Greater Hartford Residents Prefer Focus on Vibrant Communities Over Recruiting Businesses
/In a time of reduced resources and stark choices for policy makers, a survey of Greater Hartford residents suggests that investments aimed at creating vibrant communities, with the focus on local schools, transportation options, walkable, attractive physical environment is preferred to devoting greater resources to recruiting employers.
In a survey for the Hartford Foundation for Public Giving as part of the Metro Hartford Progress Points effort, and conducted by Inform CT, residents of Hartford and Tolland County, by 57 percent to 43 percent, said that investing in communities was a better approach than recruiting businesses.
The findings reaffirm one of the key goals in the new three-year strategic plan of HFPG, launched earlier this year, developing vibrant communities. The plan states that “All of our region’s residents should have the opportunity to live and contribute to strong, safe vibrant communities,” and calls for a “focus on people and places with the greatest need by engaging and supporting partners who promote meaningful civic engagement, safe affordable housing, quality health and mental health care and a rich diversity of cultural and other experiences to improve the quality of life.”
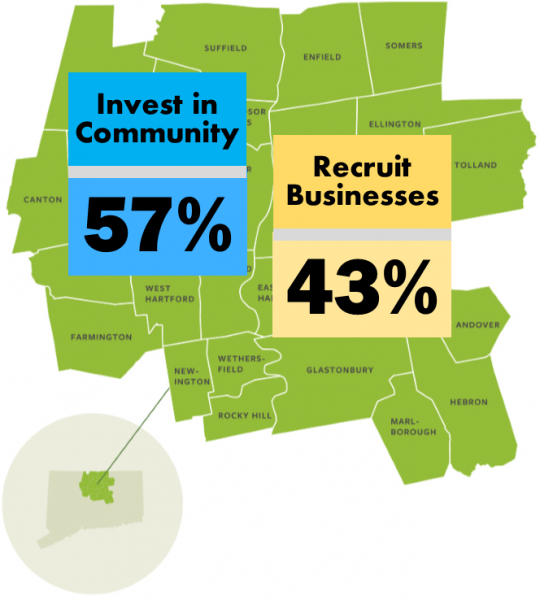 The data from the survey reflect a difference of opinion among older residents of the region. Individuals over age 46 took the opposite view from younger residents, with a majority expressing a preference for spending skewed toward recruiting companies. The reversal was dramatic, with two-thirds of those age 36-45 preferring investing in communities, by a margin of 67%-33%, and individuals age 46-55 expressing a preference for resources to be aimed at recruiting companies, with two-thirds holding the opposite view, 63%-38%.
The data from the survey reflect a difference of opinion among older residents of the region. Individuals over age 46 took the opposite view from younger residents, with a majority expressing a preference for spending skewed toward recruiting companies. The reversal was dramatic, with two-thirds of those age 36-45 preferring investing in communities, by a margin of 67%-33%, and individuals age 46-55 expressing a preference for resources to be aimed at recruiting companies, with two-thirds holding the opposite view, 63%-38%.
Across all age groups, a majority of homeowners preferred that the emphasis be on vibrant communities, 52%-48%, and an even larger majority of respondents who are not homeowners, 64%-36%, shared the same view.
The preference for policy to be targeted more towards assuring vibrant communities than recruiting companies was consistent across a majority of respondents of various education levels and among white, black and Hispanic residents of the region, according to the survey. A majority of survey respondents who are currently employed full-time, as well as those working part-time, and those unemployed all expressed a preference for investing in communities rather than recruiting companies.
The Greater Hartford survey results are not inconsistent with data gathered elsewhere. A March 2014 national survey by the American Planning Association (APA) found that Millennials and Baby Boomers want cities to focus less on recruiting new companies and more on investing in new transportation options, walkable communities, and making the area as attractive as possible. The national survey found that 65 percent of all respondents and 74 percent of millennials believe investing in schools, transportation choices and walkable areas is a better way to grow the economy than investing in recruiting companies to move to the area, according to the APA.
A 2013 study in Michigan, posing similar questions, brought similar results. In the statewide survey, 64 percent of Michigan citizens said they believed the most important thing state government can do for job creation is to “provide quality education, good roads and transportation, good public services like safety, water, fire, parks and libraries that create an environment in which people want to live, work and run a business.” This contrasts with 29 percent who said the most important thing state government can do is to “cut taxes for individuals and businesses.”
Earlier this month, at the annual Municipal Collaboration Summit organized by the Hartford Business Journal, one of the session’s was devoted to an exploration of “Building Vibrant Communities,” with observations from representatives of Connecticut Main Street Center, the Partnership for Strong Communities and the Connecticut Economic Resource Center.
The Hartford Foundation for Public Giving serves 29 towns, hundreds of nonprofits and more than 750,000 residents in the Greater Hartford region. As Greater Hartford’s community foundation, HFPG brings together members of the community to “share information, understand local problems and put resources behind effective solutions.”
Developed by a group of key regional stakeholders, Metro Hartford Progress Points is a periodic 'check-up' to build greater understanding about issues facing the Greater Hartford community. The second edition of Progress Points, released late last year, takes a deeper look at key issues impacting our communities and how they are connected, with a particular focus on access to better schools, better jobs and stronger neighborhoods. Along with the Hartford Foundation, partners include the Hispanic Health Council, MetroHartford Alliance, United Way of Central and Northeastern Connecticut, Urban League of Greater Hartford, Capitol Workforce Partners, Capitol Region Council of Governments, the Center for Urban and Global Studies at Trinity College and the City of Hartford.
The survey was conducted for the Foundation during the 4th quarter of 2015 by Inform CT.



