Marijuana, Cellphones May Increase Pedestrian Fatalities, Federal Report Suggests; Fewer Deaths in CT as 23 States See Increase
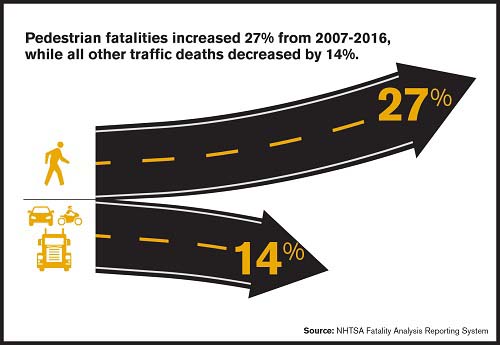
/Connecticut is one of 20 states that saw a decline in the number of pedestrian deaths in the first half of 2017, as compared with the first half of the previous year. The trend nationally, however, is in the opposite direction, as 23 states saw pedestrian deaths increase. Seven states were virtually unchanged. And the trend in recent years has also been a rising death toll. The number of pedestrian fatalities increased 27 percent from 2007 to 2016, while at the same time, all other traffic deaths decreased by 14 percent.
A new national study raises the possibility of a number of factors for the increase – an increase in the number of cars on the road, the increasing use of cell phones, and the use of marijuana, which has been legalized for recreational use in some states, including neighboring Massachusetts. The report suggests that it "provides an early look at potential traffic safety implications of increased access to recreational marijuana for drivers and pedestrians."
The Governors Highway Safety Administration (GHSA) released a 38-page study this week estimating that just under 6,000 pedestrians lost their lives last year, essentially the same death toll as 2016. The projected total in both years represent the highest levels seen since 1990, Governing magazine reported. The number of states with pedestrian fatality rates at or above 2.0 per 100,000 population has more than doubled, from seven in 2014 to 15 in 2016. From 2015 to 2016, pedestrian fatalities in the nation’s ten largest cities increased 28 percent (153 additional fatalities), according to the GHSA report.
The number of miles traveled by vehicles increased nationally by 2.8 percent between 2015 and 2016 then rose another 1.2 percent the first half of last year, according to Federal Highway Administration data The GHSA report noted that nearly 6,000 pedestrians died in motor vehicle crashes in 2016 and 2017, coming after a spike in the number of pedestrian deaths in 2015. "It has been more than 25 years since the U.S. experienced this level of pedestrian fatalities. Because both 2015 and 2016 saw large increases in pedestrian fatalities, the continuation of pedestrian fatalities at virtually the same pace in 2017 raises continued concerns about the nation’s alarming pedestrian death toll," the report stated.
“We’ve plateaued at a very bad place,” Richard Retting, who authored the report, told Governing. “This should not be a new normal.”
While pedestrian deaths have increased over the past decade, other types of traffic fatalities declined. Pedestrians accounted for 16 percent of all motor-vehicle related deaths in 2016, up from 11 percent in 2007. Federal data suggests nighttime collisions are a major problem -- three quarters of fatal crashes occurred after dark.
In Connecticut, there were 31 pedestrian fatalities in the first half of 2016; 20 in the first half of 2017, a decrease of 35 percent. Connecticut was one of 11 states, 2014-2016, where 20 percent or more of the pedestrian deaths were among people age 70 or older. Connecticut's pedestrian fatality rate in 2016 was 1.73 per 100,000 population, which ranked 20th in the U.S. In the first half of 2017, the state ranked 31st.
Retting told Governing that he suspects cellphone use by drivers and pedestrians could also be a culprit. The GHSA report stated that "Without stating a direct correlation or claiming a definitive link, more recent factors contributing to the increase in pedestrian fatalities might include the growing number of state and local governments that have decriminalized recreational use of marijuana (which can impair judgment and reaction time for all road users), and the increasing use of smart phones (which can be a significant source of distraction for both drivers and pedestrians).
 The total number of multimedia messages sent has more than tripled since 2010. The report also suggests a possible link with marijuana use. According to the report, the seven states (Alaska, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, Washington) and DC that legalized recreational use of marijuana between 2012 and 2016 reported a collective 16.4 percent increase in pedestrian fatalities for the first six months of 2017 versus the first six months of 2016, whereas all other states reported a collective 5.8 percent decrease in pedestrian fatalities.
The total number of multimedia messages sent has more than tripled since 2010. The report also suggests a possible link with marijuana use. According to the report, the seven states (Alaska, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, Washington) and DC that legalized recreational use of marijuana between 2012 and 2016 reported a collective 16.4 percent increase in pedestrian fatalities for the first six months of 2017 versus the first six months of 2016, whereas all other states reported a collective 5.8 percent decrease in pedestrian fatalities.
One example cited is Washington state, where marijuana was legalized in late 2012 and the first dispensaries opened in mid-2014. According to data from the Traffic Safety Commission, Governing reported, Washington state saw an increase in 2015 and 2016 in fatal crashes where THC, the primary psychoactive chemical in marijuana, was present in blood tests of either the pedestrian or driver.
It was noted, however, that the totals, while higher, still remain relatively small. THC levels can be detected days or even weeks after marijuana use, and Washington state’s data also indicates that between 70 and 80 percent of drivers found to have THC also tested positive for alcohol or other drugs, according to that report.
The federal report also indicates that Connecticut DOT recently completed a statewide overhaul to replace old signage, including signs for pedestrian safety. "These are new, bright signs that are up to code," the report explained. "The Highway Safety Office also launched an outreach and advertising campaign titled 'Watch for Me CT' which focuses primarily on pedestrian safety but also includes bicyclists." Law enforcement training for this issue is currently being developed, the report said.
Nationally, there were 4,457 pedestrian fatalities in 2011 and 5,987 in 2016. The data for the first half of 2017 is considered preliminary, and may rise higher as some state records are updated with additional data, the report indicated.































