Absenteeism Continues to Decline in CT Schools, Nation Looks to CT Approach
/Chronic absenteeism is down across the state, according to new data released by the State Department of Education (SDE), a trend that is gaining notice beyond Connecticut and a sign that collaborative efforts to keep students across Connecticut in school and engaged are having a positive impact. The number of chronically absent students in Connecticut dropped to 9.6 percent in 2015-16, down from 10.6 percent the year before and down from a high of 11.5 percent in 2012-13. The decline in Connecticut’s chronic absenteeism rate means that over 10,000 more students are attending school on a daily basis than four years ago. Nationally, missing too much school is a coast-to-coast crisis that affects more than 6.5 million students.
Connecticut's work is gaining attention at the national level, and was subject of an article in the education publication Kappan Magazine. The article, “Chronic early absence: What states can do” was co-authored by Hedy Chang, executive director of Attendance Works, Charlene M. Russell-Tucker, chief operating officer of the Connecticut State Department of Education, and her colleague Kari Sullivan, state attendance lead at SDE.
The data also shows that while minority students have disproportionately high rates of chronic absenteeism when compared with their white peers, rates of chronic absenteeism are decreasing for black and Hispanic students in Connecticut.
In 2015-16, the chronic absenteeism rate for Hispanic students was 15.7 percent, down from 19.1 percent in 2012-13. For black students, the rate was 14.5 percent in 2015-16, down from 16 percent in 2012-13. (The new data is available on the CSDE’s data portal, EdSight. The data was released as part of a Chronic Absenteeism presentation delivered this month to the State Board of Education.) The magazine article notes that “Low-income students are four times more likely to be chronically absent than others, often for reasons beyond their control, such as unstable housing, unreliable transportation, and a lack of access to health care.”
Chronic absenteeism is defined as missing 10 percent or more days of school for any reason, including excused absences, unexcused absences, suspensions, and other disciplinary actions.
“We have identified several areas where we are shifting our focus to fulfill our promise of an excellent public education for every Connecticut child. One of those focus areas is chronic absence,” said Commissioner of Education Dianna R. Wentzell. “We want every public school student in our state to be in school and engaged. That means we have to work with families, educators, and community stakeholders to decrease the number of days that students are out of school.”
Earlier this year, the State Board of Education adopted its Next Generation Accountability System, which uses multiple academic and non-traditional indicators to assess how well a school is performing toward the goal of preparing all students for success in college, career, and life. Chronic absenteeism is one of the new indicators included in the system, which means school districts will have to pay close attention to the problem of chronic absenteeism and take steps to ensure more students attend school on a daily basis.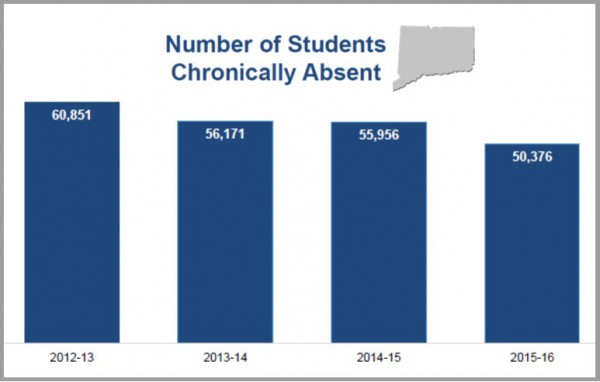
Research shows that chronic absenteeism is inextricably linked with student performance, and students who are chronically absent are less likely to read on grade level, are less likely to perform well academically, and are at a greater risk for dropping out of high school. Risk factors for chronic absence include poverty, homelessness, chronic health conditions, frequent moves, and disabilities.
The article notes that “Most school districts and states don’t look at all the right data to improve school attendance. They track how many students show up every day and how many are skipping school without an excuse but not how many are missing so many days in excused and unexcused absence that they are headed off track academically.”
Among the communities being highlighted by SDE are Killingly, where chronic absenteeism dropped from 16.2% to 9.7%; Bridgeport, where the reduction was from 25.1% to 19.0%; East Haven, where the drop was from 16.1% to 11.2%; New Britain, where absenteeism was reduced from 24.6% to 20.7%; and Danbury, which saw a reduction from 11% to 7.1% between 2012-13 and 2014-15. Attendance Works, a national and state initiative that promotes awareness of the important role that school attendance plays in achieving academic success, is also highlighting specific Connecticut districts where progress is being made, including New Britain, Middletown and Vernon. 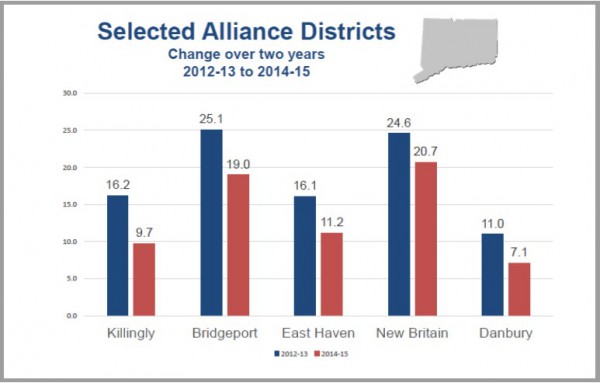
The SDE has been working with key partners such as the Governor’s Prevention Partnership, Attendance Works, the Campaign for Grade-Level Reading, and the Legislature’s Committee on Children. Chronic absenteeism is addressed in the annual Alliance District grant application for participating districts. The state is also expanding restorative justice programs, such as the Connecticut School-Based Diversion Initiative, and positive behavioral interventions and supports. Additionally, districts are increasing utilization of the Department of Children and Families’ Emergency Mobile Psychiatric Services to respond to mental health crises.
“It is critical that we all understand the importance of daily school attendance. Even in the early grades, lost time in school can put students at risk of becoming disengaged or dropping out of school down the road,” said Commissioner Wentzell. The state approach focuses on six "high-impact" strategies:
#1: Build Awareness #2: Use Data to Promote Action #3: Cultivate Champions to Build a State-Level Infrastructure #4: Build Capacity #5: Identify and Leverage Bright Spots #6: Foster Accountability
The magazine article co-authors stress that “By monitoring chronic absence in grades K-12 — and paying particular attention to the youngest students — states can address the needs of students and their families before they require more expensive intervention and remediation.”





























