Hartford Rail Line May Bring Jobs, Opportunity for Key Populations, Study of Public Transit Suggests
/As Connecticut moves closer to a significant increase in rail service connecting communities from New Haven to Springfield, MA, with the introduction of the Hartford line, anticipated in May, a report by Demos underscores the potential impact on economic opportunity and segments of the state’s population.
The report, “To Move is to Thrive: Public Transit and Economic Opportunity for People of Color,” which looked at public transportation in metropolitan areas across the country, presents a series of findings on the use of public transit by people of color and on the potential jobs benefits that people of color can gain from investments in public transit.
Its key findings on the use of public transit are:
- Racial, ethnic, and class inequities in the access to and funding of public transit continue today.
- Latino and Asian-American workers are twice as likely as white workers not to have a vehicle at home. African American workers are three times as likely. These disparities are heightened in certain metropolitan areas; Latino and black workers lack a private vehicle at as much as six times the rate of white workers in some areas.
- Asian-American and African-American workers commute by public transit at nearly four times the rate of white workers. Latino workers commute by public transit at nearly three times the white rate.
- Workers of color are overrepresented among public transit commuters with “long commutes”—one-way commutes of 60 minutes or longer.
 The key findings on the jobs benefits from investment in public transit are:
The key findings on the jobs benefits from investment in public transit are:
- America’s employment rates are still low relative to 2000, and there is a strong racial hierarchy in employment rates.
- The majority of the jobs created from infrastructure investments can be non-construction jobs.
- All racial and ethnic groups gain jobs from large infrastructure investments and, generally, the larger the investment, the more jobs for each group.
- Investments in public transit show good returns in terms of the shares of the total jobs going to workers of color.
The report also noted that “growing numbers of Americans rely on public transit in their daily lives. In 2015, passengers took 10.5 billion trips on transit systems, up 33 percent from 20 years ago. Public transit ridership has grown faster than the population. But our public transit infrastructure, like much of our infrastructure generally, is old and decrepit. And many of our transit systems were not designed to handle such heavy use.”
While Connecticut’s cities are not as large as many of the nation’s largest metropolitan areas, they do have populations with larger numbers of people of color than mnay surrounding suburbs. Providing greater ease of mobility to station stops along the Hartford line could offer impacts suggested by the study.
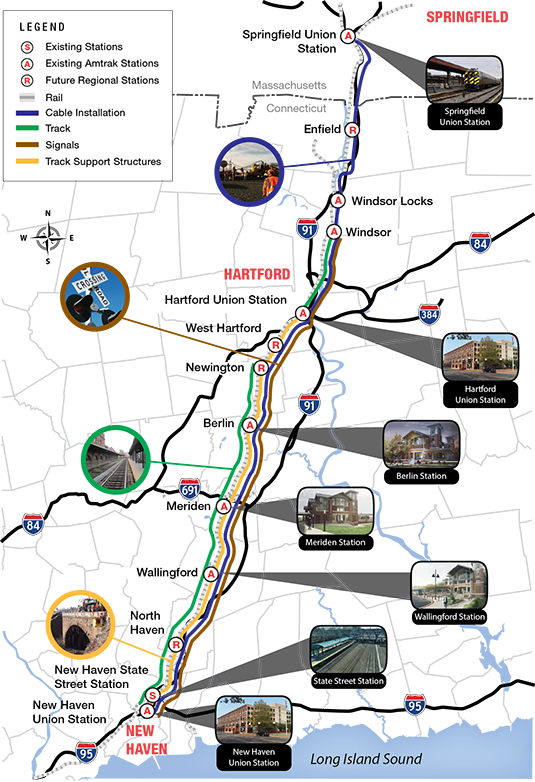
The Hartford line, which is focused on increasing the frequency of station stops from Springfield to New Haven, will also see additional stations constructed in the coming years. When the CTrail Hartford Line service launches in May, it will consist of both expanded Amtrak service and new regional trains operated by the Connecticut Department of Transportation and will offer more frequent, convenient and faster passenger rail service between New Haven, Hartford and Springfield.
Plans call for an increase in the number of round trip trains from six daily Amtrak intercity and regional trains to a total of 17 round trip trains a day to Hartford, and 12 trains per day to Springfield. In addition, trains will operate at speeds up to 110 mph, reducing travel time between Springfield and New Haven. Stops are to include rail stations in Windsor Locks, Windsor, Hartford, Berlin, Meriden, Wallingford and New Haven. New stations are to be added, refurbished or relocated in North Haven, Newington, West Hartford, Windsor, Windsor Locks and Enfield by 2020.
Projections include more than 4,500 construction related jobs and over 8,000 total jobs, including both direct and indirect jobs. Transit-oriented development, including housing is also anticipated along the route. Recently, plans to convert a long-vacant factory into housing was announced in Windsor Locks.
The national data indicates that workers of color are roughly 2 to 3 times as likely as white workers not to have a private vehicle at home: only 2.8 percent of white workers do not have a vehicle at home, but 6.9 percent of Asian-American workers, 7 percent of Latino workers, and 9.5 percent of African-American workers do not have a vehicle at home.
Nationally, 3.1 percent of white workers use public transit, while 7.8 percent of Latino workers, 11 percent of Asian-American workers, and 11.1 percent of African-American workers commute using public transit. In other words, Latino workers are almost 3 times as likely, and Asian-American and African-American workers are almost 4 times as likely as white workers to commute by public transit, the report indicated.
Based in New York, Boston and Washington D.C., Demos is a public policy organization “working for an America where we all have an equal say in our democracy and an equal chance in our economy.”




