States Under Pressure to Raise Gas Tax to Support Infrastructure Repair
/In nearly two-thirds of states, state-imposed fuel taxes have not kept up with inflation for two decades, according to a Governing analysis of state gas tax data reported to the U.S. Census Bureau. That is forcing legislators around the country to consider raising gas taxes or exploring other ways to increase transportation spending, as Congressional action on adjusting the federal portion of the gas tax to meet infrastructure needs remains stalled.
As Connecticut – with among the nation’s highest gas taxes - contemplates embarking on a decades-long comprehensive transportation infrastructure upgrade, how to fund the likely record-setting fiscal requirements has been assigned to a task force to consider and propose recommendations. Earlier this month, Michigan voters resoundingly defeated a measure -- 80 percent voted “no” -- to hike gas taxes and make many other changes to boost state transportation spending, Governing reported. Last fall, Massachusetts voters recinded (with 53% of the vote) a law that would have automatically tied gas tax rates to inflation. The law had been passed by the state legislature in 2013. 
Connecticut’s gas tax, increased most recently by about 4 cents per gallon in July 2013, based on legislation approved previously – a step not taken by many other states in recent years. The Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy reported earlier this year that 22 states hadn’t raised their gas taxes in more than a decade, according to Governing. Connecticut is not among them.
At the federal level, the gas tax was last increased in 1993. Since then, inflation, fuel-efficient vehicles and changing driving habits are all undermining the per-gallon charges that are the country’s main source for transportation funding to repair roads, bridges, and related infrastructure. In most states, just as nationally, those problems grow because lawmakers rarely adjust fuel taxes, Governing noted. Connecticut, as other states, has also seen funds derived from the gas tax diverted from transportation-related purposes through the years, adversely impacting the status of transportation infrastructure.
In January, USA Today and 24/7 Wall Street reported that Connecticut’s state fuel tax of 43.2 cents per gallon was the fifth highest in the nation, and as a percentage of the gas price, the state was third highest. At the time, Connecticut’s gas price was the sixth highest in the nation. Gas prices nationwide and in Connecticut have risen since January, and Connecticut continues to rank near the top of most gas price surveys.
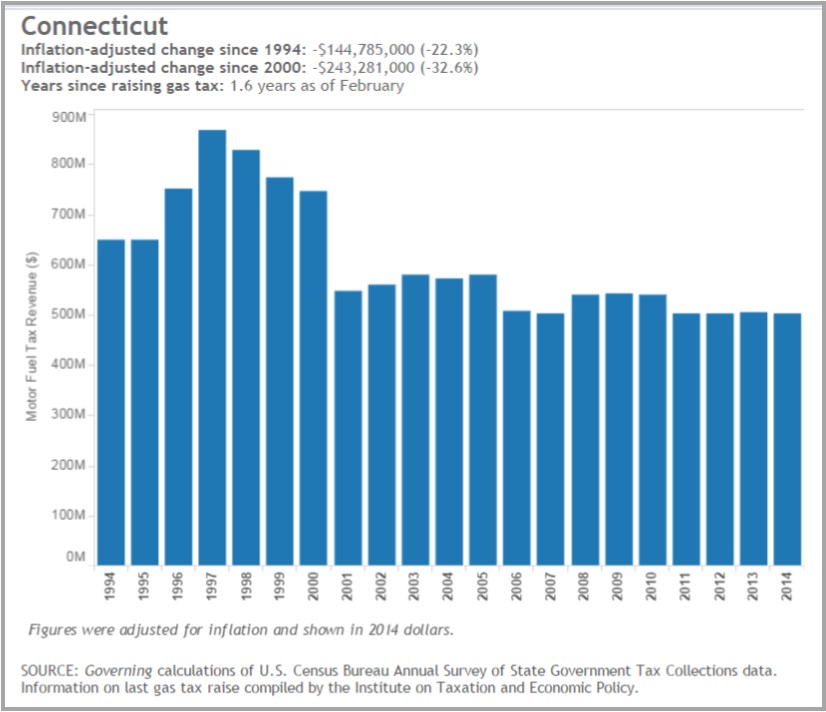 In Connecticut, the inflation-adjusted change is a reduction of in the value of the dollars provided by the tax of 32.6 percent since 2000 and 22.3 percent since 1994, according to the Governing analysis, using data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Earlier this year, Governor Malloy announced a two-part transportation plan consisting of a five-year ramp-up that utilizes $10 billion capital funding, and leads up to a 30-year vision utilizing $100 billion in funding. The Transportation Finance Panel he appointed to recommend options the state can utilize to finance the infrastructure transformation is due to report this summer (see members below).
In Connecticut, the inflation-adjusted change is a reduction of in the value of the dollars provided by the tax of 32.6 percent since 2000 and 22.3 percent since 1994, according to the Governing analysis, using data from the U.S. Census Bureau and the Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. Earlier this year, Governor Malloy announced a two-part transportation plan consisting of a five-year ramp-up that utilizes $10 billion capital funding, and leads up to a 30-year vision utilizing $100 billion in funding. The Transportation Finance Panel he appointed to recommend options the state can utilize to finance the infrastructure transformation is due to report this summer (see members below).
The federal government’s 18.4-cent gasoline tax brought in a fifth less, in inflation-adjusted dollars, in 2013 than in 1993, Governing reported. The federal government’s buying power peaked in 1994, immediately following its gas tax hike. The purchasing power of states fuel taxes peaked five years later, in 1999. In 37 states, inflation-adjusted revenues from fuel taxes slipped since 2000.
At the federal level, fuel taxes have been flat for more than 20 years, starving the Highway Trust Fund of revenue used for rising infrastructure repair costs, according to Reuters. According to Forbes, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) has estimated that in 2024 alone the Highway Trust Fund will spend $18 billion more than it brings in, Forbes has reported. The CBO estimates the cumulative shortfall over the next decade will top $160 billion.
A year ago, when gas prices nationwide were at their lowest levels in years, Republican Senator Bob Corker of Tennessee and Democrat Chris Murphy of Connecticut proposed raising federal gasoline and diesel taxes by 12 cents a gallon over two years– to bring the tax where it would have been had it kept up with inflation for the past two decades. As in the past, the prospect of a federal tax increase in the gas tax – even to address needed transportation infrastructure repairs – did not gain significant support.
At the time, it was estimated that American drivers pay an average of $94 a year to access over 11,618 miles of highways, roads and bridges. Based on data from the Government accountability Office, the National Stone, Sand & Gravel Association pointed out that “with a growing number of potholes, cracked roads and traffic jams plaguing America, we need a common-sense and responsible way to pay for improving our infrastructure.”
-
Cameron Staples (Chair): President and CEO, New England Association of Schools and Colleges; Former Co-Chair of the Finance, Revenue and Bonding Committee, Connecticut General Assembly
-
Beth Osborne: Senior Policy Advisor, Transportation for America; Former Acting Assistant Secretary for Transportation Policy, U.S. Department of Transportation
-
William Bonvillian: Director, Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Washington, D.C. Office
-
Joan Carty: President and CEO, Housing Development Fund
-
Bert Hunter: Chief Investment Officer, Connecticut Green Bank
-
Oz Griebel: President and CEO, MetroHartford Alliance
-
Paul Timpanelli: President and CEO, Bridgeport Regional Business Council
-
Stanley Mickus: Marketing and Public Affairs, Cross Sound Ferry Services
-
Emil Frankel: Consultant on transportation policy; Former Commissioner, Connecticut Department of Transportation (1991-1995); Former Assistant Secretary for Transportation Policy, U.S. Department of Transportation (2002-2005)





























