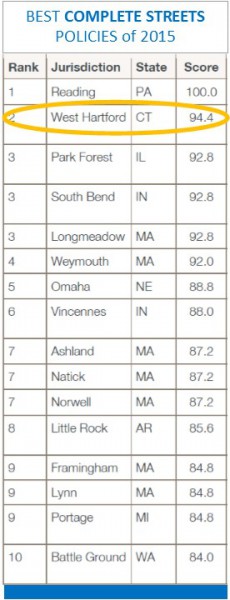
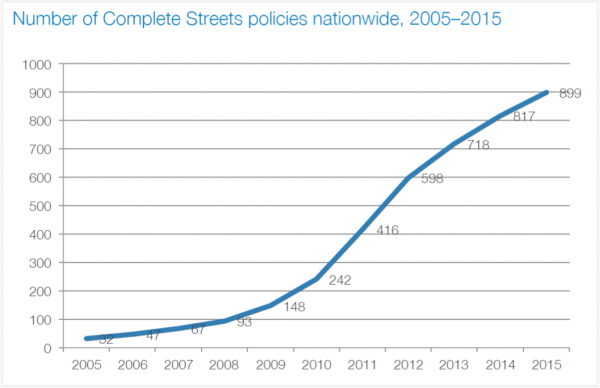
West Hartford’s Complete Streets policy, adopted in 2015, has been named the second best new policy in the nation by Smart Growth America and the Complete Streets Coalition. The coalition highlighted 16 communities nationwide for their outstanding new policies, among 82 communities that adopted Complete Streets policies during the year. Nationwide, there are now a total of 899 Complete Streets policies in place in all 50 states, the organization announced this month.
A Complete Streets approach creates an integrated transportation system that supports safe travel for people of all ages and abilities. This approach redefines what a transportation network looks like, which goals a public agency sets out to meet, and how communities prioritize their transportation spending. A Complete Streets policy is one of the best ways to set this approach into motion, Smart Growth American emphasized.
 The U.S. Surgeon General and Secretary of Transportation both spoke out for more Complete Streets last year and Congress passed a transportation bill that included Complete Streets language for the first time ever.
The U.S. Surgeon General and Secretary of Transportation both spoke out for more Complete Streets last year and Congress passed a transportation bill that included Complete Streets language for the first time ever.
The Complete Streets laws, resolutions, agency policies, and planning and design documents establish a process for selecting, funding, planning, designing, and building transportation projects that allow safe access for everyone, regardless of age, ability, income or ethnicity, and no matter how they travel.
Across the country, 32 state governments or agencies, 76 regional organizations, and 663 individual municipalities have all adopted such policies to create safer, multimodal transportation networks.
West Hartford’s policy is the result of a process that began in 2009 with the adoption of the Town’s 2009-2019 Plan of Conservation and Development,” according to town Deputy Mayor Shari Cantor. She said the plan “promote[s] an integrated and balanced “complete street” transportation system which provides the best possible service, mobility convenience and safety while reinforcing a positive social, economic, and environmental influence on West Hartford.
“Utilizing a comprehensive public participatory process, guided by the leadership of the Town Council; the advocacy efforts of various community groups in West Hartford including our Bicycle Advisory Committee, and the work of our Town staff; we were able to develop and adopt this tremendous Complete Streets Policy,” said Mrs. Cantor in response to the national recognition.
Each year, the National Complete Streets Coalition analyzes newly passed Complete Streets policies. The Coalition examines and scores policy language using the guidelines laid out in our ideal policy elements. Ideal policies state a community’s vision for transportation, provide for many types of users, complement community needs, and establish a flexible project delivery approach. Different types of policy statements are included in the Coalition’s review, including legislation, resolutions, executive orders, internal policies, and policies adopted by an elected board.
The Coalition ranks new Complete Streets policies to celebrate the people who developed exceptional policy language and to provide leaders at all levels of government with examples of strong Complete Streets policies.
Sixteen agencies led the nation in creating and adopting comprehensive Complete Streets policies in 2015. Topping the list, with the first-ever score of 100, was Reading, PA, followed by West Hartford, Park Forest, IL and South Bend, IN. Four of the next seven slots went to communities in Massachusetts: Longmeadow, Weymouth, Ashland, Natick and Norwell. The others were Omaha, NE and Incennes, IN.
Of the 663 municipalities with Complete Streets policies, 239 (or 36 percent) are suburban communities. Small towns, often in rural areas, have passed 111 policies, or 17 percent of all municipal policies. On the other end of the spectrum, 12 of the 15 most populous cities in the country have committed to Complete Streets with a policy, according to the organization’s 2015 report. 