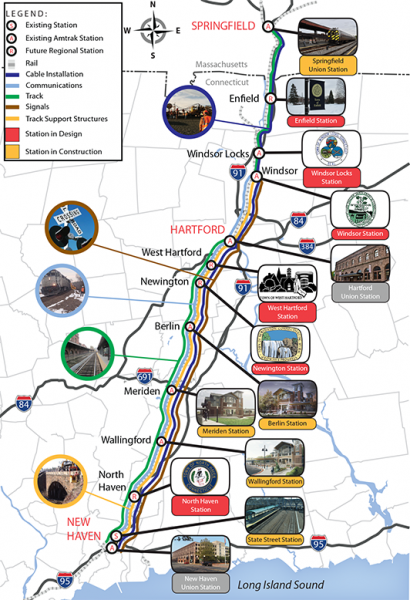 The Hartford Line will act as a regional link with connections to existing rail services, including Metro-North, Shoreline East, and Amtrak Acela high-speed rail services on both the New Haven Line to New York and on the Northeast Corridor to New London and Boston. There will also be direct bus connections to the Bradley Airport Flyer and to CTfastrak. With a heightened level of direct and connecting service linking the region, the hope is that towns along the future Hartford Line will become magnets for growth – ideal places to live and to relocate businesses that depend on regional markets and travel.
The Hartford Line will act as a regional link with connections to existing rail services, including Metro-North, Shoreline East, and Amtrak Acela high-speed rail services on both the New Haven Line to New York and on the Northeast Corridor to New London and Boston. There will also be direct bus connections to the Bradley Airport Flyer and to CTfastrak. With a heightened level of direct and connecting service linking the region, the hope is that towns along the future Hartford Line will become magnets for growth – ideal places to live and to relocate businesses that depend on regional markets and travel. Also, very much a part of the strengthening transportation options with the potential to spur economic development is
Also, very much a part of the strengthening transportation options with the potential to spur economic development is 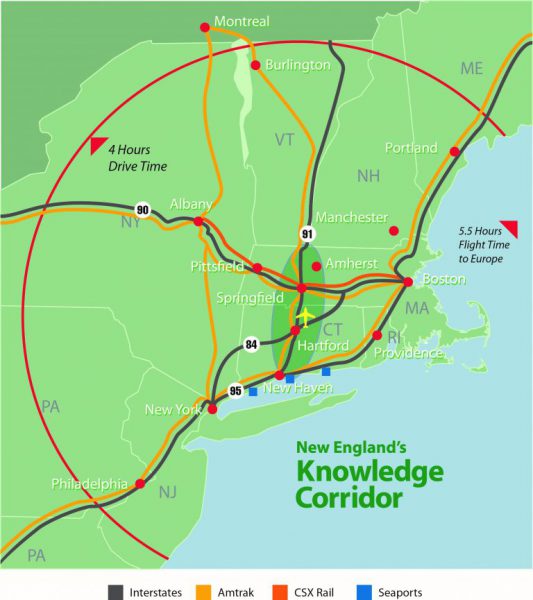

 As one example, state officials are working on a plan to replace a swinging bridge over the Norwalk River, built in 1896. "As a piece of engineering, it's just amazing," John Bernick, assistant rail administrator for the state Department of Transportation told the AP. "But, it's certainly reached its retirement age.” The computer that operates the bridge is from the 1980’s, and replacing the bridge could cost as much as $650 million.
As one example, state officials are working on a plan to replace a swinging bridge over the Norwalk River, built in 1896. "As a piece of engineering, it's just amazing," John Bernick, assistant rail administrator for the state Department of Transportation told the AP. "But, it's certainly reached its retirement age.” The computer that operates the bridge is from the 1980’s, and replacing the bridge could cost as much as $650 million.

 ses running this service are frequently at or above capacity with some occurrences where riders must be turned away. “At a minimum,” the report recommends, “additional investment of state funds would be required to support additional buses to provide a consistent level of services and improve service quality.”
ses running this service are frequently at or above capacity with some occurrences where riders must be turned away. “At a minimum,” the report recommends, “additional investment of state funds would be required to support additional buses to provide a consistent level of services and improve service quality.”




























