,000 families with additional vouchers, permanent supportive housing, and rapid rehousing assistance.
At a February public hearing at the State Capitol focused on proposed Senate Bill 10, which focuses on child care for homeless families with children. It would create a “protective services” category for children experiencing homelessness, making them “categorically eligible” for child care subsidies regardless of the parent’s work status; and, ensure immediate access to child care for all children by creating a 90-day grace period for providing documentation of health and immunization records when enrolling in a child care center, group children care home, or family child care home.
The executive director of the Partnership for Strong Communities, Alicia Woodsby, testifying in support of the legislation, expressed the hope that its passage would “assist providers in resolving each case of family homelessness more quickly,” noting that families experiencing homelessness lack employment and are struggling with extreme instability. The lack of child care makes it even more challenging for them to participate in worker training or secure new employment.”
The coalition of organizations and agencies led 2016 Homelessness & Housing Advocacy Days on March 2 and 3 at the State Capitol, drawing attention to the issue of homelessness, including homelessness among children and families.
There are wide estimates of just how many young people are homeless nationwide, according to the Child Welfare League of America, ranging from half a million to 1.6 million with estimates that up to 40 percent are gay, lesbian, questioning or transgender. Many of these young people have been kicked out of their own homes and are responsible for their own survival and are frequent targets of exploitation, trafficking and abuse while living on the streets CWLA points out.
The White House has pointed out that three years ago, in February 2013, the U.S. Interagency Council on Homelessness (USICH) issued a Framework to End Youth Homelessness detailing the steps necessary to achieve the goal of ending youth homelessness by 2020, and strategies to improve outcomes for children and youth experiencing homelessness.
Officials noted that “the framework articulates the need for government, non-profit, civic, and faith community partners to focus together on the overall well-being of youth experiencing homelessness — addressing not just their need for stable housing, but also their educational and employment goals, and the importance of permanent adult connections in their lives.”
The conclusion of that report stated flatly that “we can end youth homelessness in America by 2020.” The report emphasized that “Reaching this goal will require more resources at all levels and sectors, but resources are not enough. At all levels of policy and programming, we have to continuously challenge ourselves to gather and use better data, to leverage existing resources available to us, to implement more deliberate service strategies informed by good data and stakeholder input, and to coordinate systems and services around those strategies.”
“Access to high quality early care and education is extremely important for all children, but especially for children in vulnerable circumstances,” Rachel Leventhal-Weiner, Education Policy Fellow at Connecticut Voices for Children, told legislators. “We consider homeless children to be among the most vulnerable.”
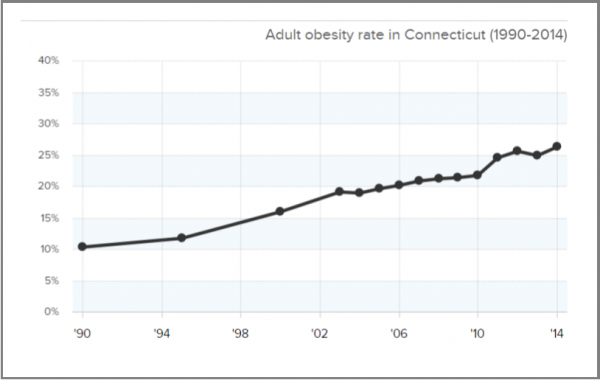
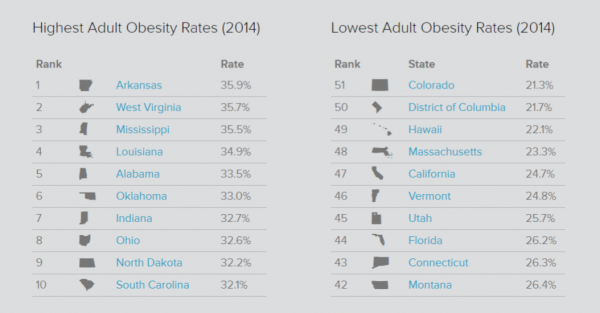


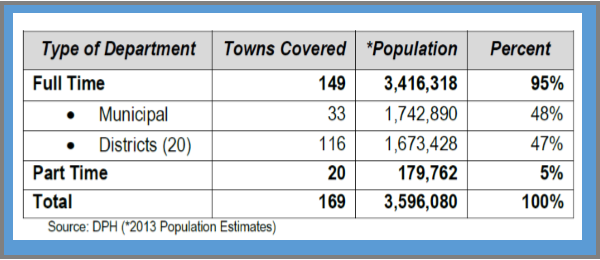


 r of unsheltered individuals in those cities went up 10.5 percent and the number of unsheltered people in homeless families grew by 18.8 percent, Governing revealed.
r of unsheltered individuals in those cities went up 10.5 percent and the number of unsheltered people in homeless families grew by 18.8 percent, Governing revealed.

 ents currently working on the Hartford Hand initiative. Each week, Welch and colleagues Yonathan Moshayev, Jake Green, Amber Sayer, and Stephen Sousa, spend several hours improving the current design to make the unique Hartford Hand a reality for patients.
ents currently working on the Hartford Hand initiative. Each week, Welch and colleagues Yonathan Moshayev, Jake Green, Amber Sayer, and Stephen Sousa, spend several hours improving the current design to make the unique Hartford Hand a reality for patients.


