Number of Special Education Students in CT Schools Continues to Increase, Data Shows
/The number of Connecticut students in kindergarten through 12th grade with disabilities eligible for special education and related services has increased by nearly 6,000 between the 2008-09 school year and the current school year, as the overall student population has dropped by more than 32,500 students in that time.
Data included in a new website developed by the Connecticut State Department of Education indicates that the prevalence of special education in Connecticut schools has increased from 11.6 percent of students to 13.4 percent of students over the past seven years.
The prevalence of autism has doubled in the overall school population, from eight-tenths of one percent in 2008-09 to 1.6 percent in the current year. The percentage of students with learning disability has also increased, while the percentage with speech or language impairment has dropped, as a percentage of the overall student population.
Overall, the Special Education K-12 count in 2008-09 was 64,187 students. In the 2015-16 school year, the number has climbed to 70,055, an eight percent increase, even as the total student count has gone from 555,411 to 522,906.
The website points out that “Prevalence rate is a statistic about the identification of students with disabilities eligible for special education and related services,” adding that “Connecticut has seen increases in the number and percent of students with disabilities statewide over the last five years.”
The site also notes that the overall decreasing public school enrollment causes the prevalence rate to appear to grow at a must faster rate than one would perceive from actual special education count data.
Connecticut State Department of Education Commissioner Dianna R. Wentzell launched the new website, www.edsight.ct.gov, in late April. It is designed to strengthen transparency and streamline online access to important school and district information. The site integrates information from over 30 different sources – some reported by districts and others from external sources.
“The launch of our new data portal is a critical step in our mission to ensure all Connecticut students have access to the kind of high-quality education that prepares them for success in college, career and civic life,” Commissioner Wentzell said.
Over the coming months, additional information and reports will be made accessible to the public through this portal. The site is the culmination of more than two years of work and development by the Department with support from important partners, including the state Department of Administrative Services.
The Department also joined the world of social media last week with the launch of an official Facebook page and Twitter account. The Department’s Facebook page address is http://www.facebook.com/ctdepartmentofeducation. On Twitter, the Department is @EducateCT.








 Already, 2.9 million freelancers earned more than $100,000 last year, up from 2 million who hit the six-figure mark just four years earlier, according to MBO Partners. The report indicated that 60 percent of freelancers surveyed said they started freelancing by choice—up from 53 percent last year—and 67percent of freelancers agree that more people are choosing to work independently today compared to three years ago.
Already, 2.9 million freelancers earned more than $100,000 last year, up from 2 million who hit the six-figure mark just four years earlier, according to MBO Partners. The report indicated that 60 percent of freelancers surveyed said they started freelancing by choice—up from 53 percent last year—and 67percent of freelancers agree that more people are choosing to work independently today compared to three years ago.

