Safety Gap: Parents Impose Rules on Teen Drivers, Teens Don’t Think So
/Teen drivers are at the highest risk for crashes and crash-related fatalities, and are particularly vulnerable to distractions while driving. The results of a new nationwide survey of teens and their parents suggest a considerable disconnect between the limitations parents believe they are imposing on driving and the use of cell phones, and their teens’ view of limitations imposed by their parents. The gap in numerous instances is wide, and has raised concerns about the resulting risks to teen drivers.
In families where parents reported limitations on their teen drivers – such as restricting cell phone use, number of teen passengers and driving times and locations – teens themselves sometimes said they did not have those limitations, according to the C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health, which indicated that parents play a key role in promoting the safety of their teens by setting expectations for driving.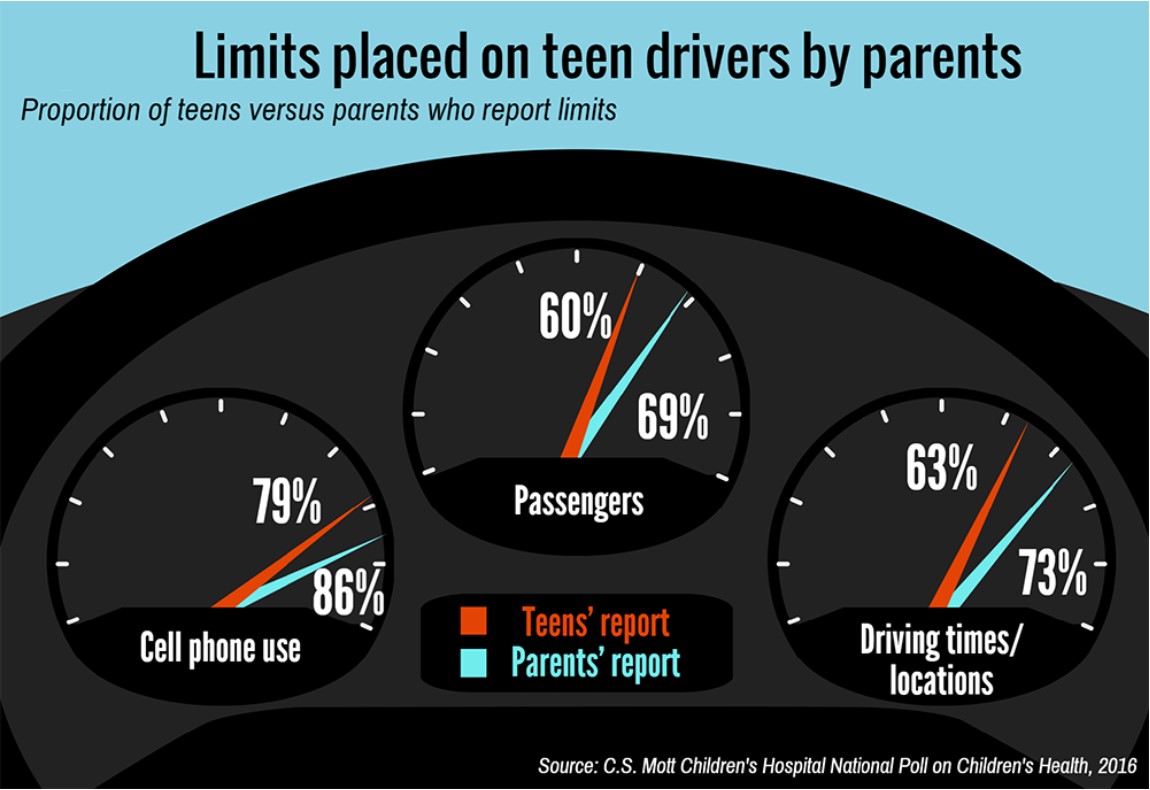
“We found that the great majority of parents do have rules for their teen drivers; however, teens consistently perceive fewer limits on their driving than what their parents report. This signals an opportunity for parents and teens to have more conversations about safe driving habits,” says lead author Michelle L. Macy, M.D., M.S., an emergency medicine physician at the University of Michigan’s C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital.
Parents of teens 13-18 years old and teens themselves were asked about limits placed on driving circumstances that can increase a teen driver’s risk of a crash. About nine in 10 parents report they place at least one limit on their teen drivers while eight out of 10 teens report having at least one driving limit placed on them by their parents.