 Just over the city line in West Hartford, ShopRite supermarket (corner of Kane and Prospect Streets) is offering a series of free courses with a registered dietician to help individuals know “where to start on your path to becoming healthier.” The “Eat Well Be Happy” Weight Management Series begins on February 24, and will be held every Wednesday from 6-7:30 p.m., for six weeks. Each class focuses on a different topic including: meal planning, portion control, importance of fiber, protein and hydration and controlling sugar cravings, among others. Individual consultation is also available, and all nutritional services are available to customers free of charge. (Interested individuals can contact shana.griffin@wakefern.com)
Just over the city line in West Hartford, ShopRite supermarket (corner of Kane and Prospect Streets) is offering a series of free courses with a registered dietician to help individuals know “where to start on your path to becoming healthier.” The “Eat Well Be Happy” Weight Management Series begins on February 24, and will be held every Wednesday from 6-7:30 p.m., for six weeks. Each class focuses on a different topic including: meal planning, portion control, importance of fiber, protein and hydration and controlling sugar cravings, among others. Individual consultation is also available, and all nutritional services are available to customers free of charge. (Interested individuals can contact shana.griffin@wakefern.com)

 y percent of the children in group placements have no documented behavioral or medical need that would warrant placement in such a restrictive setting.
y percent of the children in group placements have no documented behavioral or medical need that would warrant placement in such a restrictive setting.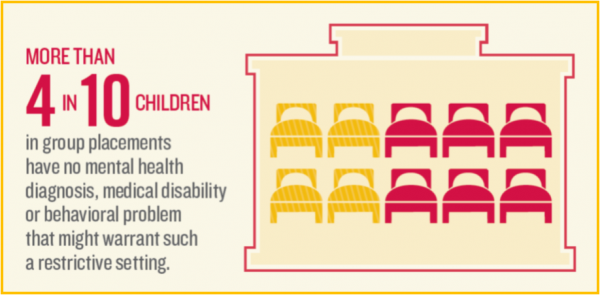

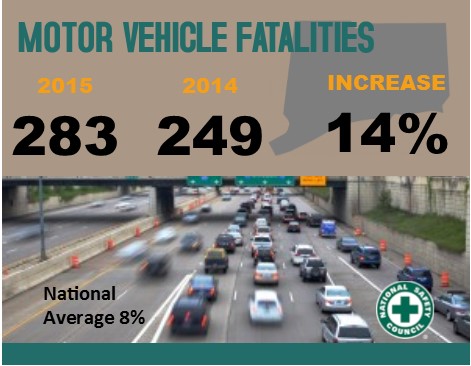 Nationally, 2015 saw the largest single-year percent increase in motor vehicle deaths since 1966. Estimates from the National Safety Council (NSC) show an 8 percent increase in 2015 compared with 2014 – with substantial changes in some states, including Connecticut. There were 283 motor-vehicle related deaths in Connecticut last year, compared with 249 in 2014 and 276 in 2013.
Nationally, 2015 saw the largest single-year percent increase in motor vehicle deaths since 1966. Estimates from the National Safety Council (NSC) show an 8 percent increase in 2015 compared with 2014 – with substantial changes in some states, including Connecticut. There were 283 motor-vehicle related deaths in Connecticut last year, compared with 249 in 2014 and 276 in 2013.
 safety, the National Safety Council recommends drivers:
safety, the National Safety Council recommends drivers:

 age, MSW, Director of Community Organizing, Yale Program for Recovery and Community Health. “We know that good nutrition plays a key role in mental health and that’s why the mental health community is here today to support the Witnesses.”
age, MSW, Director of Community Organizing, Yale Program for Recovery and Community Health. “We know that good nutrition plays a key role in mental health and that’s why the mental health community is here today to support the Witnesses.”

 Also making the list were Evariant of Farmington, a software developer, at number 272, and HP One, a software company in Trumbull at number 307. Biopharmaceutical company Alexion, in the midst of moving its headquarters from Cheshire to New Haven, was ranked at number 349, and etouches, a Norwalk software company ranked at number 357. Rounding out the Connecticut companies on the list is Wallingford oil extraction technology company APS Tecnhology, at number 466.
Also making the list were Evariant of Farmington, a software developer, at number 272, and HP One, a software company in Trumbull at number 307. Biopharmaceutical company Alexion, in the midst of moving its headquarters from Cheshire to New Haven, was ranked at number 349, and etouches, a Norwalk software company ranked at number 357. Rounding out the Connecticut companies on the list is Wallingford oil extraction technology company APS Tecnhology, at number 466. rough technology’s continued disruption and proliferation across industries,” said Sandra Shirai, principal, Deloitte Consulting LLP and US technology, media, and telecommunications leader.
rough technology’s continued disruption and proliferation across industries,” said Sandra Shirai, principal, Deloitte Consulting LLP and US technology, media, and telecommunications leader. Overall, 283 of the 500 companies were in the software sector, and 67 percent of the 500 companies have received venture capital funding at some point in their company’s history. Topping the list was StartApp, with a growth rate of 21,984 percent from 2011 to 2014. Based in New York and founded in 2010, StartApp provides a free monetization and distribution platform that integrates with applications on mobile devices.
Overall, 283 of the 500 companies were in the software sector, and 67 percent of the 500 companies have received venture capital funding at some point in their company’s history. Topping the list was StartApp, with a growth rate of 21,984 percent from 2011 to 2014. Based in New York and founded in 2010, StartApp provides a free monetization and distribution platform that integrates with applications on mobile devices.


























