Legal Challenge Seeks to End Prison Gerrymandering in CT
/In 2010, New York State enacted legislation to ensure that incarcerated persons are be counted as residents of their home communities when state and local legislative districts are redrawn in New York, in an initiative designed to end what has come to be called “prison gerrymandering.” Connecticut has repeatedly considered legislation during the past decade – in 2011, 2013, 2015 and 2016 - that would make the same policy change, but that legislation has failed to pass. A 2013 report by the Prison Policy initiative and Common Cause found that almost half of the state's prison population comes from the state's five largest cities, but almost two-thirds of the state’s prison cells are located in just five small towns - Cheshire, East Lyme, Enfield, Somers, and Suffield.
Because prisons are disproportionately built in rural areas but most incarcerated people call urban areas home, counting prisoners where they are incarcerated rather than in their home municipality results in a “systematic transfer of population and political clout” from urban to rural areas, according to the Prison Policy Initiative.
 That shift of political influence has ramification across the electoral system, and was the impetus for a lawsuit filed this summer against the state of Connecticut by the NAACP to force an end to the practice. It is the first of its kind, and being widely watched.
That shift of political influence has ramification across the electoral system, and was the impetus for a lawsuit filed this summer against the state of Connecticut by the NAACP to force an end to the practice. It is the first of its kind, and being widely watched.
The NAACP points out that Connecticut, like many states, disenfranchises prisoners and has concentrated its prisons primarily in rural areas. The effect is that white, rural voters in the districts where prisons are located have their electoral power unconstitutionally inflated, at the expense of voters of color in other, over-crowded districts.
The plaintiffs seek to compel the State of Connecticut to adopt a new redistricting map that counts incarcerated individuals in their home state legislative districts rather than in the districts where they are being incarcerated, thereby safeguarding the Fourteenth Amendment principle of “one person, one vote.”
Although a number of states continue to engage in this practice, the NAACP explains, Connecticut has some of the worst discrepancies in population numbers between its prison districts and most populated districts.
According to the complaint filed in U.S. District Court, when prisoners are reallocated to their home districts, the population of the 59th House District, which includes Enfield and East Windsor, where three state prisons are located, has an overall population that is more than 15% smaller than the most populated district in the state. The effect is that the vote of a person in that prison district counts for 15% more than each vote of a person in the largest district.
“This is about making sure everyone gets an equal voice,” said Germano Kimbro, a formerly incarcerated individual and plaintiff in the case. A resident of the 97th House District, located in New Haven, one of the most overcrowded state legislative districts in Connecticut, Kimbro argues “My vote shouldn’t count less than someone else’s just because they live near a state prison.”
The NAACP, together with the NAACP Connecticut State Conference and individual NAACP members who live in five of the most overcrowded Connecticut state legislative districts, filed the suit. The plaintiffs in the lawsuit are represented by the Rule of Law Clinic at Yale Law School and the NAACP.
“Each person’s vote is to be equal to that of their fellow citizens,” explains Alden Pinkham, a student in Yale Law School’s Rule of Law Clinic. “Using prisoners to inflate the population of the districts where prisons are located violates this principle.”
Seven states (Colorado, Mississippi, New Jersey, Virginia, Maryland, Michigan, and New York) encourage or even require local governments to exclude prison populations during redistricting. The next legal filings in the case are due just after Labor Day. A conclusion is not anticipated prior to the 2018 November elections, but with an eye toward 2020.




 American Innovation $1 coins, to be issued at a rate of four new coins per year, will bear a reverse image or images emblematic of a significant innovation, an innovator, or a group of innovators from each of the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the territories of the United States. Published reports indicate that the $1 coins would sell for more than face value — up to $1.32 — providing a healthy profit for the federal government since the coins cost less than 35 cents to make.
American Innovation $1 coins, to be issued at a rate of four new coins per year, will bear a reverse image or images emblematic of a significant innovation, an innovator, or a group of innovators from each of the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and the territories of the United States. Published reports indicate that the $1 coins would sell for more than face value — up to $1.32 — providing a healthy profit for the federal government since the coins cost less than 35 cents to make.

 Her work at C-CHANGE is designed to accelerate and strengthen public education on climate change and pollution issues, bringing the science down to the individual level, highlighting the impacts on people, rather than the planet.
Her work at C-CHANGE is designed to accelerate and strengthen public education on climate change and pollution issues, bringing the science down to the individual level, highlighting the impacts on people, rather than the planet.

