Income Inequality Ranked as World’s Top Challenge; CT Has Among Widest Disparities
/Income disparity increased in all 50 states in the last few decades, including Connecticut, according to a study released earlier this year. Now, new data indicates that the problem of inequality goes well beyond the borders of Connecticut and the United States, and is increasingly viewed as the world’s top trend requiring attention.
Connecticut’s top 1 percent captured 63.9 percent of the total income growth from 1979 to 2007 and 50 percent from 2009 to 2011, the study from the Economic Analysis and Research Network found. The top 1 percent in Connecticut also ranked number 1 out of all 50 states for the most income growth from 1979-2007 with 414.6 percent growth - over 14 times the income growth for the bottom 99 percent over the same period. They experienced 29 percent growth. 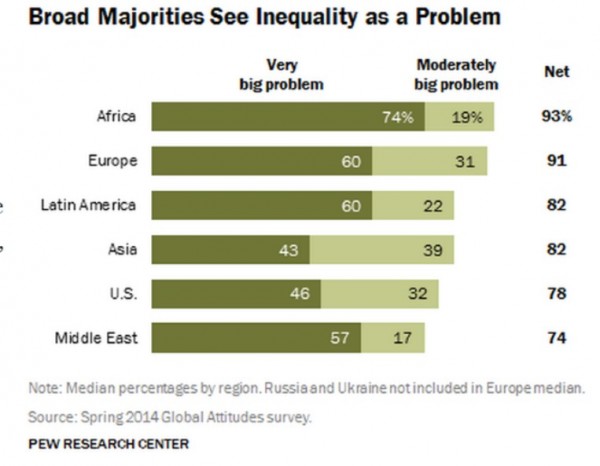
New York and Connecticut had the largest gaps between the average incomes of the top 1 percent and the average incomes of the bottom 99 percent. In both states, the top 1 percent earned roughly 40 times that of the bottom 99 percent.
Looking at inequality worldwide, Crédit Suisse reports people with a net worth of more than $1 million represent just 0.7 percent of the global population, but they have 41 percent of the world’s wealth. Meanwhile, those with a net worth of less than $10,000 represent 69 percent of the population, but just 3 percent of global wealth.
A new report by the World Economic Forum ranks rising inequality as the top trend facing the globe in 2015 (it was ranked #2 last year), according to a survey of 1,767 global leaders from business, academia, government and non-profits.
A recent Pew Research Center survey highlights the extent to which people across the globe agree that inequality is a serious challenge. In all 44 nations polled, majorities say inequality is a big problem facing their country, and majorities in 28 nations consider it a very big problem. Concerns about inequality are widespread in nations that were deeply affected by the Great Recession. For instance, more than seven-in-ten in Greece (84%), Spain (74%) and Italy (73%) say the gap between rich and poor is a very big problem.
In the United States, 46 percent view inequality as a very big problem and another 32 percent consider it to be a problem – a total of 78 percent.
The World Economic Forum’s global agenda for 2015 concluded “The inherent dangers of neglecting inequality are obvious. People, especially young people, excluded from the mainstream end up feeling disenfranchised and become easy fodder of conflict. This, in turn, reduces the sustainability of economic growth, weakens social cohesion and security, encourages inequitable access to and use of global commons, undermines our democracies, and cripples our hopes for sustainable development and peaceful societies.”