“A Complete Streets approach is about helping everyone stay safe on the road—no matter if they’re walking, biking, taking transit, using an assistive device, or driving,” said Emiko Atherton, Director of the National Complete Streets Coalition. “Passing a Complete Streets policy is one of the best actions communities can take toward achieving these goals.”
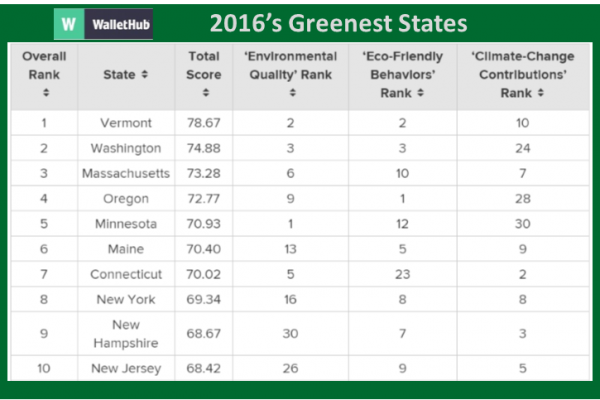
Connecticut became the 10th state in the nation to adopt a Complete Streets law, in 2009. The law mandates “accommodations for all users shall be a routine part of the planning, design, construction and operating activities” of all state highways. Connecticut’s Complete Streets law has evolved, and now (Conn. Gen. Stat. §13-153f) requires pedestrians, cyclists, and transit users to be routinely considered in the planning, designing, construction and operation of all roads.
In 2014, Bike Walk Connecticut released a first-of-its-kind ranking of the state’s cities and towns on how bike- and walk-friendly they are. Simsbury (1), New Haven (2), New Britain (3), Glastonbury (4), and Middletown (5) claimed top honors as the five most bike- and walk-friendly communities.
E arlier this year, the University of Connecticut released a study that shows how shared space, a design concept that encourages all users to share street space, can provide much greater vehicular capacity than conventional intersections and increases pedestrian convenience. The study found that by redesigning streets and intersections as human-scaled places and incorporating shared space concepts, communities of all sizes have successfully encouraged active transportation, stimulated their local economies, reduced accident severity, and lessened their environmental impacts. The study compared actual user delays at six shared space intersections to expected user delays using standard U.S. traffic modeling software. The state Department of Transportation issued a policy document in 2014 consistent with the law.
arlier this year, the University of Connecticut released a study that shows how shared space, a design concept that encourages all users to share street space, can provide much greater vehicular capacity than conventional intersections and increases pedestrian convenience. The study found that by redesigning streets and intersections as human-scaled places and incorporating shared space concepts, communities of all sizes have successfully encouraged active transportation, stimulated their local economies, reduced accident severity, and lessened their environmental impacts. The study compared actual user delays at six shared space intersections to expected user delays using standard U.S. traffic modeling software. The state Department of Transportation issued a policy document in 2014 consistent with the law.
The criteria used in the Complete Streets evaluation include:
- Vision: The policy establishes a motivating vision for why the community wants Complete Streets: to improve safety, promote better health, make overall travel more efficient, improve the convenience of choices, or for other reasons.
- All users and modes: The policy specifies that “all modes” includes walking, bicycling, riding public transportation, driving trucks, buses and automobiles and “all users” includes people of all ages and abilities.
- All projects and phases: All types of transportation projects are subject to the policy, including design, planning, construction, maintenance, and operations of new and existing streets and facilities.
- Clear, accountable exceptions: Any exceptions to the policy are specified and approved by a high-level official.
- Network: The policy recognizes the need to create a comprehensive, integrated and connected network for all modes and encourages street connectivity.
- Jurisdiction: All other agencies that govern transportation activities can clearly understand the policy’s application and may be involved in the process as appropriate.
- Design: The policy recommends use of the latest and best design criteria and guidelines, while recognizing the need for design flexibility to balance user needs in context.
- Context sensitivity: The current and planned context—buildings, land use, transportation, and community needs—is considered in when planning and designing transportation solutions.
- Performance measures: The policy includes performance standards with measurable outcomes.
- Implementation steps: Specific next steps for implementing the policy are described.
The National Complete Streets Coalition, a program of Smart Growth America, is a non-profit, non-partisan alliance of public interest organizations and transportation professionals committed to the development and implementation of Complete Streets policies and practices. A nationwide movement launched by the Coalition in 2004, Complete Streets is the integration of people and place in the planning, design, construction, operation, and maintenance of transportation networks.




