The announcement of the second round of funding for the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Insecurity Nutrition Incentive (FINI) Program, included the selection of national nonprofit Wholesome Wave to receive nearly $500,000 designated to increase affordable access to healthy food in Hartford, Connecticut, and the Northeast Kingdom of Vermont (the northeast corner of the state, comprising Essex, Orleans and Caledonia counties).
The funds will flow through an innovative Farm-to-Grocery Nutrition Incentive model, which funds coupons for fresh fruits and vegetables that match the value of SNAP spent at participating grocery stores and increases locally-grown food those stores procure from nearby farmers.
Combined with an additional $500,000 from other funding sources, this project will amount to a $1 million investment in Connecticut and Vermont’s local food economies, according to Wholesome Wave.
Wholesome Wave plans to work with two community nonprofits, Hartford Food System and Green Mountain Farm to School, and eight local grocery stores, to help an estimated 5,000 people purchase more fresh produce. Participating stores will purchase approximately $122,000 worth of regional produce from nearby farmers in Connecticut and Vermont.
The USDA award to Wholesome Wave was one of only 15 community-based initiatives across the country to be selected to receive multi-year grants. The project is expected to trigger $920,000 in SNAP and incentive purchases in its first three years, officials project. Overall, the initiative is aimed at increasing food access for low-income residents, supporting grocery stores as healthy food providers, strengthening local economies, and driving revenue to nearby farms.
 “Wholesome Wave is thrilled by the innovations that USDA is supporting through the new FINI grants, which are taking the work of increasing affordable access to healthy food to even greater levels of impact,” said Michel Nischan, CEO & Founder of Wholesome Wave. “So many SNAP shoppers are working parents with limited time to source healthier food choices. Through the new Farm-to-Grocery model, our partners in Connecticut and Vermont will be able to expand affordable access to SNAP consumers in a way that allows them to find and purchase more healthy food from a variety of retailers.”
“Wholesome Wave is thrilled by the innovations that USDA is supporting through the new FINI grants, which are taking the work of increasing affordable access to healthy food to even greater levels of impact,” said Michel Nischan, CEO & Founder of Wholesome Wave. “So many SNAP shoppers are working parents with limited time to source healthier food choices. Through the new Farm-to-Grocery model, our partners in Connecticut and Vermont will be able to expand affordable access to SNAP consumers in a way that allows them to find and purchase more healthy food from a variety of retailers.”
The areas selected both face high levels of poverty and are home to farmers seeking new markets for their healthful crops, according to Wholesome Wave. They point out that 40 percent of Hartford’s children live in poverty and 42 percent of the city’s residents use SNAP, formerly known as food stamps.
In the first iterations of healthy food incentives – which also match the value of SNAP spent – Wholesome Wave worked with local partners to offer them at farmers markets. By expanding healthy food incentives to grocery stores where many families already shop, this project is designed to offer a promising solution to each community’s food access challenges.
Wholesome Wave’s expertise in facilitating and scaling successful food access projects, combined with the local nonprofits’ experience within the communities, represents an ideal partnership to move this work forward, according to the organization.
This project builds on Wholesome Wave’s existing work across 40 states, including expansion through the large-scale FINI grant received last year, a $3.77 million grant from the USDA through the new Food Insecurity Nutrition Incentive (FINI) grant program. Wholesome Wave began in Bridgeport in 2008; a 501(c)(3) nonprofit that strives to create a vibrant, just and sustainable food system. By making fresh, locally grown fruits and vegetables affordable and available, it enables underserved consumers to make healthier food choices.
