State Report Calls for Tax Incentives, Better Insurance, Greater Flexibility to Improve Care for Rapidly Growing Older Population
/A new report by the state legislature’s Commission on Aging, examining state funding and support for home and community-based care for older adults and individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease, has issued more than a dozen recommendations, including establishment of a Dependent Care Tax Credit, release of funds to support home modifications, and extension of paid sick leave to cover care of elderly relatives. Incentives for employers to offer long-term care insurance coverage are also suggested.
The Commission on Aging is a nonpartisan public policy and research office of the Connecticut General Assembly. A law passed by the legislature last year charged the Commission with studying private sources of funding available to elderly persons and persons with Alzheimer's disease in need of home or community-based care, including the cost effectiveness of such programs funded by the state with recommendations on which state programs should be expanded.
Connecticut is the 7th oldest state in the nation. Over 70,000 people age 65 and older live with Alzheimer’s Disease or another dementia, and disabilities affect 10.4 percent of all Connecticut residents – nearly 400,000 people. Due to factors including aging demographics and consumer choice, demand for home-care based services is expected to “increase exponentially in coming decades,” according to the report. Between 2010 and 2040, Connecticut’s population of people age 65 and older is projected to grow by 57 percent, with less than 2 percent growth for people age 20 to 64 during the same period.
The 23-page report noted that “informal caregivers are the backbone of the long-term service and support system. It is estimated that the economic value of the care provided by unpaid caregivers is $5.8 billion in Connecticut. Supporting caregivers is a cost effective means of reducing the reliance on costly formal care system.” The report went on to caution that “without support, caregivers are likely to become emotionally and physically ‘burnt-out’ and find few options” short of turning to institutional care.
The report recommends amending the state tax code to include a Dependent Care Credit where the tax filer can receive a credit for care expenses incurred while a caregiver is working. Home care and adult day care costs are cited as examples of work‐related expenses that may be eligible.
To provide further support to informal caregivers, the report calls on the legislature to extend paid sick leave for those caring for an aging parent or other relative. Connecticut’s law currently allows paid sick leave to be used for a worker’s own illness or injury, or to care for the worker’s child or spouse. It does not extend to cover workers who care for a parent or other relative. 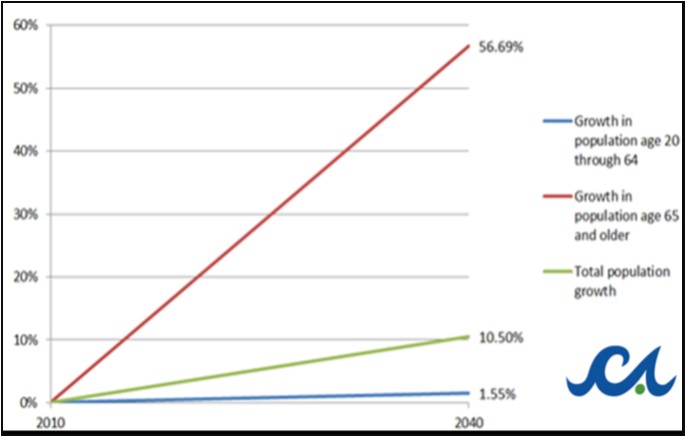
Policies that “allow for flexibility” in work schedules are also urged, cited studies have shown such schedules not only are “an import way to support a caregiver but also… positively affect recruitment and retention efforts.”
The report urges the authorization of $6 million in bond money for home modifications and adaptive technology, which was allocated by last year’s legislature, and development of a list of “vetted home repair and home modification contractors and programs” to improve the likelihood that individuals would be able to “age in place.”
The goal, the report indicated, would be to “enable them to function with greater independence in the home, remain in the community and reduce the need for human assistance. Simple modifications include adding nonslip strips to bathroom floors or other smooth surfaces, improving lighting, providing telephones with large numbers and letters, and installing grab bars. More complex (and expensive) modifications include installing ramps, chair lifts, stair glides, widened doorways, roll-in showers, and lowered countertops.”
Among the other recommendations, the report urges professional development for those whose job it is to care for individuals with Alzheimer’s and dementia, to align with changing demographics in the state’s population.
 The report also suggests that policy makers “explore the possibility of incenting employer-based long-term care insurance coverage.” In 2009 almost 25,000 employers in the U.S. offered long-term care insurance to their employees – just 35 percent of the 7.5 million insurance policies in effect. In addition, the report encourages the Connecticut Congressional delegation to support a federal tax deduction for long-term care insurance, and urges policy makers to consider making reverse mortgages “a more viable option.”
The report also suggests that policy makers “explore the possibility of incenting employer-based long-term care insurance coverage.” In 2009 almost 25,000 employers in the U.S. offered long-term care insurance to their employees – just 35 percent of the 7.5 million insurance policies in effect. In addition, the report encourages the Connecticut Congressional delegation to support a federal tax deduction for long-term care insurance, and urges policy makers to consider making reverse mortgages “a more viable option.”
Additionally, the report also considers advances in technology in the care of older residents. It describes “telehealth” as a mode of delivering health care, public health and certain non-clinical services using electronic communications technology, stating that it “represents an opportunity for Connecticut to improve access to care, coordination, quality and outcomes for individuals, all while reducing cost, promoting local economic health, and offering a patient-centered approach.” The Commission on Aging calls on Connecticut to join at least 21 other states that have telehealth parity laws for private insurance, meaning that providers can collect reimbursement for telehealth services.
The report, “Study of Funding and Support for Home and Community-Based Care for Older Adults and Persons with Alzheimer's Disease,” also recommends that the state “address service challenges specific to housing, transportation and behavioral health,” including conducting “walkability audits” to assess sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian access to essential services. It also suggests that the state “explore the use of taxi vouchers, public and private paratransit services, paid and volunteer driver services, on-demand car rental services and other forms of transportation in the growing “shared mobility” economy.



 vers.
vers.




