 The issue brief indicated that a disadvantage of a distance toll system on all limited access highways in Connecticut would be that it “could create an incentive for people to use alternative roadways. The increased use of these roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.” The advantage would be that distance tolls “could help to more efficiently allocate the cost of these roadways to drivers who use them the most.”
The issue brief indicated that a disadvantage of a distance toll system on all limited access highways in Connecticut would be that it “could create an incentive for people to use alternative roadways. The increased use of these roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.” The advantage would be that distance tolls “could help to more efficiently allocate the cost of these roadways to drivers who use them the most.” Congestion pricing, which provides for higher toll charges at peak traffic times, “helps to limit traffic on major roadways and create an incentive for people to use more environmentally friendly forms of public transportation,” the policy paper indicates. However, a congestion pricing system “could polarize roadway use by displacing low income commuters during peak driving hours. Congestion pricing could also create displacement effects whereby the increased use of local roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.”
Congestion pricing, which provides for higher toll charges at peak traffic times, “helps to limit traffic on major roadways and create an incentive for people to use more environmentally friendly forms of public transportation,” the policy paper indicates. However, a congestion pricing system “could polarize roadway use by displacing low income commuters during peak driving hours. Congestion pricing could also create displacement effects whereby the increased use of local roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.”


 When asked to think about overall business conditions in Connecticut versus 6 months ago, respondents – for the first time in three quarters – said conditions are better now than 6 months ago. The margin was narrow - with 27 percent saying “better” and 25 percent saying “worse”, but that’s a reversal from the past two quarters, when more people were of the view that business conditions has worsened (22%-24% and 24%-28% in the two previous quarters).
When asked to think about overall business conditions in Connecticut versus 6 months ago, respondents – for the first time in three quarters – said conditions are better now than 6 months ago. The margin was narrow - with 27 percent saying “better” and 25 percent saying “worse”, but that’s a reversal from the past two quarters, when more people were of the view that business conditions has worsened (22%-24% and 24%-28% in the two previous quarters).
 "There are some things that state governments can do to make their states more attractive to research and development," including R&D tax credits, Nariman Behravesh, chief economist at IHS Inc. in Lexington, Massachusetts told Governing magazine. "State governments — if they carefully target areas where they think they have a bit of a competitive advantage — they could develop a cluster around their universities, as well."
"There are some things that state governments can do to make their states more attractive to research and development," including R&D tax credits, Nariman Behravesh, chief economist at IHS Inc. in Lexington, Massachusetts told Governing magazine. "State governments — if they carefully target areas where they think they have a bit of a competitive advantage — they could develop a cluster around their universities, as well."



 with the addition of headrest and ceiling speakers.
with the addition of headrest and ceiling speakers.

 The OLR report also indicates that a Federal Highway Administration pilot program permits up to three states to toll existing Interstate highways that they could not otherwise adequately maintain or improve, and increase funding available for public transportation initiatives. In addition, $2.6 billion is provided to Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor (and $5.4 billion to other Amtrak lines) over five years. It separates the Northeast Corridor, from Boston to Washington, D.C, from other Amtrak accounts to ensure that the amounts assigned to that Corridor are used there, OLR reports.
The OLR report also indicates that a Federal Highway Administration pilot program permits up to three states to toll existing Interstate highways that they could not otherwise adequately maintain or improve, and increase funding available for public transportation initiatives. In addition, $2.6 billion is provided to Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor (and $5.4 billion to other Amtrak lines) over five years. It separates the Northeast Corridor, from Boston to Washington, D.C, from other Amtrak accounts to ensure that the amounts assigned to that Corridor are used there, OLR reports. ecessarily result in that many jobs,” according to the website
ecessarily result in that many jobs,” according to the website  . Boston may be in the running for similar relocations.
. Boston may be in the running for similar relocations. The Crain’s article reports that headquarters began shrinking a decade ago, but the trend has accelerated in the past three years, according to Vinay Couto, a consultant in the Chicago office of Strategy&. In recent years, 16 companies have relocated their main headquarters to the city from the suburbs. Seventeen came from outside the metro area. The phenomenon, he points out, is driven by the outsourcing of shared services such as IT, accounting and human resources, as well as by a mindset borrowed from private equity to cut overhead and make every part of a business count toward profitability.
The Crain’s article reports that headquarters began shrinking a decade ago, but the trend has accelerated in the past three years, according to Vinay Couto, a consultant in the Chicago office of Strategy&. In recent years, 16 companies have relocated their main headquarters to the city from the suburbs. Seventeen came from outside the metro area. The phenomenon, he points out, is driven by the outsourcing of shared services such as IT, accounting and human resources, as well as by a mindset borrowed from private equity to cut overhead and make every part of a business count toward profitability.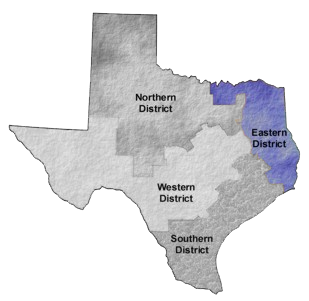 While action to combat the rapidly escalating challenge to businesses of every size has been unable to navigate through a divided Congress, the problem is growing. One jurisdiction in particular is a hospitable home for the legal attacks. Federal court in the Eastern District of Texas is the epicenter of patent troll litigation, and nearly 50 Connecticut companies are among those hauled into court there under dubious circumstances.
While action to combat the rapidly escalating challenge to businesses of every size has been unable to navigate through a divided Congress, the problem is growing. One jurisdiction in particular is a hospitable home for the legal attacks. Federal court in the Eastern District of Texas is the epicenter of patent troll litigation, and nearly 50 Connecticut companies are among those hauled into court there under dubious circumstances.



