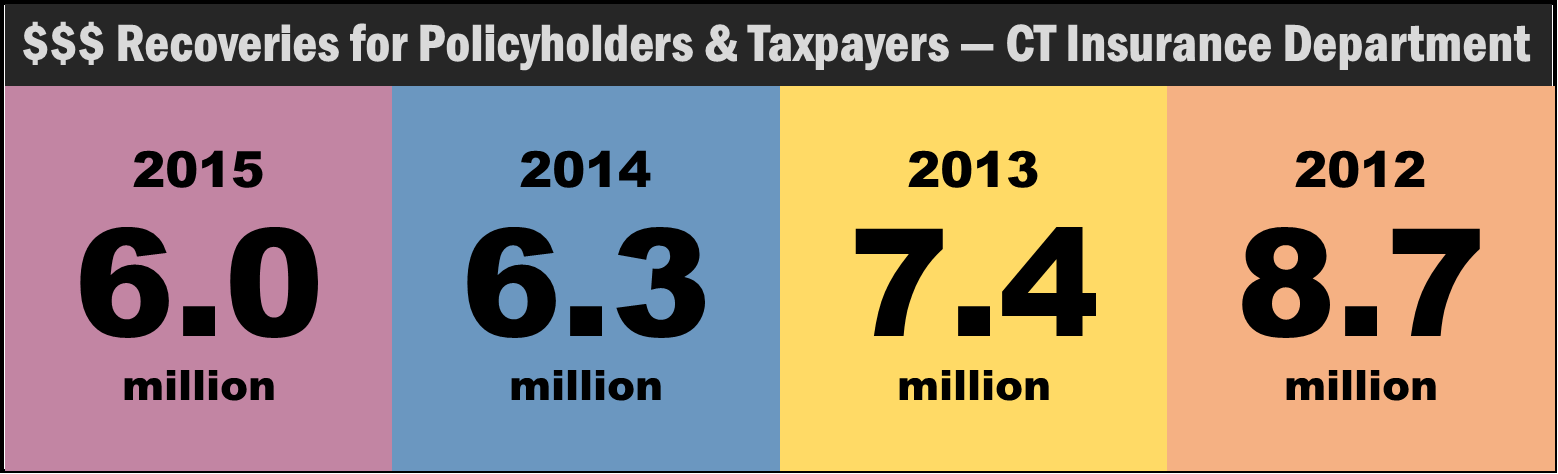
 The Mattress Recycling Council (MRC), a non-profit organization established by the mattress industry that created and manages the program in Connecticut, California and Rhode Island, presented its inaugural
The Mattress Recycling Council (MRC), a non-profit organization established by the mattress industry that created and manages the program in Connecticut, California and Rhode Island, presented its inaugural  “We are pleased with the program’s productive start and will continue to work with city leaders, businesses and the state to improve the program, expand the number of communities served, and increase the volume of mattresses recycled,” said Ryan Trainer, President of MRC and the International Sleep Products Association.
“We are pleased with the program’s productive start and will continue to work with city leaders, businesses and the state to improve the program, expand the number of communities served, and increase the volume of mattresses recycled,” said Ryan Trainer, President of MRC and the International Sleep Products Association.


 Studies show that there is no unmet demand for natural gas in Connecticut, opponents of the planned pipeline said, stressing that gas pipelines are routinely only half full now and electricity demand in New England has remained virtually flat over more than 10 years. Proponents have
Studies show that there is no unmet demand for natural gas in Connecticut, opponents of the planned pipeline said, stressing that gas pipelines are routinely only half full now and electricity demand in New England has remained virtually flat over more than 10 years. Proponents have 


 for a proposed mixed use development project at 161-177 State Street, which is phase one of a multi-phase project that includes demolition of the Mills public housing project and implementation of the Harbor Brook Flood Control project north of the Hub site. The new building will be within walking distance of Meriden`s new Transit center.
for a proposed mixed use development project at 161-177 State Street, which is phase one of a multi-phase project that includes demolition of the Mills public housing project and implementation of the Harbor Brook Flood Control project north of the Hub site. The new building will be within walking distance of Meriden`s new Transit center. In February, the Connecticut Small Business Development Center (CTSBDC), the City of Meriden and The Midstate Chamber of Commerce announced the opening of the newest CTSBDC office, to be located at Meriden City Hall.
