Who Knew? Northeast is Hotbed of Entrepreneurial Activity, For Some More than Others
/Takes one to know one. Or, more accurately, know one and you may become one. That’s the bottom line of an exploration into entrepreneurship by a Kauffman Foundation researcher, who found that the Northeast is the best place to catch the entrepreneurial bug.
As Connecticut sinks increasing dollars into initiatives to encourage entrepreneurship, develop jobs, and turn ideas into business es (often with state financial incentives) the report offers guidance of factors influencing the frequency of entrepreneurial launches. Connecticut Innovations, established and supported by state government, helps Connecticut businesses grow through creative financing and strategic assistance, and is the nation's sixth most-active early stage investor.
es (often with state financial incentives) the report offers guidance of factors influencing the frequency of entrepreneurial launches. Connecticut Innovations, established and supported by state government, helps Connecticut businesses grow through creative financing and strategic assistance, and is the nation's sixth most-active early stage investor.
The survey indicated that the likelihood of a person knowing entrepreneurs varied widely by location, income, gender, and age. Respondents were much more likely to know entrepreneurs if they were male, had modest income, or were middle-aged. And they were much less likely to know entrepreneurs (or be entrepreneurs) if they were female, had a higher income, or were located in the Midwest or South.
The study suggests that there could be “material increases in entrepreneurship simply through doing a better job of exposing people to existing entrepreneurs, especially peers or contemporaries.” Entrepreneurship grows, the study found, where it is planted.
Key factors to consider when attempting to encourage entrepreneurship, according to the study:
- Women have less exposure to growth entrepreneurs than men
- The young have much more exposure to growth entrepreneurs
- People in lower income strata are much less likely to be exposed to growth entrepreneurs
The study concluded that “In all cases, an individual’s exposure to entrepreneurs—and to growth entrepreneurs in particular—may increase his or her likelihood of being one. Entrepreneurship can be viral, but must be introduced early and often in environments where it is least often seen.”
The study distinguished between entrepreneurial companies and “growth entrepreneurial companies,” those companies growing more than 20 percent a year and with more than $1 million in sales, generate more employment and contribute more to wealth and GDP than do slower-growing ventures.
The likelihood of a respondent reporting knowing an entrepreneur 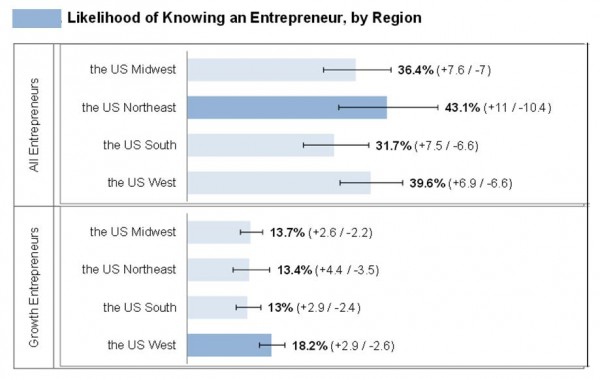 in the United States was 36.7 percent. The likelihood of knowing a growth entrepreneur was considerably lower, at 15.4 percent.
in the United States was 36.7 percent. The likelihood of knowing a growth entrepreneur was considerably lower, at 15.4 percent.
When broken down by gender, the likelihood of males knowing an entrepreneur was 39.9 percent, females 35.8 percent. For growth entrepreneurs, the gender gap was considerably wide, 24.8 percent to 12.1 percent.
A year ago, CTNext, Connecticut’s innovation ecosystem managed by Connecticut Innovations (CI), announced the launch of the Entrepreneur Innovation Awards (EIA), a competitive pitch process that provides awards up to $10,000 to entrepreneurs in Connecticut for growth-related activities. CI helps innovative companies in four key ways: by offering equity, debt, grants and strategic guidance.
A month ago CTNext announced the winners of the latest round of EIA awards; Connecticut-based companies and entrepreneurs, received $10,000 for their project ideas. CI also selected David Wurzer, formerly a senior managing director at CI, to be chief investment officer and executive vice president. As part of his new role, Wurzer will be responsible for the management of the investment function, staffing needs, portfolio and risk management, outreach to stakeholders, budget planning and performance measurement.
The study “Getting the Bug: Is (Growth) Entrepreneurship Contagious?” was conducted by Paul Kedrosky of the Kansas City-based Kauffman Foundation, and is aimed at providing data to guide efforts across the country to grow entrepreneurship. The survey, which categorizes responses of 2,000 individuals by age, income, gender, and location, was done via Consumer Google Survey.































