Financial Cost to Connecticut Smokers Among Highest in the Nation
/The financial cost of smoking in Connecticut is higher than just about anywhere in the United States. The total cost over a lifetime per smoker is $2,183,204, the third highest in the nation, and the annual cost per year per smoker of $42,808, is also third highest in the nation, just behind New York and Massachusetts. The lifetime health care cost per smoker, $274,272 in Connecticut, is higher than every state but one, (Massachusetts), and the out-of-pocket cost per smoking individual of $170,513 for smokers living in Connecticut is third highest in the nation.
The data was compiled by the financial website WalletHub, where analysts calculated the potential monetary losses — including the cumulative cost of a cigarette pack per day over several decades, health-care expenditures, income losses and other costs — brought on by smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke. 
Emphasizing that “the negative physical and financial effects of smoking can be significant,” WalletHub noted that Connecticut’s rankings placed it as among the most costly in every category.
Over a lifetime, the financial opportunity cost for smokers living in Connecticut was $1.436,335 and the income loss per smoker was calculated at $286,950. Other costs per smoker, such as not being able to qualify for homeowner’s insurance discounts for non-smokers, were $15,133. In each instance, the costs in Connecticut were among the three highest among the 50 states and District of Columbia.
Annual income loss for Connecticut smokers is calculated at $5,626. Only Maryland, Alaska, New Jersey and D.C. were higher, according to the analysis. Attributable factors included absenteeism, workplace bias or lower productivity due to smoking-induced health problems. The website also noted that according to a recent study from the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta, smokers earn 20 percent less than nonsmokers, 8 percent of which is attributed to smoking and 12 percent to other factors.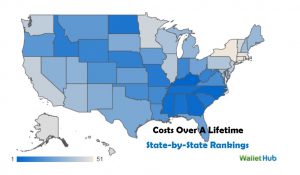
For the calculations, WalletHub assumed an adult who smokes one pack of cigarettes per day beginning at age 18, when a person can legally purchase tobacco products in the U.S., and a lifespan thereafter of 51 years, taking into account that 69 is the average age at which a smoker dies. Data used in developing the ranking were collected from the U.S. Census Bureau, Bureau of Labor Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Insurance Information Institute, NYsmokefree.com, Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED), Kaiser Family Foundation and the Independent Insurance Agents & Brokers of America.
In 2016, the American Lung Association gave Connecticut an “F” grade in its spending of tobacco prevention and control funds. The ALA points out that 40 states and Washington D.C. spend less than half of what the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends on their state tobacco prevention programs. Overall, states spend less than two cents of every dollar they get from tobacco settlement payments and tobacco taxes to fight tobacco use. Each day, more than 2,600 kids under 18 try their first cigarette and about 600 kids become new, regular smokers, according to nationwide data from ALA.
A report on Connecticut's spending on tobacco prevention just over a year ago found that the state was being outspent over 67 times by tobacco companies' marketing efforts - due in large part to the state spending only a small portion of tobacco settlement funds on anti-smoking efforts.
 The report, “Broken Promises to our Children: A State-by-State Look at the 1998 State Tobacco Settlement 17 Years Later," said the state was spending $1.2 million in FY 2016 to fight tobacco use. That's compared to an estimated marketing investment of $80.4 million by tobacco companies in Connecticut that year. The national average shows a margin of 20.1 to 1. At that time, Connecticut ranked 38th in spending on a percentage basis. The state has consistently spend less than the CDC has recommended.
The report, “Broken Promises to our Children: A State-by-State Look at the 1998 State Tobacco Settlement 17 Years Later," said the state was spending $1.2 million in FY 2016 to fight tobacco use. That's compared to an estimated marketing investment of $80.4 million by tobacco companies in Connecticut that year. The national average shows a margin of 20.1 to 1. At that time, Connecticut ranked 38th in spending on a percentage basis. The state has consistently spend less than the CDC has recommended.
The annual report was developed by the Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids (CTFK), a coalition that includes the American Heart Association, the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the American Lung Association, the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Americans for Nonsmokers’ Rights, and the Truth Initiative.
A year later, the next report ranked Connecticut last, as Connecticut’s projected spending on smoke cessation and tobacco prevention efforts for FY 2017 dropped to zero. The report found that 13.5 percent of adult state residents are smokers, and 10.3 percent of high school students smoke. Just under 5,000 deaths each year are caused by smoking in Connecticut, and 27 percent of cancer deaths are attributable to smoking. Connecticut’s cigarette excise tax, $3.90 per pack, is the second highest in the nation. It was estimated that the state would collect $519.7 million in revenue this year from the 1998 state tobacco settlement and tobacco taxes, but will spend none of it on tobacco prevention programs.