Among parents and teens who both responded, teens consistently say they have fewer limits on their driving than were reported by their parents. Overall, 81 percent of teens report having at least one driving limit placed on them by their parents. In families where parents report limits on cell phone use, 13 percent of teens say they have no limits. In families where parents report limits on passengers or driving times/locations, 20 percent of teens say they have no such limits.
Limits on cell phone use and texting while driving are most commonly reported by parents and their teens. Fewer limits are set on passengers and driving times/locations. As many as one-quarter of parents report placing no limits on teen passengers or nighttime or highway driving, suggesting opportunities to increase teen driver safety by encouraging parents to place limits on these high-risk driving conditions, officials indicated. Among the key limitations parents impose, according to the survey:
Limits on cell phone use include:
- requiring teens to park to use their cell phones (86%)
- forbidding texting while driving (73%)
- having cell phone turned off or put away (62%)
Limits on passengers include:
- allowing only 1-2 friends in the car (59%)
- allowing only certain friends (54%)
- no teen passengers allowed (40%)
Limits on driving times/locations include:
- no driving after 10 p.m. (61%)
- driving only to/from school, work, or activities (57%)
- no highway driving (36%)
Parents who judge their teens’ driving ability as “above average” (32% of all parents) are less likely to place limits on passengers and driving times/locations. Sixty-seven percent of parents set limits on passengers for their “above-average” teen drivers, compared with 81percent of parents who perceive their teen drivers as “below average.” Similarly, 69 percent of parents set limits on driving times/locations for their above-average teen drivers, compared with 85 parents of parents who perceive their teen as below average. In contrast, parents do not adjust their restrictions on cell phone use in relation to their teens’ driving ability.
There was greater agreement between parents and teens on limits placed on cell phones than on passengers or driving times/locations, according to the national survey, conducted in September 2015 and released earlier this year.
“This may indicate that parents communicate to their teens more clearly their expectations around cell phone use while driving than for other driving situations. It is also possible that parents and teens have greater awareness of the risks of using cell phones while driving, due to media attention on cell phone distractions as a common cause of crashes,” the survey analysis points out.
The analysis also indicated that the higher degree of disagreement between teens and parents in relation to the limits set for passengers and driving times/locations suggests the need for more dialogue in families to ensure rules and expectations around driving are understood. Written parent-teen driving agreements are one way for parents to clearly communicate rules and expectations, officials indicated.
Connecticut’s Tim Hollister, author of two books about parenting and safe teen driving and the website From Reid’s Dad, recently developed a video for parents, with financial support from the Travelers, which underscores the influence of parents in teen driving. Hollister will be speaking on the subject at the Easton Public Library on February 10 and the Newington Public Library on February 24. Hollister, whose son Reid died as a result of a car accident at age 17, will share information parents should know regarding teen driving and discuss his most recent book, His Father Still.
https://youtu.be/QmCJKvyXhEQ
https://youtu.be/wccN8aqOWA4

 ation for Traffic Safety indicates that high school-aged teens report using their phones or texting while driving substantially less often than adults do. The AAA survey found that adult drivers ages 25-39 were the most likely to admit engaging in these risky behaviors behind the wheel.
ation for Traffic Safety indicates that high school-aged teens report using their phones or texting while driving substantially less often than adults do. The AAA survey found that adult drivers ages 25-39 were the most likely to admit engaging in these risky behaviors behind the wheel.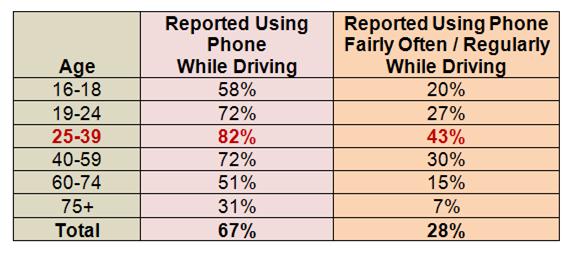
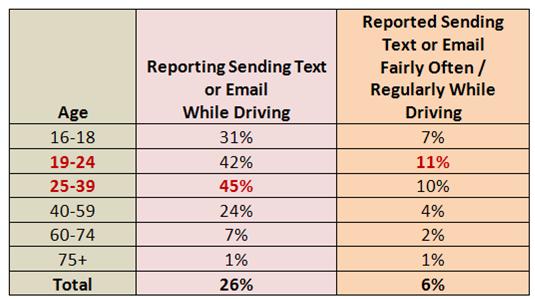 of electronic devices in vehicles.
of electronic devices in vehicles.































