CT Playing Catch-up to Other States in Reducing Childhood Obesity
/Although Connecticut has fared comparatively well to other states in adult obesity rates, the state does “not do as well for children, especially low-income children,” according to two new national reports, the Child Health and Development Institute (CHDI) of Connecticut indicates in the organization’s latest issue brief. “Preventing children from being overweight or obese requires action in the earliest years since experts agree that reversing these trends later in life can be very difficult,” CHDI points out. “It is currently estimated that one in four children are overweight or obese by the time they enter kindergarten.
The reports highlight how Connecticut is doing relative to other states on early childhood obesity prevention. Data for low-income children was drawn from families participating in the federal Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC).
The Trust for America’s Health and Robert Wood Johnson Foundation’s State of Obesity in America report shows that Connecticut ranks:
- 12th out of 50 states for highest WIC obesity rates (low-income children ages 2-4 years old)
- 27th out of 37 states for highest adolescent obesity rates (students grades 9-12) Mississippi high schoolers have the highest obesity rate in US: 18.9%. Montana the lowest: 10.3% Connecticut is 12.3%
- 42nd out of 50 states for highest adult obesity rates (18 and older)
A new report from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), Early Care and Education State Indicator Report, tracks state policies aimed at preventing obesity in child care settings and shows that Connecticut is missing opportunities to address healthy nutrition in early childhood and education settings (ECE).
The 2016 report examines 15 data indicators including, assessing each state’s licensing regulations for high impact obesity prevention standards. Connecticut only had 2 out of 47 obesity prevention standards in State licensing regulations for early care and education programs and lacked ECE professional development training on obesity prevention that 42 other states offer.
CHDI explains that since 2014, Connecticut state agencies have started to address early childhood nutrition through licen sing and training. The State is currently in the process of reviewing Early Childhood Education (ECE) licensing regulations, and has developed general training for some early childhood providers on nutrition and fitness.
sing and training. The State is currently in the process of reviewing Early Childhood Education (ECE) licensing regulations, and has developed general training for some early childhood providers on nutrition and fitness.
Additionally, the Department of Public Health offers training to ECE providers via funding through the Centers for Disease Control and is working with the Connecticut State Department of Education (SDE), Office of Early Childhood (OEC), and the UConn Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity to enhance professional development training focused on obesity prevention.
“Despite this progress,” the CHDI stresses, “more needs to be done to catch up with other states and reduce obesity rates among young children.” CHDI adds that “Connecticut must look at best practice standards related to early childhood obesity prevention and do better for our children to ensure that they grow at a healthy weight.”
Connecticut now has the 10th lowest adult obesity rate in the nation, according to The State of Obesity: Better Policies for a Healthier America released September 2016. Connecticut's adult obesity rate is currently 25.3 percent, up from 16.0 percent in 2000 and from 10.4 percent in 1990.



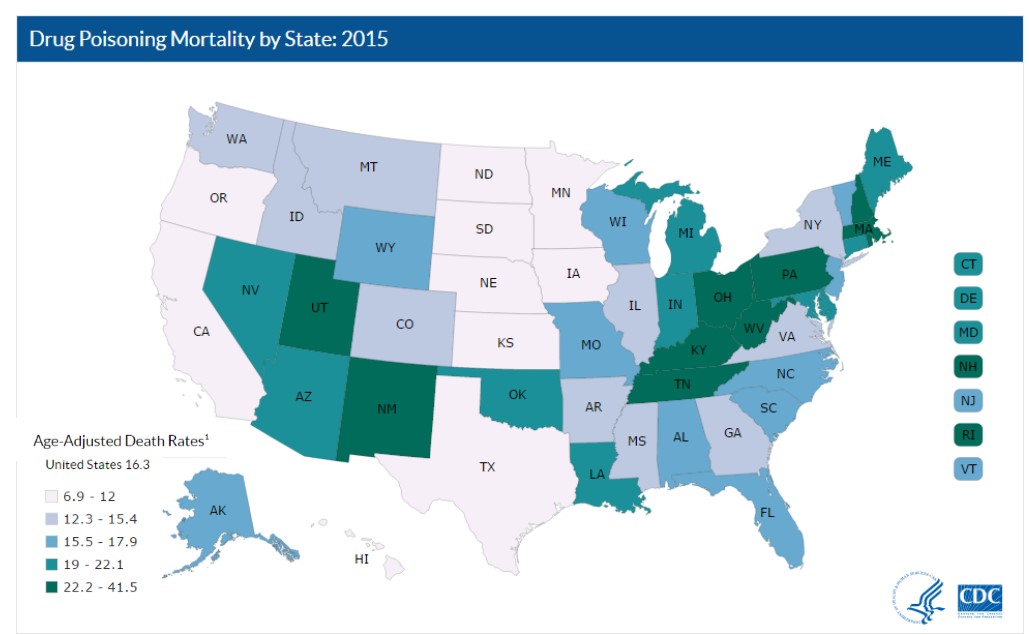 The five states with the highest rates of death due to drug overdose were West Virginia (41.5 per 100,000), New Hampshire (34.3 per 100,000), Kentucky (29.9 per 100,000), Ohio (29.9 per 100,000), and Rhode Island (28.2 per 100,000).
The five states with the highest rates of death due to drug overdose were West Virginia (41.5 per 100,000), New Hampshire (34.3 per 100,000), Kentucky (29.9 per 100,000), Ohio (29.9 per 100,000), and Rhode Island (28.2 per 100,000). The review and analysis found at least seven areas in Connecticut, based on zip code geography, where the percentage of children found to have elevated lead levels exceeded – more than doubled – the percentage in Flint.
