How Connected is Connecticut? State Ranks 6th in the USA
/Internet access is as good in Connecticut as just about anywhere else in the country. A new report on the Top Connected States in America ranks Connecticut as the 6th most connected state in the nation. The analysis, by USDish.com, found that the top 10 states showing excellent connectivity to broadband all value connecting rural citizens to the resources they need to succeed economically, both in school and at work.
“Overall we found that the most important factor in these states’ ability to connect rural citizens to the internet were the use of government funded broadband task forces, infrastructure maintenance, and local support. The states that listened to the community were more likely to connect them to proper resources and economic growth flourished.”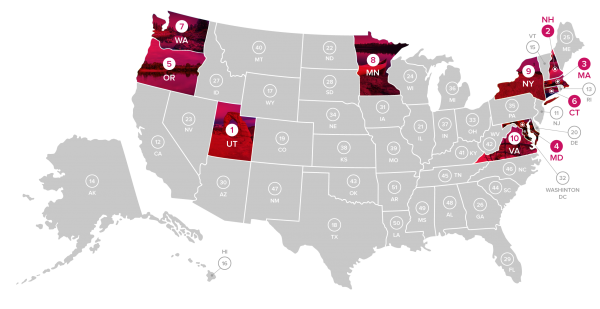
While Connecticut ranked 6th overall, the state’s ranking varied in each of the categories of the analysis: Connecticut ranked 10th in Access, 1st in Rural Access, 12th in Speed, and 21st in Support (by government).
Analysts compiled and ranked the report using data from the American Community Survey, conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau, the EducationSuperHighway non-profit, Fastmetrics, the National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL) and the Institute for Local Self-Reliance.
Connecticut ranked 10th in Access, 1st in Rural Access, 12th in Speed, and 21st in Support. The top five states for Rural Access were all in the Northeast – Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, and Rhode Island. “Perhaps the emphasis on education and communication makes it easier to access the internet as a student, even in a rural area like Connecticut,” the analysis stated.
 The analysis points out that a main reason why people don’t have access to broadband internet is due to a lack of income. Cited is a Pew Research poll that found 23 percent of people making under $30,000 per year don’t use the internet, possibly because of the high price for something they don’t consider a basic need. Most rural schools across the country still lack access to fiber and pay more than twice as much for bandwidth.
The analysis points out that a main reason why people don’t have access to broadband internet is due to a lack of income. Cited is a Pew Research poll that found 23 percent of people making under $30,000 per year don’t use the internet, possibly because of the high price for something they don’t consider a basic need. Most rural schools across the country still lack access to fiber and pay more than twice as much for bandwidth.
In contrast, Minnesota, New Hampshire, Oregon, and Maryland all have state government broadband task forces which promote the expansion of internet access throughout their rural areas, the analysis points out.
For internet access per state, the USDish team analyzed the percentage of school districts meeting a minimum of 100 Kbps per student. They also examined the percentage of those with an internet subscription, and the total percentage of users with any access to the internet at all, be it in the form of a community library, town hall, or school.
Speed was analyzed by the average Mbps per state, and they evaluated states on whether they had a stimulus project, broadband task force, or whether the state had barriers preventing them from expanding the connectivity of those living in the area (i.e. laws, infrastructure support, prohibitions, etc.). As for rural area access, data on the number of households that had broadband internet in both urban and rural areas was used. USDish.com is an authorized retailer of DISH Network.