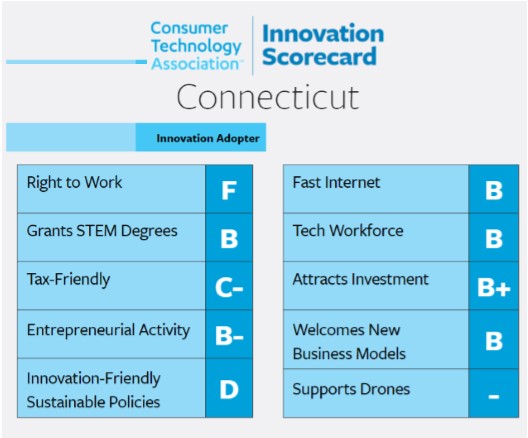

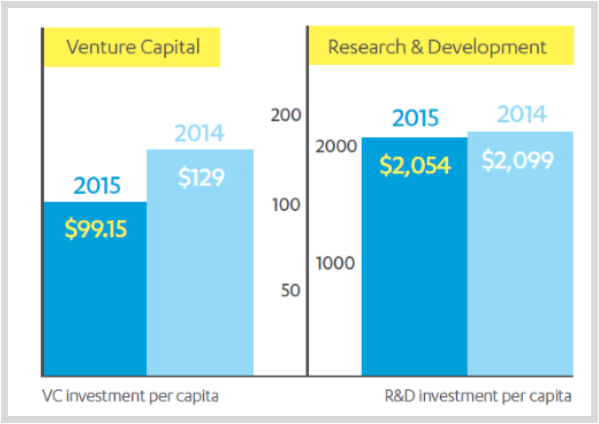 The report also highlights an area of decline in Connecticut: “Over $100 million of venture capital left Connecticut in 2015, causing the state to lose ground after earning an ‘A-’ in the category in the inaugural 2015 Scorecard. Connecticut should improve its tax code, which is among the least growth-friendly in the country, and reform regulations that stifle innovation.”
The report also highlights an area of decline in Connecticut: “Over $100 million of venture capital left Connecticut in 2015, causing the state to lose ground after earning an ‘A-’ in the category in the inaugural 2015 Scorecard. Connecticut should improve its tax code, which is among the least growth-friendly in the country, and reform regulations that stifle innovation.”



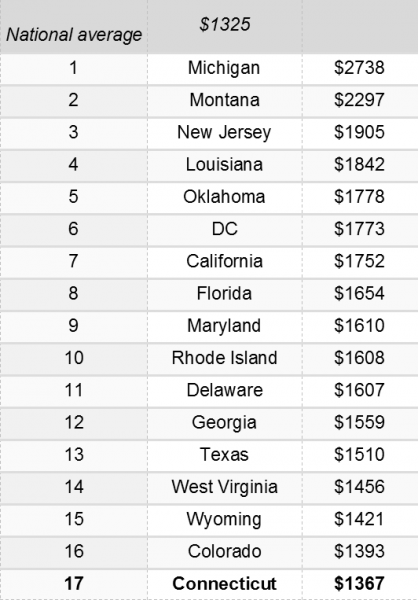
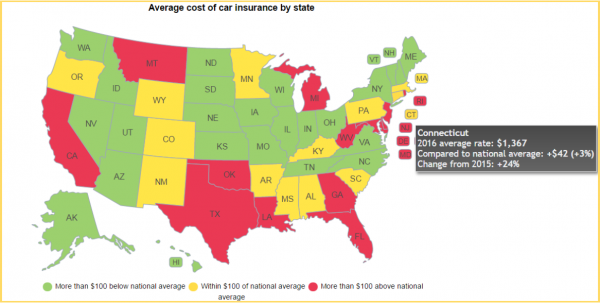 The national average for a full-coverage policy as featured in the Insure.com report came in at $1,325 this year – a slight increase from last year’s average of $1,311. Rates varied from a low of $808 a year in Maine to a budget-busting $2,738 in Michigan. Insurance rates in Michigan are more than double (107 percent) the national average.
The national average for a full-coverage policy as featured in the Insure.com report came in at $1,325 this year – a slight increase from last year’s average of $1,311. Rates varied from a low of $808 a year in Maine to a budget-busting $2,738 in Michigan. Insurance rates in Michigan are more than double (107 percent) the national average. "There are some things that state governments can do to make their states more attractive to research and development," including R&D tax credits, Nariman Behravesh, chief economist at IHS Inc. in Lexington, Massachusetts told Governing magazine. "State governments — if they carefully target areas where they think they have a bit of a competitive advantage — they could develop a cluster around their universities, as well."
"There are some things that state governments can do to make their states more attractive to research and development," including R&D tax credits, Nariman Behravesh, chief economist at IHS Inc. in Lexington, Massachusetts told Governing magazine. "State governments — if they carefully target areas where they think they have a bit of a competitive advantage — they could develop a cluster around their universities, as well."


 ents currently working on the Hartford Hand initiative. Each week, Welch and colleagues Yonathan Moshayev, Jake Green, Amber Sayer, and Stephen Sousa, spend several hours improving the current design to make the unique Hartford Hand a reality for patients.
ents currently working on the Hartford Hand initiative. Each week, Welch and colleagues Yonathan Moshayev, Jake Green, Amber Sayer, and Stephen Sousa, spend several hours improving the current design to make the unique Hartford Hand a reality for patients.



























