Nationwide, Parents Seek Expanded Health Curriculum in Schools
/In Connecticut, a planned, sequential PK-12 Coordinated School Health (CSH) education curriculum is a system designed to addresses the physical, mental, emotional and social dimensions of health. CSH aims to improve students’ health and their capacity to learn through the support of families, communities and schools working together.
A new nationwide survey indicates that the broader, comprehensive definition of health education is precisely what families are seeking in the health education of children. Teaching kids about drugs, alcohol and sex appears to be less controversial than ever before with the majority of parents in a new poll saying schools should and do teach these subjects.
Many parents want more — saying those topics are not enough — finds the University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health. Researchers surveyed a nationally representative sample of parents with kids in middle or high school. Two-thirds of parents polled say schools should definitely cover emotional and mental health issues — which may include such subjects as dealing with depression, stress and bullying — yet only a third say these topics are currently covered by their child’s school. Another 68 percent of parents want to see schools cover basic first aid, and 63 percent say kids should learn CPR.
A coordinated approach to school health aligns health and education efforts and leads to improved physical, mental and developmental outcomes for students, according to the State Department of Education (SDE) website. The department’s overview of the program indicates that “Students’ physical, social and emotional development requires the same level of ongoing assessment and support as their academic development.”
“Research has consistently concluded that student health and academic achievement are directly connected and, in fact, that student health is one of the most significant influences on learning and achievement,” SDE points out.
In the national survey, parents “clearly perceive a gap between what their children need and what they are receiving in the area of mental health education, as well as basic first aid and CPR,” says Sarah Clark, M.P.H., co-director of the C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health. “We are seeing increasing concerns for such issues as stress, depression and suicide among young people, and parents want schools to be a part of the solution. These results suggest that the stigma of mental health issues may have relaxed among today’s parents, in favor of using a broad array of resources to help children and adolescents with these critical areas.”
The Connecticut curriculum is designed to “motivate children and youth to maintain and improve their health, prevent disease, reduce health-related risk behaviors and develop and demonstrate health-related knowledge, attitudes, skills and practices.”
Nearly four in 10 parents (39 percent) in the Mott survey believe schools should educate students on how to use the health care system. But only one in 10 parents say the topic is covered in their child’s school. Low-income parents are more likely to say schools should teach students how to use the health care system—perhaps, Clark notes, because these parents face challenges themselves in accessing health care. The survey does not include a state-by-state breakdown of the data.



 According to the most recent data, adult obesity rates now exceed 35 percent in four states, 30 percent in 25 states and are above 20 percent in all states. Louisiana has the highest adult obesity rate at 36.2 percent and Colorado has the lowest at 20.2 percent.
According to the most recent data, adult obesity rates now exceed 35 percent in four states, 30 percent in 25 states and are above 20 percent in all states. Louisiana has the highest adult obesity rate at 36.2 percent and Colorado has the lowest at 20.2 percent.

 “Every student deserves the opportunity to receive a math education that is rich and rigorous, and equips them with the skills needed to graduate from high school prepared to be successful in both college and career,” said Commissioner Wentzell. “These recommendations by the Council on Mathematics have created a clear path that will help the State Department of Education take the steps needed to ensure that every student in our state receives a high-quality mathematics education.”
“Every student deserves the opportunity to receive a math education that is rich and rigorous, and equips them with the skills needed to graduate from high school prepared to be successful in both college and career,” said Commissioner Wentzell. “These recommendations by the Council on Mathematics have created a clear path that will help the State Department of Education take the steps needed to ensure that every student in our state receives a high-quality mathematics education.”
 Council members included parents, teachers, curriculum specialists, principals, superintendents, board of education members, higher education professors, business leaders, and State Department of Education staff members with the purpose of closely examining the current state of mathematics education in Connecticut.
Council members included parents, teachers, curriculum specialists, principals, superintendents, board of education members, higher education professors, business leaders, and State Department of Education staff members with the purpose of closely examining the current state of mathematics education in Connecticut.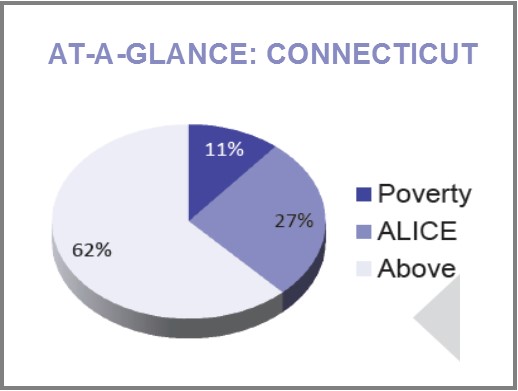




