Hit-and-Run Crash Deaths Increase in Connecticut and Nationally, Analysis Reveals
/At the beginning of this month, Connecticut State Police investigated a hit and run car crash that killed one person on I-84 near exit 2 in Danbury. Less than a week later, in Middletown, a person sought in a hit and run accident that resulted in a death last November was arrested. Just two weeks earlier, Bridgeport police made an arrest in connection with a hit-and-run crash that killed an elderly man last June.
 If you have a sense that reports of hit-and-run accidents have increased in frequency, you’re correct.
If you have a sense that reports of hit-and-run accidents have increased in frequency, you’re correct.
Data compiled by the AAA Foundation of Traffic Safety from 2006 to 2016, found there were 148 hit-and-run crashes involving at least one fatality in Connecticut. There also appeared to be a spike in fatalities from 2015, when there were 14 incidents, compared to 2016 where there were 24 such incidents.
Connecticut is not alone.
Hit and run crashes have killed more than 2,000 people in 2016, which equates to more than 1 such crash every minute on U.S. roads, according to a new study from AAA. That’s the highest number of these types of crashes on record and a 60% increase since 2009.
With the number of hit-and-run crashes on the rise, AAA is calling for drivers to be alert on the road to avoid a deadly crash and remain on the scene if a crash occurs.
In the study, AAA researchers found:
- An average of 682,000 hit-and-run crashes occurred annually since 2006.
- Nearly 65% of people killed in hit-and-run crashes were pedestrians or bicyclists.
- Hit-and-run deaths in the U.S. have increased an average of 7.2% each year since 2009.
In Connecticut over the six-year span, it was determined more than half of the fatal crashes occurred overnight, primarily on weekends, in the Fall. Earlier this year, a Connecticut man was sentenced to six years in prison for a hit-and-run that authorities say killed a mother after she pushed her 7-year-old daughter to safety in October 2016.
“Hit-and-run crashes in the United States are trending in the wrong direction, especially in Connecticut,” said Fran Mayko of AAA Northeast. “The analysis shows such crashes are a growing traffic safety challenge and the AAA Foundation wants to work with all stakeholders to help curtail this problem.”
 In all states, it’s the drivers legal and moral responsibility to avoid hitting pedestrians, bicyclists, or another vehicle; and leaving a crash scene significantly increases the penalties, whether or not the driver caused the crash, AAA emphasized.
In all states, it’s the drivers legal and moral responsibility to avoid hitting pedestrians, bicyclists, or another vehicle; and leaving a crash scene significantly increases the penalties, whether or not the driver caused the crash, AAA emphasized.
In the US, state laws make it illegal for drivers involved in crashes to flee the scene. Penalties vary depending upon crash type and guilty parties may face large fines, lose their license or spend time in prison. In Connecticut, drivers who hit a vulnerable user is required to stop, remain on the scene, render aid if necessary, and notify law enforcement.
In the latest analysis, New Mexico, Louisiana and Florida have the highest rate of fatal hit-and-run crashes on a per-capita basis while New Hampshire, Maine and Minnesota have the lowest rates.





 Stating that “justice should not have an expiration date,” the organization points out that eight states have no statute of limitations for felony sexual assault crimes, and 28 states have a statute of limitations of 21 years or more. Only 10 states, including Connecticut, have a statute of limitation of 10 years or less.
Stating that “justice should not have an expiration date,” the organization points out that eight states have no statute of limitations for felony sexual assault crimes, and 28 states have a statute of limitations of 21 years or more. Only 10 states, including Connecticut, have a statute of limitation of 10 years or less. According to the National Institutes of Health, sexual violence is the leading cause of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in women.
According to the National Institutes of Health, sexual violence is the leading cause of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in women.  In comparing the average annual opioid-related death rates per 100,000 population in 2012-13, 2014-15, and 2016-17, the dramatic increases across communities statewide is quite evident. The data analysts point out that data are where deaths from 'any opioid' (meaning some type of opioid were found in the person) take place. Therefore, they explain, one would expect to see higher rates in places with large hospitals (hence high rates in cities). They add that one can also not discount that these places are also seeing higher rates among its residents.
In comparing the average annual opioid-related death rates per 100,000 population in 2012-13, 2014-15, and 2016-17, the dramatic increases across communities statewide is quite evident. The data analysts point out that data are where deaths from 'any opioid' (meaning some type of opioid were found in the person) take place. Therefore, they explain, one would expect to see higher rates in places with large hospitals (hence high rates in cities). They add that one can also not discount that these places are also seeing higher rates among its residents.
 The Connecticut Data Collaborative has posted on its
The Connecticut Data Collaborative has posted on its 

