Metro Hartford Progress Points Report Looks at Promise in Communities Amidst Considerable Challenges
/First, the bad news. The Metro Hartford region “has not produced meaningful job growth in the past 25 years, despite having advanced industries that offer a family-sustaining wage and having residents eager to work.” The region’s spending on local schools continues to increase, even as enrollment declines, and the region “retains the fewest four-year graduates of any metro region in the country – with 60 percent of recent graduates citing jobs as their primary reason for leaving.” Even in the region’s traditional strength in advanced industries, such as aerospace manufacturing and computer systems designs, “our competitive advantage may be eroding.”
If the goal of the latest edition of the Metro Hartford Progress Points report, driven by the Hartford Foundation for Public Giving, is to push a region-wide conversation that spurs progress, the data highlighting five key issues impacting the region’s 38 communities may have just enough unsettling news and rays of hope to do just that. “The need for systemic change,” the report indicates, “requires leadership and more regional coordination and integration.”
The third annual edition of the report is the result of collaboration between nine stakeholders representing local government, businesses, nonprofits, academic and philanthropic institutions and organizations committed to making long-term progress in the region.
The 2016 report focuses on five related themes: attracting and retaining a skilled workforce; better connecting people to opportunity; aligning workforce and economic development strategies; ensuring a quality education for all despite scarce resources and building collaborative leadership and civic engagement to create long-term progress.
The data suggests that the region may be poised for greater success, but not without accelerated efforts, noting flatly that “more is needed.”
The report notes that the beginnings of “meaningful change” is evident, with towns creating walkable areas near transportation through transit-oriented development along the CT Fasttrak corridor and the New Haven-Hartford-Springfield rail line, expanding transportation options to meet the needs of today’s population and employers, an expanding presence of colleges in downtown Hartford, and regional collaboratives creating career pathways and bridging the divide among differing aspects of the education system from middle school through the workforce.
 Local and regional organizations and associations, such as the MetroHartford Alliance’s HYPE, reSET, United Way’s Emerging Leaders and the Urban League’s Young Professionals “engage and connect millennials” and offer “business advisory services and other supports to help small businesses thrive,” the report explains, providing “a great start” on what needs to be done.
Local and regional organizations and associations, such as the MetroHartford Alliance’s HYPE, reSET, United Way’s Emerging Leaders and the Urban League’s Young Professionals “engage and connect millennials” and offer “business advisory services and other supports to help small businesses thrive,” the report explains, providing “a great start” on what needs to be done.
The report notes that “regional thinking is not new to Metro Hartford, even if successes have been intermittent. Without regional government, we must rely on informal, voluntary collaboration among leaders to address regional challenges.”
Among the findings:
- Most job openings in the future will be in either high-wage jobs that require advanced degrees (27 percent) or low-skill jobs with wages that cannot sustain a family (72 percent).
- While school enrollment in our region has declined by 7 percent since 2001, amounting to 29,000 additional empty seats in our region’s classrooms, education expenditures have increased 25 percent.
- Millennials are projected to be the largest workforce segment by 2025, but who are they? Nearly half (43%) of the region’s 18- to 34-year-olds live in households that don’t earn family-sustaining wages.
- Millennials and those aged 45-64 are moving out of our state in large numbers, along with those with post-secondary education, and are taking $912 million of their income with them. Overall, college graduates, individuals with advanced degrees and older residents are moving out of state, while younger and less educated people are moving in.
Regarding economic growth – or the lack thereof – the Hartford region ranks at the bottom of the list among Cleveland, Buffalo and New Orleans over the past quarter-century. Topping the list are Austin, Las Vegas, Orlando and Raleigh.
 The report includes a timeline of past efforts aimed at addressing the region’s long-standing challenges, “not to be disheartening, but instead to highlight where positive changes have been made” and how collaborative efforts can “create opportunities for all Greater Hartford residents.” The report also indicates that:
The report includes a timeline of past efforts aimed at addressing the region’s long-standing challenges, “not to be disheartening, but instead to highlight where positive changes have been made” and how collaborative efforts can “create opportunities for all Greater Hartford residents.” The report also indicates that:
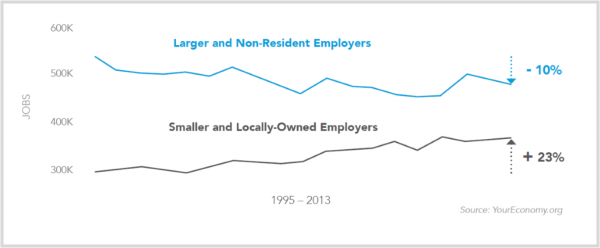
- While net job growth in our region has been flat, the region’s smaller and locally-owned businesses have increased employment by 23 percent between 1995 and 2013. Unfortunately, larger and employers headquartered out of state have decreased employment by 10 percent during this same time period.
- New and proposed rail, bus and highway projects offer the promise of access to jobs, housing and amenities that can spur economic growth.
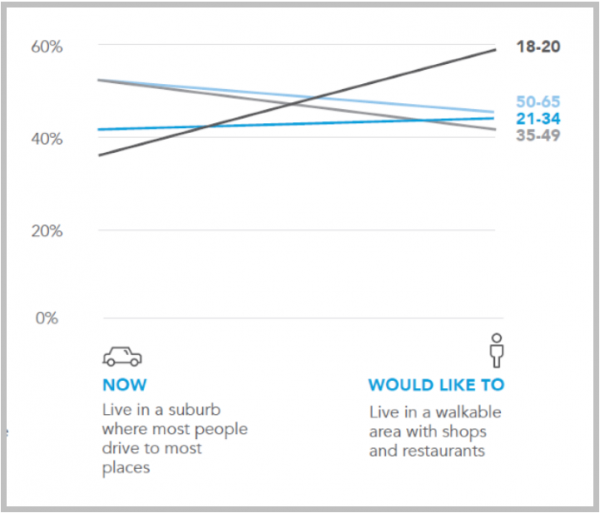
- Many of the region’s residents – of all ages – would like to live where they can walk to shops, restaurants and other amenities, compared to where they lie today. That is true of 60 percent of those ages 18-20, and more than 40 percent of other age demographics.
The Metro Hartford region consists of 1 million people living in Hartford, New Britain and the 36 surrounding communities. The partners in the initiative expressed the hope that the latest edition of the Progress Points report creates the “sense of urgency necessary to address shared regional challenges.”
The Metro Hartford Progress Points Partners are: Capitol Region Council of Governments, Capital Workforce Partners, City of Hartford, Hartford Foundation for Public Giving, Hispanic Health Council, MetroHartford Alliance, Trinity College Center for Urban and Global Studies, United Way of Central and Northeastern Connecticut, and Urban League of Greater Hartford.
https://youtu.be/0zTQjsbNlw0





























