Five Connecticuts: Disparities Persist, Continue to Adversely Impact State's Children
/Connecticut is among the wealthiest states in the country, and aggregated statewide economic, health, and education indicators suggest that children and families fare better here than in much of the United States. According to a new report developed by the Connecticut Association of Human Services, the reality on the ground is not what it appears to be.
“Race Equity in the Five Connecticuts: A Kids Count Special Report,” found that Blacks’ and Hispanics’ poverty rates are lower in Connecticut than nationally, and Blacks’ median incomes are higher. However, “as we have seen when looking within communities, historic patterns of inequality observed nationally do indeed persist here.”
The report indicates that as is the case nationally, Blacks and Hispanics in Connecticut are “disproportionately impoverished, and have the highest rates of negative outcomes for most of our indicators. Merely being a resident of one of the most affluent states in the U.S. is not a sufficient buffer against the intransigent inequality that affects our children and families along racial and ethnic lines,” the report explains.
"Not all children in our wealthy state are doing well," summed up Jim Horan, Chief Executive Officer of the Connecticut Association of Human Services, in releasing the report at a State Capitol complex conference. "All children, regardless of the color of their skin or their zip code, should have the opportunity to succeed. Connecticut can do much more to provide opportunity for all and address the huge inequities we see today, so that all children will prosper and contribute to and share in Connecticut’s growth," he said in the report's Foreword.
“Five Connecticut’s” refers to a breakdown developed by the Connecticut Data Center based upon each town’s median income, population density, and population below 100% of the poverty threshold (Levy, et al, 2004).
- Wealthy Connecticut towns have “exceptionally high-income, low poverty, and moderate population density.”
- Suburban towns have “above average income, low poverty, and moderate population density.”
- Rural towns are those with “average income, below average poverty, and the lowest population density.”
- Urban Periphery towns are marked by “below average income, average poverty, and high population density.”
- Urban Core towns have “the lowest income, highest poverty, and the highest population density.”
The report used data from communities representing each of the five Connecticuts: Wealthy (New Canaan, W3ilton, Weston, Easton, Fairfield); Urban Periphery (East Hartford and Manchester); Urban core (Hartford); Suburban (Branford, East haven, North Branford, Guilford and Madison); and Rural (Ashford, Brooklyn, Canterbury, Chaplin, Eastford, Hampton, Killingly, Plainfield, Pomfret, Putnam, Scotland, Sterling, Thompson, Woodstock, and Windham).
“Blacks are more segregated in Connecticut than in Arkansas and Hispanics are more segregated than in Texas,” pointed out Orlando Rodriquez, research associate at the UConn Health Disparities Institute, speaking at a forum on the report at the Legislative Office Building, noting that Connecticut is among the nation’s most segregated states.
Demographically, Connecticut, like the nation, is becoming more racially and ethnically diverse. It is estimated that by 2055, America will not have a single racial or ethnic majority. From 2000 to 2015, as the total population grew by 5%, Connecticut’s Black, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American populations combined grew by 42.3%. In 2000, Connecticut’s population was 22.5% Non-White; in 2015, it was 30.8%.
The research also found that “place can correlate somewhat with the degree of the differences observed across these indicators, with outcomes either ameliorated or exacerbated depending on one’s ‘Connecticut’ of residence.”
The general trend, the analysis indicated, “is that White and Asian children and families experience positive outcomes, while their Hispanic and Black counterparts are almost invariably worse off. Even in those areas where Hispanic and Black households have relatively higher median incomes, they often still have worse outcomes than White and Asian households for many non-economic indicators.”
“Place remains tightly intertwined with opportunity, compounding the effects we observe along racial lines,” the report indicated.
“While more affluent suburban towns offer safer neighborhoods and greater social and economic opportunity to residents,67 these neighborhoods and towns tend to have less affordable housing and perhaps less economic opportunity for employees of limited credentials. Finances tie less affluent families to areas of low opportunity, contributing to a cycle of poor outcomes.”
Officials said the report is intended to be the beginning of a “more nuanced and continuous conversation about the role of place in social and economic equity in the State of Connecticut,” to assist in the development of “policies that work earnestly to close the racial and ethnic gaps among our families and children.”
In 2000, Connecticut’s population totaled 3,405,565, with 2,638,845 non-Hispanic Whites, 309,843 Blacks, 320,323 Hispanics, 9,639 Native Americans, and 82,313 Asians. In 2015, the estimated total population was 3,593,222, with 2,478,119 non-Hispanic Whites, 346,206 non-Hispanic Blacks, 526,508 Hispanics, 8,908 Native Americans of any ethnicity, and 149,368 non-Hispanic Asians.


 ess to the issue of childhood drownings. Steven Hernández,, Executive Director of the Commission on Women,
ess to the issue of childhood drownings. Steven Hernández,, Executive Director of the Commission on Women,  The statistics about children’s drowning deaths have not changed over time, implying that current strategies for prevention are not enough, officials said. Increasing children’s access to swim lessons, encouraging schools to teach water safety skills to students and giving parents easy-to-use and engaging tools to talk to their children about how to be safe around water are just a few actions that can have a big effect in reducing drowning rates, officials stressed.
The statistics about children’s drowning deaths have not changed over time, implying that current strategies for prevention are not enough, officials said. Increasing children’s access to swim lessons, encouraging schools to teach water safety skills to students and giving parents easy-to-use and engaging tools to talk to their children about how to be safe around water are just a few actions that can have a big effect in reducing drowning rates, officials stressed.
 The overall rankings were weighted 80-20 between Entertainment & Recreation and Nightlife. The Entertainment & Recreation categories included restaurants, beaches, movie theaters, national parks, arts venues, and state spending on parks and recreation. The nightlife category included average beer & wine prices, movie costs, music festivals and access to bars.
The overall rankings were weighted 80-20 between Entertainment & Recreation and Nightlife. The Entertainment & Recreation categories included restaurants, beaches, movie theaters, national parks, arts venues, and state spending on parks and recreation. The nightlife category included average beer & wine prices, movie costs, music festivals and access to bars.