 The Gold Star Memorial Bridge, described as “Connecticut’s most iconic structure,” is the largest bridge in the State of Connecticut. It is 6,000 feet long and over 150 feet tall at the center span. The bridge is actually a pair of steel truss bridges that span over the Thames River, between New London and Groton, according to the project website.
The Gold Star Memorial Bridge, described as “Connecticut’s most iconic structure,” is the largest bridge in the State of Connecticut. It is 6,000 feet long and over 150 feet tall at the center span. The bridge is actually a pair of steel truss bridges that span over the Thames River, between New London and Groton, according to the project website.
 “Repairs and maintenance of the bridge’s structural steel includes steel girder end repairs, bolt replacements, and bearing replacement and maintenance. Repairs to the substructure include concrete repairs and crack sealing,” the website explains.
“Repairs and maintenance of the bridge’s structural steel includes steel girder end repairs, bolt replacements, and bearing replacement and maintenance. Repairs to the substructure include concrete repairs and crack sealing,” the website explains. teachers and administrators are armed,” 85 percent said they would not; 15 percent thought they would.
teachers and administrators are armed,” 85 percent said they would not; 15 percent thought they would.


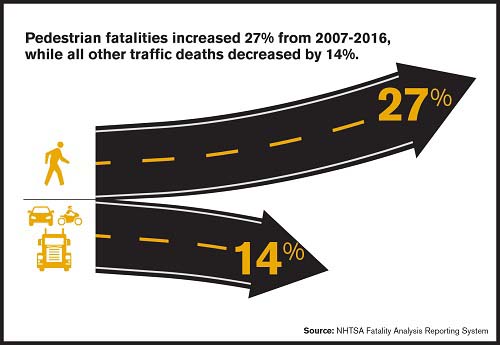 The total number of multimedia messages sent has more than tripled since 2010. The report also suggests a possible link with marijuana use. According to the report, the seven states (Alaska, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, Washington) and DC that legalized recreational use of marijuana between 2012 and 2016 reported a collective 16.4 percent increase in pedestrian fatalities for the first six months of 2017 versus the first six months of 2016, whereas all other states reported a collective 5.8 percent decrease in pedestrian fatalities.
The total number of multimedia messages sent has more than tripled since 2010. The report also suggests a possible link with marijuana use. According to the report, the seven states (Alaska, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Oregon, Washington) and DC that legalized recreational use of marijuana between 2012 and 2016 reported a collective 16.4 percent increase in pedestrian fatalities for the first six months of 2017 versus the first six months of 2016, whereas all other states reported a collective 5.8 percent decrease in pedestrian fatalities.
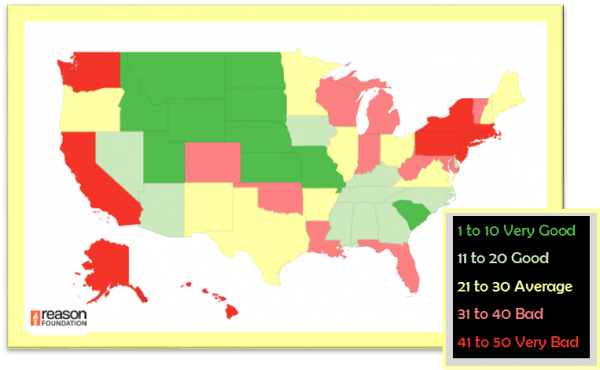 Reason Foundation’s Annual Highway Report ranks the performance of state highway systems in 11 categories, including spending per mile, pavement conditions, deficient bridges, traffic congestion, and fatality rates. At the bottom were New Jersey, Rhode Island, Alaska, Hawaii and Connecticut. Topping the list were North Dakota, Kansas, South Dakota, Nebraska, South Carolina and Montana. New York and Massachusetts were also in the bottom ten, ranked just above Connecticut.
Reason Foundation’s Annual Highway Report ranks the performance of state highway systems in 11 categories, including spending per mile, pavement conditions, deficient bridges, traffic congestion, and fatality rates. At the bottom were New Jersey, Rhode Island, Alaska, Hawaii and Connecticut. Topping the list were North Dakota, Kansas, South Dakota, Nebraska, South Carolina and Montana. New York and Massachusetts were also in the bottom ten, ranked just above Connecticut. The report also considered costs related to state roads and bridges.
The report also considered costs related to state roads and bridges.


























