Report: Medicaid's Impact Goes Beyond Health Care to Economy
/Medicaid is, at its core, a health insurance program that provides coverage to low-income Connecticut residents. A new report in Connecticut finds that the program also plays a key role in the state’s economy, budget, and ability to weather economic challenges. The report was developed for, and released by, the Connecticut Health Foundation.
In Connecticut, Medicaid is known as HUSKY and covers approximately one in five state residents – close to 800,000 people. HUSKY covers more than one third of Connecticut children, nearly 47 percent of non-elderly adults with disabilities, 15 percent of seniors, and 70 percent of nursing home residents.
The report, developed by the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families, finds that the program is deeply woven into Connecticut’s health care system and plays a major role in a sector of the economy that has been central to job growth in the state. Health care makes up nearly 15 percent of the state’s gross domestic product. Medicaid finances about 20 percent of health care expenditures in Connecticut.
“It is important for policymakers to understand the full impact of Medicaid in the state, particularly as they face difficult budget decisions,” said the report’s author, Edwin Park, research professor at the Georgetown University Center for Children and Families. “Medicaid plays a key role in the state’s economy and is linked to long-term positive outcomes for children like better health, obtaining a college degree, and higher earnings.”
 Among the report’s other key findings:
Among the report’s other key findings:
- Research has linked Medicaid coverage of children and pregnant women to long-term health and economic benefits when children reach adulthood: better health outcomes, greater educational attainment such as completing high school and obtaining a college degree, and higher employment and earnings.
- Medicaid can help states cope with recessions and economic downturns because it automatically increases federal funding in response to higher state costs, such as those resulting from enrollment increases as people lose their jobs and health insurance.
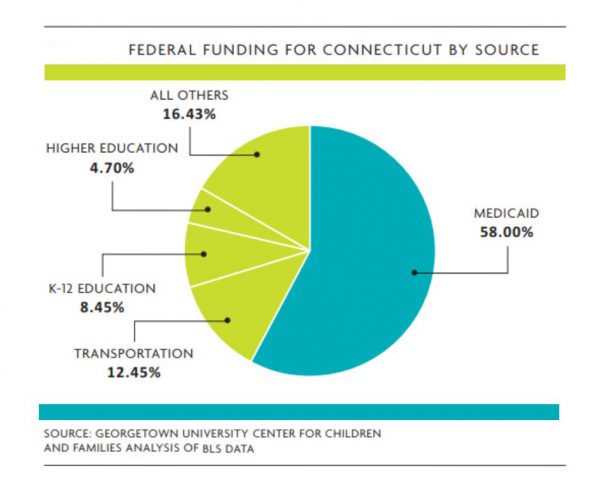
- Medicaid contributes the majority of the federal funding spent through Connecticut’s state budget – 58 percent in the 2016 fiscal year. The federal government pays more than half of the state’s Medicaid costs. For every $10 spent on Medicaid in Connecticut, approximately $5.92 comes from the federal government.
“Connecticut invests significant resources in HUSKY and the findings of this report underscore the impact of this investment,” said Patricia Baker, president and CEO of the Connecticut Health Foundation.
The report also indicted that “research has found that Medicaid eligibility during childhood is tied to higher wages and cumulative higher tax payments made as young adults. It also increases employment and reduces the need for public assistance, especially assistance needed due to disability. According to the report, in 2016 Medicaid covered:
- 4 percent of the nearly 400,000 hospital discharges and 12.9 percent of hospital payments.
- 63 percent of the 373,200 patients who received care at community health centers.
The Connecticut Health Foundation is the state’s largest independent health philanthropy dedicated to improving health outcomes for people of color. Since its creation in 1999, the foundation has awarded more than $62 million to nonprofit organizations and public entities to expand health equity, reduce health disparities, expand health coverage, and improve the health of all Connecticut residents.




 Atop the rankings in the pediatric specialty were Children’s National Medical Center (Washington, DC), Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Boston Children’s Hospital, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Rainbow Babies and Children’s Hospital (Cleveland), UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital of San Francisco and Oakland, New York-Presbyterian Morgan Stanley-Komansky Children’s Hospital, St. Louis Children’s Hospital-Washington University, and C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital – Michigan Medicine (Ann Arbor).
Atop the rankings in the pediatric specialty were Children’s National Medical Center (Washington, DC), Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Boston Children’s Hospital, Children’s Hospital Colorado, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Rainbow Babies and Children’s Hospital (Cleveland), UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital of San Francisco and Oakland, New York-Presbyterian Morgan Stanley-Komansky Children’s Hospital, St. Louis Children’s Hospital-Washington University, and C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital – Michigan Medicine (Ann Arbor). e, infection rates in the NICU and other data collected from a detailed U.S. News clinical survey of children's hospitals, produced 85 percent of each hospital's score. The other 15 percent reflects nominations from pediatric specialists and subspecialists who responded to surveys in 2016, 2017 and 2018 and recommended the hospital for serious cases in their specialty.
e, infection rates in the NICU and other data collected from a detailed U.S. News clinical survey of children's hospitals, produced 85 percent of each hospital's score. The other 15 percent reflects nominations from pediatric specialists and subspecialists who responded to surveys in 2016, 2017 and 2018 and recommended the hospital for serious cases in their specialty.


