Reversal of Fortunes: A Decade Up, A Decade Down for Connecticut’s Economy
/Connecticut’s economy is now smaller that it was 2004. The state’s lackluster performance stands in sharp contrast with all of the other New England states, whose economies have seen real growth, as have those of New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania. The state’s economy contracted in 2017, as it did in 2014 and 2016, and its overall performance for the year ranked 49th, topping only Louisiana. An analysis by the University of Connecticut’s Connecticut Center for Economic Analysis (CCEA) points out that since 2008, Connecticut’s economy, measured in real GDP (corrected for inflation) has contracted every year, except for 2015. That year’s positive blip of 1.1 percent growth was quickly overtaken by contraction in the two subsequent years.
The suddenness of this persistent downturn for Connecticut has been dramatic. Between 1997 and 2007, the state’s economy grew by 3 percent annually, outpacing Massachusetts (2.9%), Rhode Island (2.5%), and New York (2.3%), based on the compound rate of annual real GDP growth. In the decade since, through 2016, the Connecticut econom y contracted by 0.9 percent annually while Massachusetts and New York grew by 1.6 percent and Rhode Island by .6 percent, according to data from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis.
y contracted by 0.9 percent annually while Massachusetts and New York grew by 1.6 percent and Rhode Island by .6 percent, according to data from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis.
The Bureau reports the state's GDP shrank 0.2 percent last year—one of just three states with negative growth— after contracting by 0.3% the previous year. At the same time, the national economy expanded 2.1 percent, CBIA recently pointed out. CBIA economist Pete Gioia said “We are missing the economic growth party that the region and most of the country are experiencing." He noted that through March this year, Connecticut has recovered just 80 percent of all jobs lost in the 2008-2010 recession, the slowest recovery in New England. The U.S. has recovered 219 percent of jobs lost.
At the same time the state economy has contracted, Connecticut has seen 78 continuous months of job creation, measured year over year, since 2010, the CCEA analysis acknowledges. While private sector jobs are now above their previous peak, public sector jobs- including those at Foxwoods and Mohegan Sun - have been contracting, and will likely continue to contract for a couple more years, points out Center Director Fred Carstensen. He adds that jobs created in the private sector have been broadly of lower quality than that of jobs lost. Thus real personal income, like real output, has been contracting even as employment has grown. So the common focus on job creation has been deceptive: rising job  numbers has not meant economic growth.
numbers has not meant economic growth.
Adding to the complexity of the situation in Connecticut, Carstensen explains, is the increasing number of residents who work out of state. Since 2016, more than 35,000 additional Connecticut residents have found job outside of the state —so the number of Connecticut residents employed is near an all-time peak. Unfortunately, those 35,000 all pay their income tax first to the state where they work, thus contributing to the fiscal crisis in Connecticut, Carstensen noted.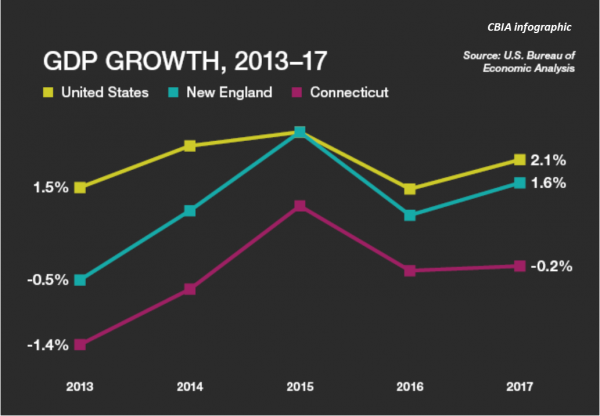
In 2017, Massachusetts led the way in New England with 2.6 percent growth, followed by 1.9% in New Hampshire, with Rhode Island (1.6%), Maine (1.4%), and Vermont (1.1%) all showing growth, unlike Connecticut. In November, 2017, the Connecticut Department of Labor reported that total payroll employment in the state had fallen below the level of February, 1989, according to CCEA.
“The dramatic reversal in fortunes for Connecticut, shifting from a decade and more of strong growth to a persistently contracting economy, is nearly unprecedented among state economies. The next Governor and Legislature need to make a determined effort—absent to date—to understand what drove this climatic reversal of fortunes in Connecticut’s economy health. Such an understanding is central to adopting policies and initiatives to reverse the state’s decline,” Carstensen argued.
The Connecticut Center for Economic Analysis (CCEA), under the direction of Carstensen, is a University Center located within the School of Business at UConn. CCEA specializes in economic impact and policy analysis studies, as well as advising clients regarding business strategy, market analysis, and related topics. CBIA’s research department, led by Goia, provides in-depth economic and policy analysis and survey research assistance to CBIA’s legal, insurance, and human resources divisions and member companies.