In particular, this year’s FINI grant expands on the successes of Wholesome Wave’s and partners’ efforts to pilot nutrition incentives in grocery stores in Connecticut and Vermont.
In the first few months of 2016, Wholesome Wave invested in the Hartford food system by providing SNAP consumers with $23,000 in nutrition incentives to spend on fresh fruits and vegetables at two locally-owned grocery stores. During the program period, attributable at least in part to this project, SNAP sales at the local C-Town supermarket increased 7 percent and produce sales increased by 19 percent over the same period in 2015. 
Executive Director of Hartford Food System, Martha Page, said: “As demonstrated in the pilot program, the SNAP Up! nutrition incentives are an excellent way to get more fresh fruits and vegetables on Hartford dinner tables. The enthusiastic response to the incentives by Hartford SNAP participants clearly shows that there is a demand for affordable, high quality produce. For our local farmers, this will represent a new customer base that they have not been able to easily access. We are so excited at the opportunity to bring Hartford area farmers and Hartford consumers together; we believe that we will prove that good food is good business!”
National leaders emphasize how this new model will benefit their state’s economies, while increasing access to produce for low-income residents and improving the bottom line for regional farmers.
“Increasing access to fresh, healthy food for the low-income residents of food deserts will help move our communities one step closer to ending food insecurity. The federal funding awarded to Bridgeport’s Wholesome Wave to help provide fresh produce to Hartford’s local grocers is an investment in an incredible partnership that will help ensure the well-being and health of Hartford’s residents,” said U.S. Sen. Richard Blumenthal.
“Just a few days ago, I was at Hartford Regional Market talking to local farmers and Hartford community leaders about better connecting local food to city grocery stores,” recalled U.S. Sen. Chris Murphy. “This grant for Wholesome Wave is a great opportunity to make that happen. It just makes sense—we should help families afford locally-grown, fresh food at the grocery stores they already shop at. We worked so hard to get North Hartford its Promise Zone designation so that the city can hop to the front of the line when it comes to getting federal grants. This shows why that’s so important.”
“Food deserts correlate very highly with areas of poverty across our country, and a lack of healthy and affordable food options can have a very detrimental effect, especially on children,” said U.S. Rep. Jim Himes, who represents the Congressional District that includes Bridgeport. “With this grant, we will be able to help more families eat nutritiously in Hartford and also support the excellent work that Wholesome Wave is doing right here in Bridgeport, creating innovative ways to bring healthy, local produce into more stores and kitchens.”
In the initiative, neighborhood grocery stores will become access points for fresh local produce, and experience increased revenues. Beyond direct impact to the community, Wholesome Wave expects to use this project in the two states to develop a replicable Farm-to-Grocery Nutrition Incentive model that the organization hopes can spread nationally through their national network of over 110 organizations in 40 states – including 12 in Connecticut - with the promise of impact on a national scale.
The second-round USDA funding award to Wholesome Wave, announced this month, is for $499,720. The programs in Hartford and Vermont’s Northeast Kingdom are expected to launch in August.
https://youtu.be/BU0sOg9GhWA
 The NCHS data also ranked Connecticut 12th in the Cesarean Delivery Rate.
The NCHS data also ranked Connecticut 12th in the Cesarean Delivery Rate. Regarding the percentage of babies born to unmarried mothers, a statistic long tracked by federal health officials, three states saw more than half the children born in that category. The highest percentages were in Mississippi (54.0%), Louisiana (52.7) and New Mexico (51.3%).
Regarding the percentage of babies born to unmarried mothers, a statistic long tracked by federal health officials, three states saw more than half the children born in that category. The highest percentages were in Mississippi (54.0%), Louisiana (52.7) and New Mexico (51.3%).