 The review of the research, conducted by Connecticut-based Rodriguez Data Solutions, points out that policymakers often promote K-12 regionalization as a way to achieve cost savings, but often fail to consider the consequences for student educational achievement. The report reviewed initiatives to promote K-12 regionalization in several states including Connecticut, Maine, New York and Vermont. Among the findings:
The review of the research, conducted by Connecticut-based Rodriguez Data Solutions, points out that policymakers often promote K-12 regionalization as a way to achieve cost savings, but often fail to consider the consequences for student educational achievement. The report reviewed initiatives to promote K-12 regionalization in several states including Connecticut, Maine, New York and Vermont. Among the findings:

 han 90 percent of the cost of the program, allowing Connecticut to cover more than 200,000 people with a relatively small budgetary impact.” Currently, the federal government pays 94 percent of the cost of coverage and the state pays 6 percent. The report also identifies challenges associated with HUSKY D, including concerns raised by health care providers about Medicaid payment rates and uncertainty in federal funding.
han 90 percent of the cost of the program, allowing Connecticut to cover more than 200,000 people with a relatively small budgetary impact.” Currently, the federal government pays 94 percent of the cost of coverage and the state pays 6 percent. The report also identifies challenges associated with HUSKY D, including concerns raised by health care providers about Medicaid payment rates and uncertainty in federal funding.
 The survey found that 38 percent of students whose grades were mostly A’s texted or e-mailed while driving a car on at least one occasion in the 30 days prior to the survey. The percentage was slightly less among students with lower grades: 31% of students with mostly B’s, 30% of students with mostly C’s and 23% of students with mostly D’s and F’s.
The survey found that 38 percent of students whose grades were mostly A’s texted or e-mailed while driving a car on at least one occasion in the 30 days prior to the survey. The percentage was slightly less among students with lower grades: 31% of students with mostly B’s, 30% of students with mostly C’s and 23% of students with mostly D’s and F’s. The ranking does not capture the full extent of deprivations or hardships affecting children. Instead, it focuses on some key rights, or “guarantees” of childhood: life, healthy growth and development, education and protection from harm. If a child experiences all of these, his/her childhood is considered to be “intact.”
The ranking does not capture the full extent of deprivations or hardships affecting children. Instead, it focuses on some key rights, or “guarantees” of childhood: life, healthy growth and development, education and protection from harm. If a child experiences all of these, his/her childhood is considered to be “intact.”
 The report notes that “While children are only 20 percent of the population, they are 100 percent of America’s future.” Save the Children’s ranking reveals children in New Jersey, Massachusetts, Vermont and New Hampshire are far more likely to experience safe, secure and healthy childhoods than children in Louisiana, Mississippi, Oklahoma and New Mexico.
The report notes that “While children are only 20 percent of the population, they are 100 percent of America’s future.” Save the Children’s ranking reveals children in New Jersey, Massachusetts, Vermont and New Hampshire are far more likely to experience safe, secure and healthy childhoods than children in Louisiana, Mississippi, Oklahoma and New Mexico.
 “This is an exciting opportunity for all of us at Foodshare. More produce and healthier options: that’s the future of food banking,” said Jason Jakubowski, President and CEO of Foodshare.
“This is an exciting opportunity for all of us at Foodshare. More produce and healthier options: that’s the future of food banking,” said Jason Jakubowski, President and CEO of Foodshare.
 by the Common Core Standards and provides a pathway for 21st Century Skills.
by the Common Core Standards and provides a pathway for 21st Century Skills. Globally-Focused Coursework would require at least 7.0 credits or demonstration of mastery and Globally-focused Student Activities would require competency in global citizenship through active participation in “at least one or more co-curricular and other school-sponsored or endorsed activities over at least 3 years of their high school experience with suggested involvement of a total of at least 15 hours.”
Globally-Focused Coursework would require at least 7.0 credits or demonstration of mastery and Globally-focused Student Activities would require competency in global citizenship through active participation in “at least one or more co-curricular and other school-sponsored or endorsed activities over at least 3 years of their high school experience with suggested involvement of a total of at least 15 hours.”




