 Unite For Sight's international eye care services with partner local eye clinics are provided year-round and are comprehensive, including examinations by local eye doctors, diagnosis and care for treatable conditions, education, and preventative care. The organization’s website indicates that Unite For Sight has provided eye care services to more than 2.1 million people worldwide, including more than 93,166 sight-restoring surgeries.
Unite For Sight's international eye care services with partner local eye clinics are provided year-round and are comprehensive, including examinations by local eye doctors, diagnosis and care for treatable conditions, education, and preventative care. The organization’s website indicates that Unite For Sight has provided eye care services to more than 2.1 million people worldwide, including more than 93,166 sight-restoring surgeries.
 The conference also includes Social Impact Labs, which provide an opportunity for selected speakers to present their new idea in the format of a 5-minute pitch. All of the presentations are ideas that are being developed, meaning that the ideas are in the brainstorming, early development, or early implementation stage. Following each presenter’s 5-minute pitch, there is a 15-minute period for discussion and coaching with two expert speakers, questions, answers, and feedback from the audience.
The conference also includes Social Impact Labs, which provide an opportunity for selected speakers to present their new idea in the format of a 5-minute pitch. All of the presentations are ideas that are being developed, meaning that the ideas are in the brainstorming, early development, or early implementation stage. Following each presenter’s 5-minute pitch, there is a 15-minute period for discussion and coaching with two expert speakers, questions, answers, and feedback from the audience. The U.S. Department of Education July 2016 Data Point report from the National Center for Education Statistics includes data from the School Crime Supplement (SCS) to the National Crime Victimization Survey, a nationally representative sample survey of students ages 12 through 18, which were used to analyze trends in hate-related words. The SCS study is completed every other year.
The U.S. Department of Education July 2016 Data Point report from the National Center for Education Statistics includes data from the School Crime Supplement (SCS) to the National Crime Victimization Survey, a nationally representative sample survey of students ages 12 through 18, which were used to analyze trends in hate-related words. The SCS study is completed every other year. oped by the federal Health Resources and Services Administration notes that “indirect bullying” includes “rumor spreading or encouraging others to exclude a peer.” Bullying is described as “a public health problem and requires a coordinated community response.”
oped by the federal Health Resources and Services Administration notes that “indirect bullying” includes “rumor spreading or encouraging others to exclude a peer.” Bullying is described as “a public health problem and requires a coordinated community response.”
 “The practice of selling look-alike Smart Snacks in schools likely benefits the brands,” says Harris, “but may not improve children’s overall diet, and undermines schools’ ability to teach and model good nutrition.”
“The practice of selling look-alike Smart Snacks in schools likely benefits the brands,” says Harris, “but may not improve children’s overall diet, and undermines schools’ ability to teach and model good nutrition.” The
The  A minimum-wage worker in Connecticut would need to work full time for 36 weeks, or from January to September, just to pay for child care for one infant. And a typical child care worker in Connecticut would have to spend 63.6% of her earnings to put her own child in infant care, according to the data.
A minimum-wage worker in Connecticut would need to work full time for 36 weeks, or from January to September, just to pay for child care for one infant. And a typical child care worker in Connecticut would have to spend 63.6% of her earnings to put her own child in infant care, according to the data.


 The New Haven Register
The New Haven Register 
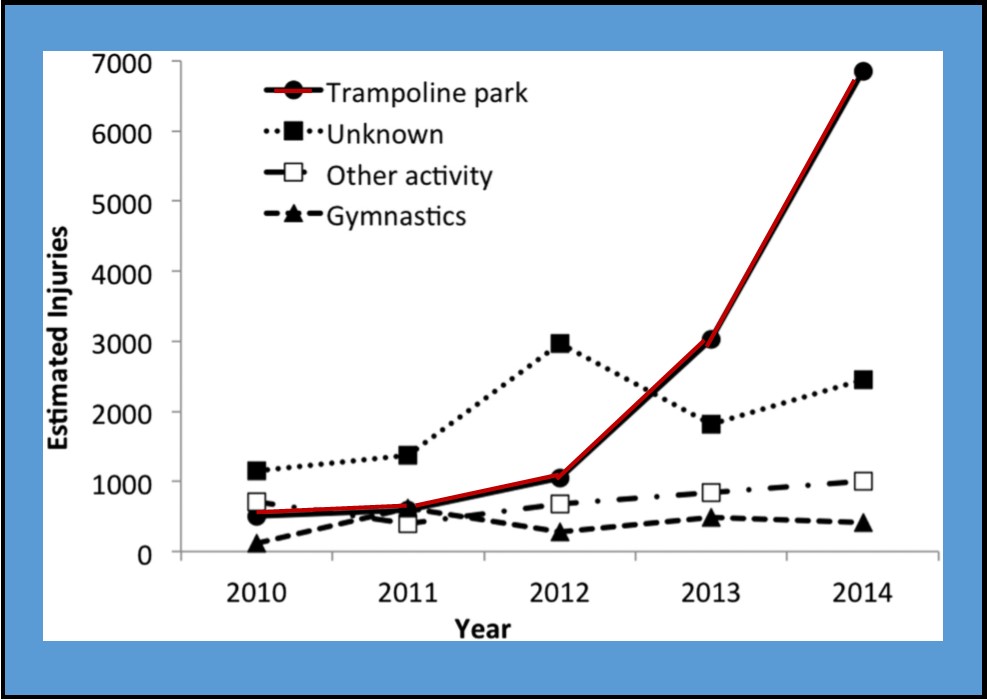 running in communities including Hartford, New Britain, Trumbull, Bethel, Stamford, Norwalk, Manchester, Milford, Danbury, New Milford, Ridgefield, Brookfield, Wallingford. Another is expected soon in East Haven.
running in communities including Hartford, New Britain, Trumbull, Bethel, Stamford, Norwalk, Manchester, Milford, Danbury, New Milford, Ridgefield, Brookfield, Wallingford. Another is expected soon in East Haven. s," the organization said following publication of the study.
s," the organization said following publication of the study.



