 Using a dataset on the compactness of U.S. House districts—with multiple measures generated by geographic information system (GIS) analyses over two redistricting cycles, UConn Associate Professor Jeffrey Ladewig estimated the effects of congressional district compactness on electoral turnout. The conclusion: compactness matters. The
Using a dataset on the compactness of U.S. House districts—with multiple measures generated by geographic information system (GIS) analyses over two redistricting cycles, UConn Associate Professor Jeffrey Ladewig estimated the effects of congressional district compactness on electoral turnout. The conclusion: compactness matters. The 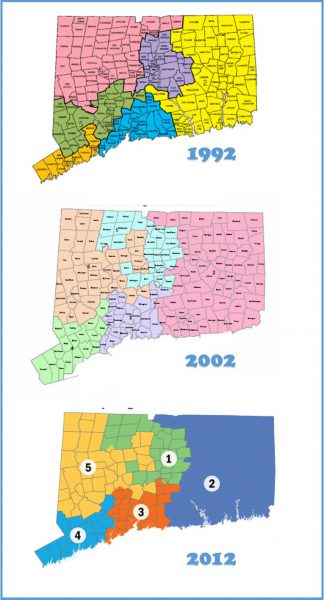
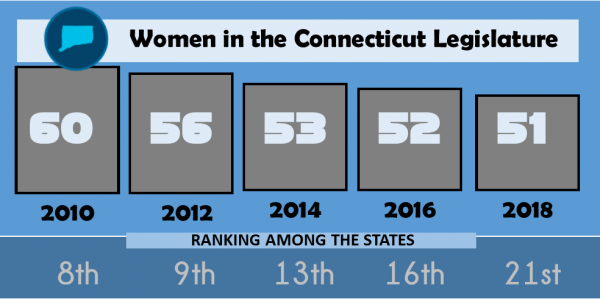 The 2018 election year has been widely declared the year of the woman in politics, a reaction to the MeToo movement and related issues that have risen to the top of many political agendas. It appears that Connecticut ballots may have a record number of women candidates in November, depending upon the outcome of the August 14 primaries in some legislative districts.
The 2018 election year has been widely declared the year of the woman in politics, a reaction to the MeToo movement and related issues that have risen to the top of many political agendas. It appears that Connecticut ballots may have a record number of women candidates in November, depending upon the outcome of the August 14 primaries in some legislative districts. Leading the nation were Arizona (40%), Vermont (40%), Nevada (38.1%), Colorado (38%), Washington (37.4%), and Illinois (35.6%). Women make up 25.4 percent of all state legislators
Leading the nation were Arizona (40%), Vermont (40%), Nevada (38.1%), Colorado (38%), Washington (37.4%), and Illinois (35.6%). Women make up 25.4 percent of all state legislators 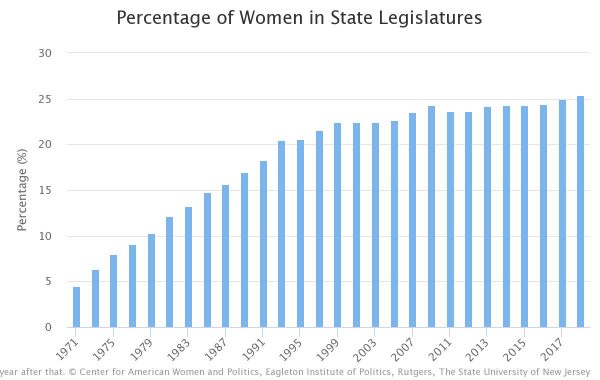


 According to the Nature Conservancy, Bridgeport currently has a 19% tree canopy cover, for example. If all open spaces, vacant lots and parking lots could be planted, the city would have a 62% tree canopy cover. The ramifications would be substantial, impacting various health and quality of life factors.
According to the Nature Conservancy, Bridgeport currently has a 19% tree canopy cover, for example. If all open spaces, vacant lots and parking lots could be planted, the city would have a 62% tree canopy cover. The ramifications would be substantial, impacting various health and quality of life factors.


 Satisfied Connecticut companies in 2016 include Windsor-based
Satisfied Connecticut companies in 2016 include Windsor-based 
 by the Common Core Standards and provides a pathway for 21st Century Skills.
by the Common Core Standards and provides a pathway for 21st Century Skills. Globally-Focused Coursework would require at least 7.0 credits or demonstration of mastery and Globally-focused Student Activities would require competency in global citizenship through active participation in “at least one or more co-curricular and other school-sponsored or endorsed activities over at least 3 years of their high school experience with suggested involvement of a total of at least 15 hours.”
Globally-Focused Coursework would require at least 7.0 credits or demonstration of mastery and Globally-focused Student Activities would require competency in global citizenship through active participation in “at least one or more co-curricular and other school-sponsored or endorsed activities over at least 3 years of their high school experience with suggested involvement of a total of at least 15 hours.”


