 The keynote address will be provided by Camara P. Jones, MD, MPH, PhD, research director on social determinants of health and equity in the Division of Adult and Community Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and President of the American Public Health Association (APHA).
The keynote address will be provided by Camara P. Jones, MD, MPH, PhD, research director on social determinants of health and equity in the Division of Adult and Community Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and President of the American Public Health Association (APHA).




 In addition to its impact on drivers, the AMA notes that blue-rich LED streetlights operate at a wavelength that most adversely suppresses melatonin during night. It is estimated that white LED lamps have five times greater impact on circadian sleep rhythms than conventional street lamps, the AMA indicated. Recent large surveys, according to the AMA, found that brighter residential nighttime lighting is associated with reduced sleep times, dissatisfaction with sleep quality, excessive sleepiness, impaired daytime functioning and obesity.
In addition to its impact on drivers, the AMA notes that blue-rich LED streetlights operate at a wavelength that most adversely suppresses melatonin during night. It is estimated that white LED lamps have five times greater impact on circadian sleep rhythms than conventional street lamps, the AMA indicated. Recent large surveys, according to the AMA, found that brighter residential nighttime lighting is associated with reduced sleep times, dissatisfaction with sleep quality, excessive sleepiness, impaired daytime functioning and obesity.
 The Conversation website is a collaboration between editors and academics to provide "informed news analysis and commentary that’s free to read and republish." It
The Conversation website is a collaboration between editors and academics to provide "informed news analysis and commentary that’s free to read and republish." It  PHOTO: Traditional street lighting (left) vs. LED lighting (right).
PHOTO: Traditional street lighting (left) vs. LED lighting (right).
 “Wholesome Wave is thrilled by the innovations that USDA is supporting through the new FINI grants, which are taking the work of increasing affordable access to healthy food to even greater levels of impact,” said Michel Nischan, CEO & Founder of Wholesome Wave. “So many SNAP shoppers are working parents with limited time to source healthier food choices. Through the new Farm-to-Grocery model, our partners in Connecticut and Vermont will be able to expand affordable access to SNAP consumers in a way that allows them to find and purchase more healthy food from a variety of retailers.”
“Wholesome Wave is thrilled by the innovations that USDA is supporting through the new FINI grants, which are taking the work of increasing affordable access to healthy food to even greater levels of impact,” said Michel Nischan, CEO & Founder of Wholesome Wave. “So many SNAP shoppers are working parents with limited time to source healthier food choices. Through the new Farm-to-Grocery model, our partners in Connecticut and Vermont will be able to expand affordable access to SNAP consumers in a way that allows them to find and purchase more healthy food from a variety of retailers.”


 In 2015, Charter Oak Health Center was one of 12 community health centers in the state to receive Expanded Service Awards from the Health Resources and Service Administration (HRSA) Health Center Program within the Department of Health and Human Services.
In 2015, Charter Oak Health Center was one of 12 community health centers in the state to receive Expanded Service Awards from the Health Resources and Service Administration (HRSA) Health Center Program within the Department of Health and Human Services.
 nter located in southern Hartford and provides Medical, Dental, and Behavioral Health services to over 18,000 patients annually.
nter located in southern Hartford and provides Medical, Dental, and Behavioral Health services to over 18,000 patients annually.
 With locations in New Haven and East Haven,
With locations in New Haven and East Haven, 


 Among the nation’s top businesses for new dad, an analysis by the website Fatherly, determined that two Connecticut-based companies – alcoholic beverages producer Diageo and financial data and analysis provider FactSet, earned slots in the top 50. Fatherly is a digital lifestyle guide for men entering parenthood.
Among the nation’s top businesses for new dad, an analysis by the website Fatherly, determined that two Connecticut-based companies – alcoholic beverages producer Diageo and financial data and analysis provider FactSet, earned slots in the top 50. Fatherly is a digital lifestyle guide for men entering parenthood. were Netflix, Spotify, Facebook, Patagonia, Bank of America, Pinterest, Google, Microsoft, Twitter, Airbnb, Johnson & Johnson, Accenture, MasterCard, Intuit and Intel.
were Netflix, Spotify, Facebook, Patagonia, Bank of America, Pinterest, Google, Microsoft, Twitter, Airbnb, Johnson & Johnson, Accenture, MasterCard, Intuit and Intel.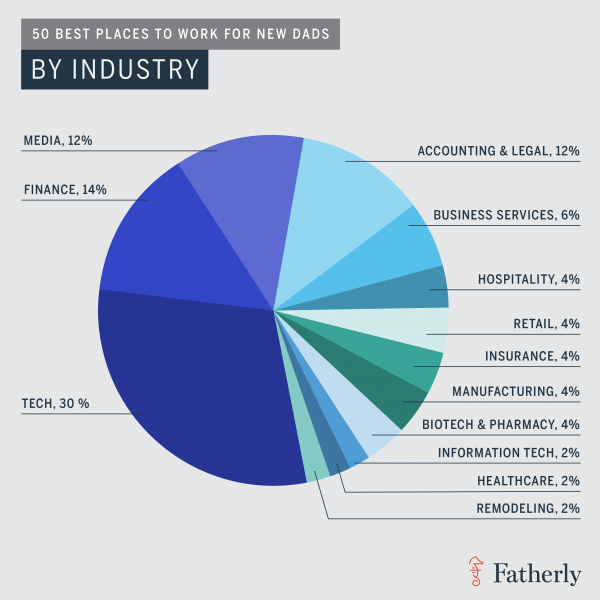




 tion into one composite indicator of entrepreneurial business growth.”
tion into one composite indicator of entrepreneurial business growth.”






















