Four Stores in CT Warned by FDA for Selling e-Cigarettes to Minors as Popularity, Concern Grows
/The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has sent out warning letters to 40 retailers in 17 states – including four in Connecticut - as part of a “concerted effort to ensure youth are not able to access” e-cigarettes – specifically responding to what officials describe as the “surging youth uptake” of JUUL products.
According to the federal agency, those receiving the warnings in recent weeks included four Connecticut retailers: Discount Tobacco and Vape in Vernon, Mobil Mart in Waterbury, Shell/Henny Penny in Lisbon, and Smoker’s Outlet in West Hartford. The retailers were warned about selling the increasingly popular – but hazardous – products to minors.
The FDA explained that warning letters are sent to retailers the first time a tobacco compliance check inspection reveals a violation of the federal tobacco laws and regulations that FDA enforces. During undercover buy inspections by agency representatives, “the retailer is unaware an inspection is taking place” and the minor and inspector “will not identify themselves.”
Published reports nationwide indicate that vaping is increasing rapidly in popularity with young people, especially with the most popular brand, JUUL. Its devices are tiny, and look like a pen or flash drive. When someone vapes, there is no fire, ash or smoky odor — instead, the devices heat up and vaporize a liquid or solid. School bathrooms, where cigarette smoking was done in “secret” a generation ago, are now often referred to as “juul rooms” according to numerous reports – the nicotine fix of choice of the current generation. A recent New York Times article prominently featured a description of the magnitude of the problem in a suburban Connecticut high school.
“The FDA has been conducting a large-scale, undercover nationwide blitz to crack down on the sale of e-cigarettes – specifically JUUL products – to minors at both brick-and-mortar and online retailers,” said FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, M.D.
Gottlieb highlighted the danger – and the attraction – of the products to youth.
 “We understand, by all accounts, many of them may be using products that closely resemble a USB flash drive, have high levels of nicotine and emissions that are hard to see. These characteristics may facilitate youth use, by making the products more attractive to children and teens. These products are also more difficult for parents and teachers to recognize or detect. Several of these products fall under the JUUL brand, but other brands, such as myblu and KandyPens, that have similar characteristics are emerging.”
“We understand, by all accounts, many of them may be using products that closely resemble a USB flash drive, have high levels of nicotine and emissions that are hard to see. These characteristics may facilitate youth use, by making the products more attractive to children and teens. These products are also more difficult for parents and teachers to recognize or detect. Several of these products fall under the JUUL brand, but other brands, such as myblu and KandyPens, that have similar characteristics are emerging.”
Businesses receiving the warning letters are directed to provide, within 15 days, “an explanation of the steps you will take to correct the violation(s) and prevent future violations (for example, retrain your employees, remove the problematic items, etc.),” the agency website points out. In addition to federal restrictions, purchase/possession of an electronic nicotine delivery system or vapor product by persons under age 18 is prohibited in Connecticut.
The FDA also sent an official request for information directly to JUUL Labs, requiring the company to submit important documents to better understand the reportedly high rates of youth use and the particular youth appeal of these products.
Said Gottlieb: “We don’t yet fully understand why these products are so popular among youth. But it’s imperative that we figure it out, and fast. These documents may help us get there.” The agency plans what it calls a “full-scale e-cigarette prevention effort” in the fall.
In addition, the FDA also recently contacted eBay to raise concerns over several listings for JUUL products on its website. eBay took what the agency described as “swift action to remove the listings and voluntarily implement new measures to prevent new listings” from being posted to the website.



