Cellphone Likely Won’t Tell 911 Operator Your Location
/The Federal Communications Commission has estimated that about 70 percent of 911 calls are placed from wireless phones, and that percentage is growing. For many Americans, according to the federal agency, “the ability to call 911 for help in an emergency is one of the main reasons they own a wireless phone.” Yet, in an emergency, a cell phone may provide potential first responders with less information than one would expect.
The National Emergency Number Association (NENA),which represents dispatchers, supervisors and private-sector service providers, points out that “when 9-1-1 calls are made from wireless phones, the call may not be routed to the most appropriate 9-1-1 center, and the call taker doesn't receive the callback phone number or the location of the caller. This presents life threatening problems due to lost response time, if callers are unable to speak or don't know where they are, or if they don't know their wireless phone callback number and the call is dropped.” The organization’s motto is “emergency help, any time, anywhere, any device.”
Recent published reports in Governing magazine indicate that “when you check movie times on your cellphone, search for a restaurant or hail a ride, the device automatically knows exactly where you are and can suggest things nearby. So it’s understandable that many people assume the same holds true when they call 911 for emergency assistance. But the fact is, 911 call centers frequently receive imprecise locations of callers from wireless carriers -- and some don’t get any location information at all. Calls from landline phones are linked to addresses.”
The FCC website explains that “since wireless phones are mobile, they are not associated with one fixed location or address. While the location of the cell site closest to the 911 caller may provide a general indication of the caller's location, that information is not always specific enough for rescue personnel to deliver assistance to the caller quickly.”
More reliable and specific location information could save lives, advocates say, and earlier this year an order from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) set targets for companies to improve both the availability and accuracy of location information. But those upgrades remain a long way off.
Under the new rules, carriers will have to provide caller location info within 50 meters 80 percent of the time by 2021, along with vertical location information, if the call is being made from an apartment building or high rise office tower -- that would have to be in place in major markets by 2023.
Some have said the industry needs to provide those capabilities much sooner. While 911 dispatchers routinely ask callers for their location, callers at times hang up before providing that information, for any number of reasons. And, they argue, if a cell phone knows where you are, that information should be instantly made available to 911 dispatchers as well.
The latest FCC guidelines are available for public review. “We would have liked to have seen a more compressed timetable,” NENA CEO Brian Fontes told Governing.
Published reports in Connecticut indicate that some communities are moving forward with new technology. The town of Wolcott, according to reports, has begun using a system that will allow police to pinpoint the location of emergency calls made from cell phones. The Republican-American newspaper reports the town was the first in the state to use the next-generation system in a pilot program that was slated to include the New Britain, Wilton, Enfield, Newington, Valley Shore, Fairfield, Middletown, Mashantucket and Shelton police departments . The new system shows dispatchers the caller’s location within a 50-foot radius, compared with the old system which would indicate the location of a wireless 911 call within a quarter-mile radius.
Plans are also in the works that would permit individuals to text 911 from their cell phones. The CT Post reported last month that about 24 dispatch centers out of 110 statewide are being upgraded to the text-to-911 system. Stratford and Fairfield will be among the first towns in the state to get the texting capability. Officials hope the entire state will have text-to-911 by late 2016 or early 2017, the newspaper reported.


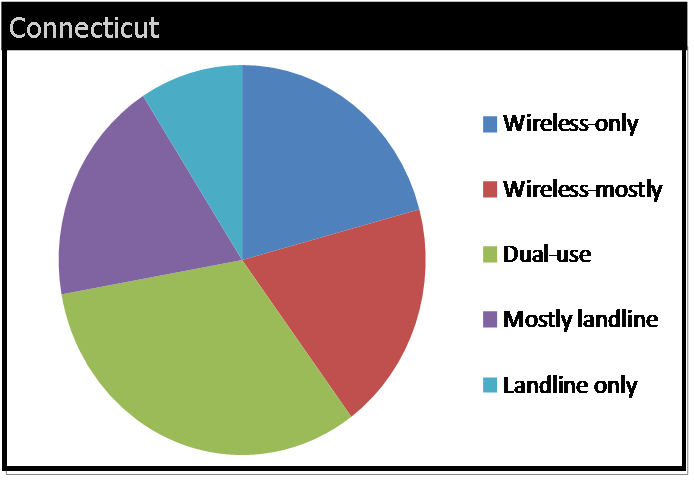
 t joined New Jersey with prevalence rates below 25 percent, including Connecticut (20.6%), Delaware (23.3%), New York (23.5%), Massachusetts (24.1%), and Rhode Island (24.9%).
t joined New Jersey with prevalence rates below 25 percent, including Connecticut (20.6%), Delaware (23.3%), New York (23.5%), Massachusetts (24.1%), and Rhode Island (24.9%).