 That is the highest number of states falling short of revenue projections since 36 states budgets missed their mark in 2010, according to the NASBO report and
That is the highest number of states falling short of revenue projections since 36 states budgets missed their mark in 2010, according to the NASBO report and 

 Louise DiCocco, Assistant Counsel for the Connecticut Business & Industry Association, noted that “24 years ago, more than 80 percent of Connecticut votes overwhelmingly approved a spending cap to keep the cost of state government within the taxpayers’ means to afford it. Voters demanded the cap as an offset to the persona income tax in Connecticut. The state must enact a spending cap that is ironclad and works.”
Louise DiCocco, Assistant Counsel for the Connecticut Business & Industry Association, noted that “24 years ago, more than 80 percent of Connecticut votes overwhelmingly approved a spending cap to keep the cost of state government within the taxpayers’ means to afford it. Voters demanded the cap as an offset to the persona income tax in Connecticut. The state must enact a spending cap that is ironclad and works.” State Senator Toni Boucher of Danbury told the Commission: “I hope that the commission to adopt a definition of general budget expenditures that is comprehensive and gives a complete and realistic account of all the money that the state spends… it is equally critical that the legislature not be allowed to move what was once an expenditure included under the cap to bonding or fund it with a revenue intercept for the purpose of undermining the cap’s integrity.”
State Senator Toni Boucher of Danbury told the Commission: “I hope that the commission to adopt a definition of general budget expenditures that is comprehensive and gives a complete and realistic account of all the money that the state spends… it is equally critical that the legislature not be allowed to move what was once an expenditure included under the cap to bonding or fund it with a revenue intercept for the purpose of undermining the cap’s integrity.”

 In recent months, First Niagara did consolidate five Connecticut branches (Woodstock, Dayville, Hamden, East Haven and Madison), and all of the employees who worked at those branches were offered positions within the bank, officials indicated, and no layoffs were associated with that consolidation.
In recent months, First Niagara did consolidate five Connecticut branches (Woodstock, Dayville, Hamden, East Haven and Madison), and all of the employees who worked at those branches were offered positions within the bank, officials indicated, and no layoffs were associated with that consolidation.
 At #296 is Glastonbury-based Fiondella Milone & LaSaracina. FML was founded in 2002 “for the purpose of providing professional auditing, tax and business consulting services to a wide range of clients and industries throughout the Northeast,” the company’s website indicates. After working together at Ernst & Young, the firm’s founding partners, Jeff Fiondella, Frank Milone and Lisa LaSaracina launched FML.
At #296 is Glastonbury-based Fiondella Milone & LaSaracina. FML was founded in 2002 “for the purpose of providing professional auditing, tax and business consulting services to a wide range of clients and industries throughout the Northeast,” the company’s website indicates. After working together at Ernst & Young, the firm’s founding partners, Jeff Fiondella, Frank Milone and Lisa LaSaracina launched FML. counting newsletter and the award-winning National Benchmarking Report.
counting newsletter and the award-winning National Benchmarking Report.
 e: Financing Women’s Growth-Oriented Firms (published by Stanford University Press), which points to “three essential factors that women entrepreneurs need to thrive: knowledge, networks, and investors. In tandem, these three ingredients connect and empower emerging entrepreneurs with those who have succeeded in growing their firms while also realizing the financial and economic returns that come with doing so.”
e: Financing Women’s Growth-Oriented Firms (published by Stanford University Press), which points to “three essential factors that women entrepreneurs need to thrive: knowledge, networks, and investors. In tandem, these three ingredients connect and empower emerging entrepreneurs with those who have succeeded in growing their firms while also realizing the financial and economic returns that come with doing so.”


 suranceQuotes, found that the average increase in premiums across the country when a teen driver is added to an existing policy is 79 percent. That is a slight improvement from a few years ago, when the increase nationwide averaged 84 percent.
suranceQuotes, found that the average increase in premiums across the country when a teen driver is added to an existing policy is 79 percent. That is a slight improvement from a few years ago, when the increase nationwide averaged 84 percent.
 Perhaps the most significant underlying factor is that each state regulates insurance differently, and those regulatory differences account for some of the variations in the study’s findings, according to insuranceQuotes. For instance, Hawaii is the only state that doesn't allow insurance providers to consider age, gender or length of driving experience when determining premiums. That means that the cost for teens doesn't differ much from the cost for adults buying auto insurance. This may also account for lower increases in states such as New York, Michigan and North Carolina, where insurance is regulated more strictly and rating factors are more stringent, insuranceQuotes points out. The increases in those states when adding a teen to an existing policy were all below 60 percent, among the lowest increases in the nation.
Perhaps the most significant underlying factor is that each state regulates insurance differently, and those regulatory differences account for some of the variations in the study’s findings, according to insuranceQuotes. For instance, Hawaii is the only state that doesn't allow insurance providers to consider age, gender or length of driving experience when determining premiums. That means that the cost for teens doesn't differ much from the cost for adults buying auto insurance. This may also account for lower increases in states such as New York, Michigan and North Carolina, where insurance is regulated more strictly and rating factors are more stringent, insuranceQuotes points out. The increases in those states when adding a teen to an existing policy were all below 60 percent, among the lowest increases in the nation.



