 “The U.S. population is increasingly diverse. Cultural competency is essential to deliver health care services that meet the needs of each individual and improves overall health,” said Christina Stasiuk, D.O., National Medical Director for Health Equity at Cigna.
“The U.S. population is increasingly diverse. Cultural competency is essential to deliver health care services that meet the needs of each individual and improves overall health,” said Christina Stasiuk, D.O., National Medical Director for Health Equity at Cigna.


 “More than Food focuses on promoting healthy food in pantries and helping people access other resources to find a job. We’re proud to support a partnership that is trying to find a solution to the hunger problem,” said Chris Traczyk, executive director of the Farmington Bank Community Foundation. “It’s a comprehensive, collective-impact project.” Dr. Katie Martin, assistant professor and director of the Public Health Program at USJ, and her research team developed a nutrition stoplight system called Supporting Wellness at Pantries, or “SWAP”, which helps food pantry clients choose healthier foods.
“More than Food focuses on promoting healthy food in pantries and helping people access other resources to find a job. We’re proud to support a partnership that is trying to find a solution to the hunger problem,” said Chris Traczyk, executive director of the Farmington Bank Community Foundation. “It’s a comprehensive, collective-impact project.” Dr. Katie Martin, assistant professor and director of the Public Health Program at USJ, and her research team developed a nutrition stoplight system called Supporting Wellness at Pantries, or “SWAP”, which helps food pantry clients choose healthier foods.

 d childcare slots for fifteen percent of the county’s children ages 0 to 2, and enough subsidized slots to cover only twenty-two percent of these youngest children in low-income households.
d childcare slots for fifteen percent of the county’s children ages 0 to 2, and enough subsidized slots to cover only twenty-two percent of these youngest children in low-income households.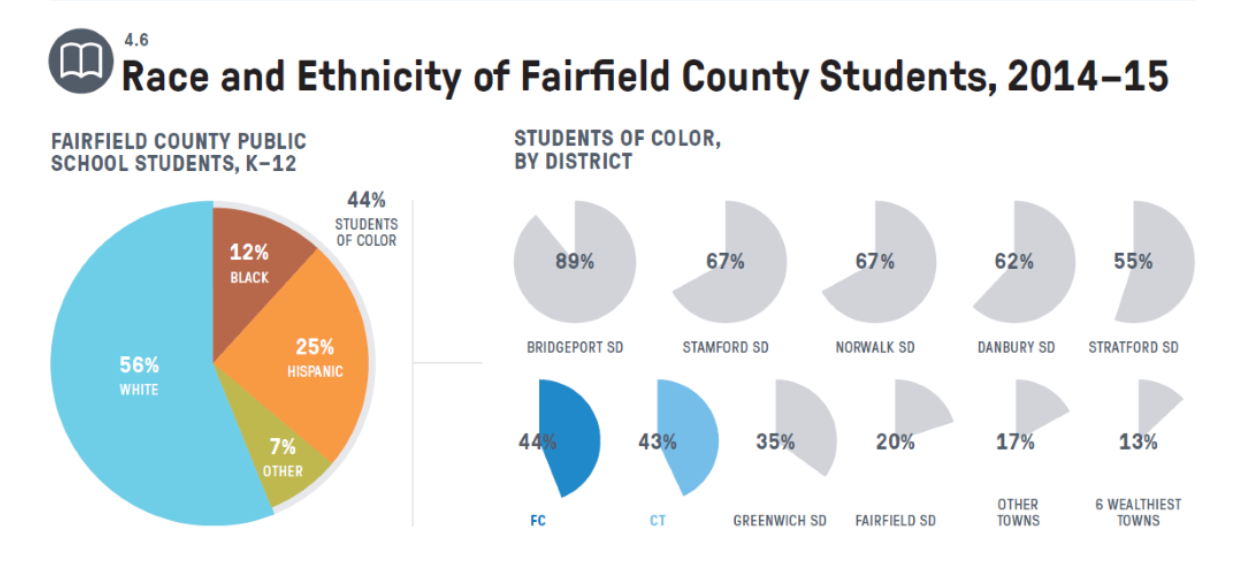


 ped the list in two additional categories: Lowest Percentage of Adults Who Experienced Pain in the Past Year Due to Oral Condition and Lowest Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Among Adolescents. The state also ranked in a tie for third for having the lowest percentage of elderly population with no natural teeth.
ped the list in two additional categories: Lowest Percentage of Adults Who Experienced Pain in the Past Year Due to Oral Condition and Lowest Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption Among Adolescents. The state also ranked in a tie for third for having the lowest percentage of elderly population with no natural teeth.
 serves as an expert resource on oral health policy; and publicizes oral health policy analysis and recommendations.
serves as an expert resource on oral health policy; and publicizes oral health policy analysis and recommendations.
 The Connecticut Health Policy Project is a non-profit, non-partisan research and educational organization dedicated to improving access to affordable, quality health care for all Connecticut residents.
The Connecticut Health Policy Project is a non-profit, non-partisan research and educational organization dedicated to improving access to affordable, quality health care for all Connecticut residents.


























