Income Inequality Around Bridgeport Has Grown, Among Nation’s Largest Gaps, Research Shows
/Commuting zones surrounding Bridgeport are among the commuting regions in the United States where neighborhood income inequality has grown notably most severe over the past 20 years, according to a new analysis developed by the Urban Institute and published in Governing magazine. From 1990 to 2010, inequality in the United States increased in many ways, the report explains, highlighting that the income, wealth, and educational attainment of residents in the most privileged neighborhoods in the U.S. escalated rapidly over these two decades. Meanwhile, “residents of the most disadvantaged neighborhoods gained little; many of these neighborhoods grew poorer,” the report indicated.
 As a result, the study found that inequality between “top and bottom income” neighborhoods intensified in the great majority of commuting zones. Even where inequality dropped, the story was not always positive: it often occurred because top-neighborhood incomes fell in the wake of economic stagnation.
As a result, the study found that inequality between “top and bottom income” neighborhoods intensified in the great majority of commuting zones. Even where inequality dropped, the story was not always positive: it often occurred because top-neighborhood incomes fell in the wake of economic stagnation.
The research report, “World Apart: Inequality between America’s Most and Least Affluent Neighborhoods,” found that “the national trend toward rising incomes among top-earning households” was reflected in the nation’s top tracts show growth from $123,000 to $138,300, over 12 percent” during the period 1990-2010. Some top neighborhoods, including those surrounding Bridgeport, “had increases of over $30,000 at the top.”
Annual income in bottom tracts, meanwhile, grew from $36,800 to $37,150 – less than 1 percent over the twenty year period. The average income of bottom tracts declined in 209 of the 570 commuting zones studied, the report indicated. The most severe losses at the bottom among large commuting zones, the report found, occurred in Bridgeport, Newark and Dallas. Bridgeport is one of the ten cities with the largest “neighborhood inequality index.”
The report flatly stated that “Bridgeport, which includes the entirety of Connecticut, already was one of the most unequal commuting zones in 1990. Its top and bottom neighborhoods pulled further apart in income between 1990 and 2010; practically all its top neighborhoods are still in the suburbs and practically all its bottom neighborhoods are in central cities.”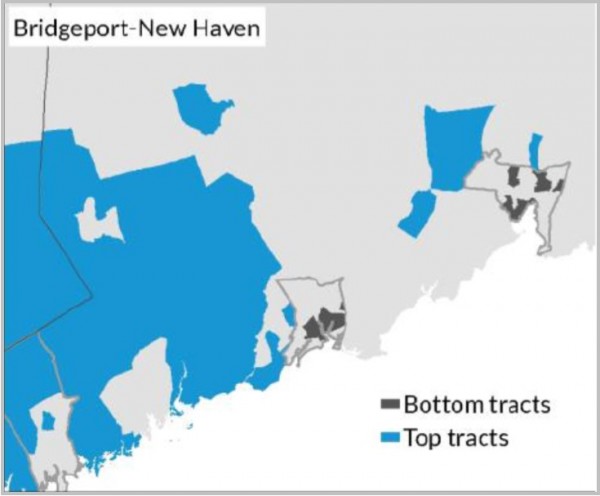
The only cities with commuting zones of over 250,000 people with a higher “neighborhood inequality index” than Bridgeport, as of 2010, are Austin, Baltimore, Birmingham, Columbus, Houston, Nashville, Richmond, and St. Louis.
As a result of changes at the top and bottom, the report noted, income inequality between top and bottom tracts grew from 1990 to 2010 in 433 of the 570 commuting zones. In 237 CZs, income inequality grew because of rapid increases at the top coupled with modest increases at the bottom.
To understand the differences between neighborhoods that share the same housing and labor markets, the Urban Institute analysis used commuting zones (CZs), county-based regions defined in the 1990s. Unlike metropolitan areas, commuting zones cover the entirety of the United States, and their definitions are constant over time.
The study ranked every CZ’s tracts from lowest to highest neighborhood advantage score. Then they identified the top 10 percent and the bottom 10 percent of tracts—the most advantaged and least advantaged neighborhoods in each CZ—for further exploration. There are described as top and bottom tracts. The study analyzed the 570 CZs that had at least 10 census tracts in 2010.
The nonprofit Urban Institute is dedicated to elevating the debate on social and economic policy. The organization’s website explains that “For nearly five decades, urban scholars have conducted research and offered evidence-based solutions that improve lives and strengthen communities across a rapidly urbanizing world. Their objective research helps expand opportunities for all, reduce hardship among the most vulnerable, and strengthen the effectiveness of the public sector.”


 reas such as New York, Philadelphia, Chicago, Boston, Atlanta, and Washington.
reas such as New York, Philadelphia, Chicago, Boston, Atlanta, and Washington. based on their level of income inequality and identified the 50 with the greatest inequality. T
based on their level of income inequality and identified the 50 with the greatest inequality. T





