In February, the Connecticut Small Business Development Center (CTSBDC), the City of Meriden and The Midstate Chamber of Commerce announced the opening of the newest CTSBDC office, to be located at Meriden City Hall.
 The U.S. Surgeon General and Secretary of Transportation both spoke out for more Complete Streets last year and Congress passed a transportation bill that included Complete Streets language for the first time ever.
The U.S. Surgeon General and Secretary of Transportation both spoke out for more Complete Streets last year and Congress passed a transportation bill that included Complete Streets language for the first time ever.

 arlier this year, the University of Connecticut released
arlier this year, the University of Connecticut released 


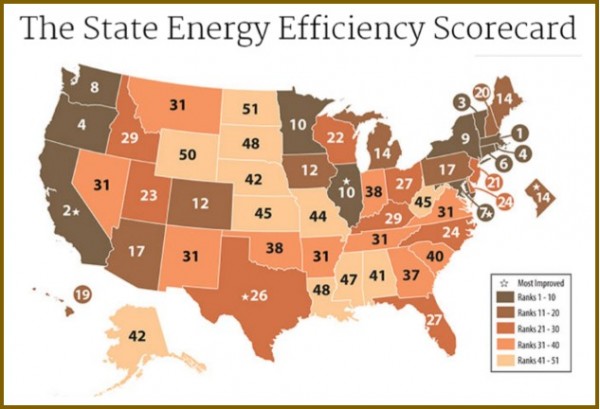 nd compliance efforts, earned 3 points out of 4 for its combined heat and power policies and programs, 5.5 out of 7 points for state-led energy efficiency initiatives, and 1 point out of 2 for appliance standards.
nd compliance efforts, earned 3 points out of 4 for its combined heat and power policies and programs, 5.5 out of 7 points for state-led energy efficiency initiatives, and 1 point out of 2 for appliance standards.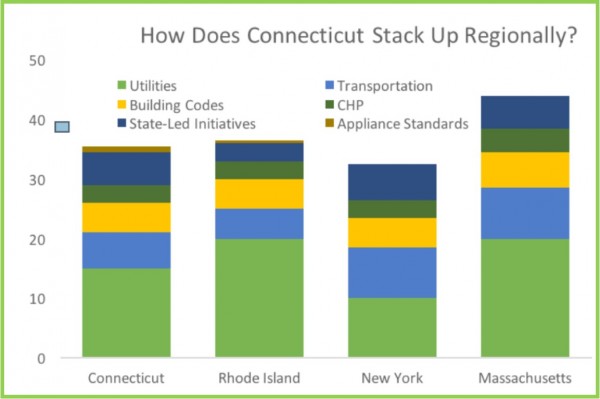 olar power in Connecticut has grown 221 percent per Capita since 2012, ranking the state 13th in the nation, the report points out. The top solar growth states in the nation, like Connecticut, have adopted renewable energy requirements, strong laws allowing solar customers to sell their excess power to the electric grid, and other policies encouraging growth of the industry, the report indicates. The industry is also adding jobs much faster than the overall economy, employing 1,600 people in Connecticut last year, according to
olar power in Connecticut has grown 221 percent per Capita since 2012, ranking the state 13th in the nation, the report points out. The top solar growth states in the nation, like Connecticut, have adopted renewable energy requirements, strong laws allowing solar customers to sell their excess power to the electric grid, and other policies encouraging growth of the industry, the report indicates. The industry is also adding jobs much faster than the overall economy, employing 1,600 people in Connecticut last year, according to  ."
."

 The
The  Plans for the new Academic Science & Laboratory Building at Southern began back in 2007 with a comprehensive 10-year capital improvement plan, dubbed CSUS 2020, for upgrading the four institutions of the Connecticut State University System. Approved by the state legislature and signed into law by Gov. M. Jodi Rell, the plan was developed during the administration of Chancellor David G. Carter. It included upgrades and repairs to existing facilities, as well as construction of a new Visual & Performing Arts Center at Western Connecticut State University, which
Plans for the new Academic Science & Laboratory Building at Southern began back in 2007 with a comprehensive 10-year capital improvement plan, dubbed CSUS 2020, for upgrading the four institutions of the Connecticut State University System. Approved by the state legislature and signed into law by Gov. M. Jodi Rell, the plan was developed during the administration of Chancellor David G. Carter. It included upgrades and repairs to existing facilities, as well as construction of a new Visual & Performing Arts Center at Western Connecticut State University, which 


