The review and analysis found at least seven areas in Connecticut, based on zip code geography, where the percentage of children found to have elevated lead levels exceeded – more than doubled – the percentage in Flint.
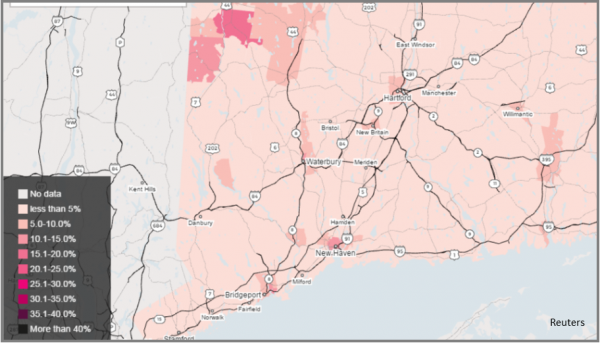
 each year, the report indicated.
each year, the report indicated.
 The Mattress Recycling Council (MRC), a non-profit organization established by the mattress industry that created and manages the program in Connecticut, California and Rhode Island, presented its inaugural
The Mattress Recycling Council (MRC), a non-profit organization established by the mattress industry that created and manages the program in Connecticut, California and Rhode Island, presented its inaugural  “We are pleased with the program’s productive start and will continue to work with city leaders, businesses and the state to improve the program, expand the number of communities served, and increase the volume of mattresses recycled,” said Ryan Trainer, President of MRC and the International Sleep Products Association.
“We are pleased with the program’s productive start and will continue to work with city leaders, businesses and the state to improve the program, expand the number of communities served, and increase the volume of mattresses recycled,” said Ryan Trainer, President of MRC and the International Sleep Products Association.
 explains. “Anyone can become a victim of abuse, but vulnerable older Americans — especially those who are women, have disabilities and rely on others for care or other type of assistance — are among the easiest targets for such misconduct.”
explains. “Anyone can become a victim of abuse, but vulnerable older Americans — especially those who are women, have disabilities and rely on others for care or other type of assistance — are among the easiest targets for such misconduct.”
 As of June 28, 2016, there were 2,007 bakery-cafes in 46 states and in Ontario, Canada operating under the Panera Bread, Saint Louis Bread Co. or Paradise Bakery & Cafe names. Published reports indicate the company has 97,000 employees nationwide and saw a 3.4 percent growth in sales in its third quarter this year. In 2015, it reportedly generated roughly $2.7 billion in revenue. Founder and CEO Ron Shaich
As of June 28, 2016, there were 2,007 bakery-cafes in 46 states and in Ontario, Canada operating under the Panera Bread, Saint Louis Bread Co. or Paradise Bakery & Cafe names. Published reports indicate the company has 97,000 employees nationwide and saw a 3.4 percent growth in sales in its third quarter this year. In 2015, it reportedly generated roughly $2.7 billion in revenue. Founder and CEO Ron Shaich 
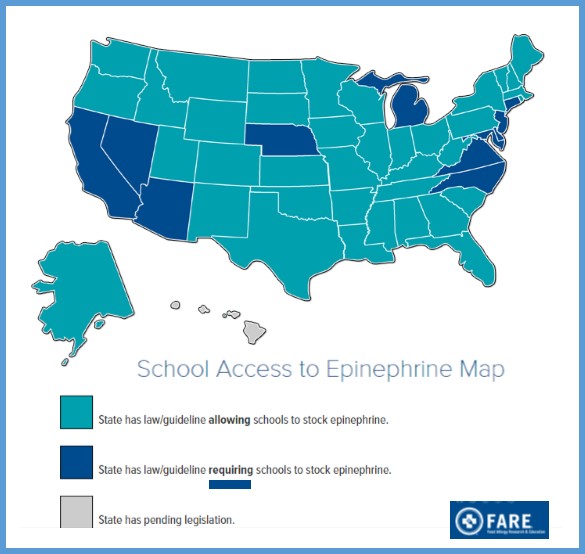
 In 2015 the legislature considered, but did not pass, a bill requiring the insurance commissioner to study and report on health insurance coverage of and out-of-pocket expenses for EpiPens, according to the OLR report. The 2014 legislation requires (a) schools to designate and train nonmedical staff to administer EpiPens to students having allergic reactions who were not previously known to have serious allergies and (b) the public health and education departments to jointly develop an annual training program for emergency EpiPen administration.
In 2015 the legislature considered, but did not pass, a bill requiring the insurance commissioner to study and report on health insurance coverage of and out-of-pocket expenses for EpiPens, according to the OLR report. The 2014 legislation requires (a) schools to designate and train nonmedical staff to administer EpiPens to students having allergic reactions who were not previously known to have serious allergies and (b) the public health and education departments to jointly develop an annual training program for emergency EpiPen administration.

 cal Centers is a joint venture between two leading health care organizations – GuideWell Mutual Holding Company and Organización Sanitas Internacional. GuideWell is a U.S.-based not-for-profit mutual holding company and the parent to a family of forward-thinking companies focused on transforming healthcare.
cal Centers is a joint venture between two leading health care organizations – GuideWell Mutual Holding Company and Organización Sanitas Internacional. GuideWell is a U.S.-based not-for-profit mutual holding company and the parent to a family of forward-thinking companies focused on transforming healthcare.
 The findings included in this report “provide policymakers, health professionals, public health advocates, industry representatives, and parents an opportunity to address misinformation conveyed through marketing of baby and toddler food and drinks.”
The findings included in this report “provide policymakers, health professionals, public health advocates, industry representatives, and parents an opportunity to address misinformation conveyed through marketing of baby and toddler food and drinks.”

