 Stating that “justice should not have an expiration date,” the organization points out that eight states have no statute of limitations for felony sexual assault crimes, and 28 states have a statute of limitations of 21 years or more. Only 10 states, including Connecticut, have a statute of limitation of 10 years or less.
Stating that “justice should not have an expiration date,” the organization points out that eight states have no statute of limitations for felony sexual assault crimes, and 28 states have a statute of limitations of 21 years or more. Only 10 states, including Connecticut, have a statute of limitation of 10 years or less. According to the National Institutes of Health, sexual violence is the leading cause of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in women.
According to the National Institutes of Health, sexual violence is the leading cause of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in women. 
 Topping the national rankings were Falls Church, Virginia; Douglas County, Colorado; Broomfield County, Colorado; Los Alamos County, New Mexico; and Dukes County, Massachusetts.
Topping the national rankings were Falls Church, Virginia; Douglas County, Colorado; Broomfield County, Colorado; Los Alamos County, New Mexico; and Dukes County, Massachusetts. 
 In comparing the average annual opioid-related death rates per 100,000 population in 2012-13, 2014-15, and 2016-17, the dramatic increases across communities statewide is quite evident. The data analysts point out that data are where deaths from 'any opioid' (meaning some type of opioid were found in the person) take place. Therefore, they explain, one would expect to see higher rates in places with large hospitals (hence high rates in cities). They add that one can also not discount that these places are also seeing higher rates among its residents.
In comparing the average annual opioid-related death rates per 100,000 population in 2012-13, 2014-15, and 2016-17, the dramatic increases across communities statewide is quite evident. The data analysts point out that data are where deaths from 'any opioid' (meaning some type of opioid were found in the person) take place. Therefore, they explain, one would expect to see higher rates in places with large hospitals (hence high rates in cities). They add that one can also not discount that these places are also seeing higher rates among its residents.
 The Connecticut Data Collaborative has posted on its
The Connecticut Data Collaborative has posted on its 


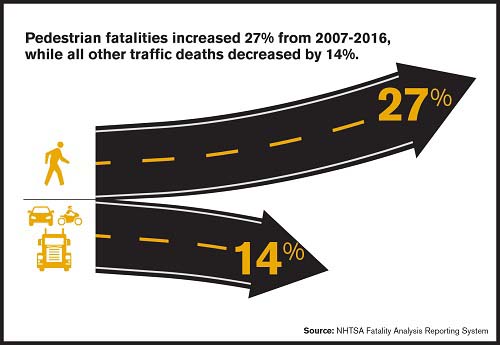 The total number of multimedia messages sent has more than tripled since 2010. The report also suggests a possible link with marijuana use. According to the report, the seven states (Alaska, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, Washington) and DC that legalized recreational use of marijuana between 2012 and 2016 reported a collective 16.4 percent increase in pedestrian fatalities for the first six months of 2017 versus the first six months of 2016, whereas all other states reported a collective 5.8 percent decrease in pedestrian fatalities.
The total number of multimedia messages sent has more than tripled since 2010. The report also suggests a possible link with marijuana use. According to the report, the seven states (Alaska, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, Washington) and DC that legalized recreational use of marijuana between 2012 and 2016 reported a collective 16.4 percent increase in pedestrian fatalities for the first six months of 2017 versus the first six months of 2016, whereas all other states reported a collective 5.8 percent decrease in pedestrian fatalities.
 The report defines Eastern Connecticut as the Community Foundation of Eastern Connecticut service area: 42 towns that include 453,000 people, 227,000 women. The population of the region is 80% white, 9% Latina, 4% Black and 4% Asian. Approximately 33,700 residents, or 7 percent, are foreign born. Looking ahead, the report noted that the population of women ages 65 and up is projected to grow significantly over the next decade; estimated to increase 44 percent by 2025.
The report defines Eastern Connecticut as the Community Foundation of Eastern Connecticut service area: 42 towns that include 453,000 people, 227,000 women. The population of the region is 80% white, 9% Latina, 4% Black and 4% Asian. Approximately 33,700 residents, or 7 percent, are foreign born. Looking ahead, the report noted that the population of women ages 65 and up is projected to grow significantly over the next decade; estimated to increase 44 percent by 2025.


 image of Michelle Obama’s face,” the researchers pointed out.
image of Michelle Obama’s face,” the researchers pointed out.


 For three decades, since 1979,
For three decades, since 1979, 






















