Driver Distraction Continues Almost 30 Seconds After Text is Sent, Research Reveals
/Groundbreaking research by the AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety reveals that the distraction drivers experience using voice activated technology - or their smartphones - to make a call, change music or send a text can linger for almost 30 seconds after the task is complete.
“This should be a wakeup call to anyone who feels safe texting while sitting at a red light”, says AAA spokesperson Amy Parmenter. “Just because you can hit the gas when the light turns green, doesn’t mean you’re good to go.”
Researchers studying various push-to-talk technologies found that potentially unsafe levels of mental distraction lasted for as long as 27 seconds after completing a task in the worst-performing systems. And, at the 25 MPH speed limit in the study, drivers traveled the length of nearly three football fields during this time. Using the least distracting systems, drivers still remained impaired for more than 15 seconds.
The researchers discovered the residual effects of mental distraction while comparing the voice activated technology in ten 2015 vehicles and three types of smart phones. The analysis found that all systems studied increased mental distraction to potentially unsafe levels.
“Automakers often promote everything their connected cars can do, but this research paints a frightening picture of what drivers can’t do if they use the popular features” Parmenter says. “Hands free does not mean risk free. It’s that simple”.
Last month, CT by the Numbers reported that in-car electronics that allow drivers to listen to, read and send text messages while at the wheel may be skirting the spirit, if not the letter, of Connecticut law. In Connecticut, Public Act 10-109, enacted in 2010, states that “no person shall operate a motor vehicle … while using a hand-held mobile telephone to engage in a call or while using a mobile electronic device while such vehicle is in motion. An operator of a motor vehicle who types, sends or reads a text message with a hand-held mobile telephone or mobile electronic device while such vehicle is in motion shall be in violation of this section.”
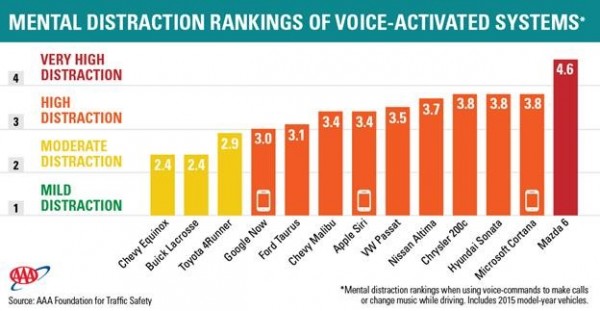
In the AAA study, researchers rated driver distraction on a scale of 1-5, with 1 being relatively safe, about equal to listening to the radio, and 5 being highly challenging in such a way as to overload the driver’s attention. The best performing system was the Chevy Equinox with a cognitive distraction rating of 2.4, while the worst performing system was the Mazda 6 with a cognitive distraction rating of 4.6.
The systems that performed best generally had fewer errors, required less time on task and were relatively easy to use. The researchers also studied voice activated smartphone technology and found that Google Now outperformed Apple Siri and Microsoft Cortana but, they say, all were dangerously distracting with ratings of 3.1, 3.4 and 3.8 respectively.
Dr. David Strayer and Dr. Joel Cooper of the University of Utah conducted the research. A total of 257 drivers ages 21-70 participated in the study of 2015 model-year vehicles, while 65 additional drivers ages 21-68 tested the three phone systems. Over the last two weeks, AAA has shared its findings with policymakers, safety advocates and manufacturers in hopes of improving the safety of future technology.


 ation for Traffic Safety indicates that high school-aged teens report using their phones or texting while driving substantially less often than adults do. The AAA survey found that adult drivers ages 25-39 were the most likely to admit engaging in these risky behaviors behind the wheel.
ation for Traffic Safety indicates that high school-aged teens report using their phones or texting while driving substantially less often than adults do. The AAA survey found that adult drivers ages 25-39 were the most likely to admit engaging in these risky behaviors behind the wheel.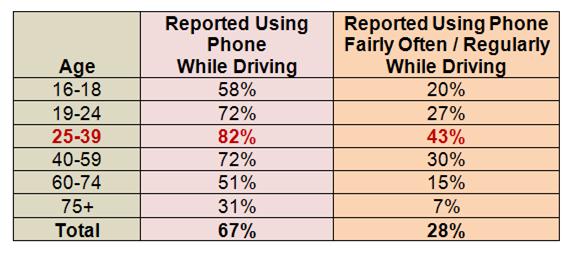
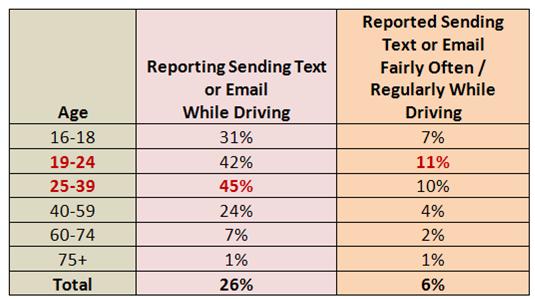 of electronic devices in vehicles.
of electronic devices in vehicles.






























