Health Care Providers, Insurers Need to Collaborate to Improve Care, Rein in Costs
/When Eric Schultz began his keynote remarks, the President and CEO of Massachusetts-based Harvard Pilgrim Health Care made sure to alert his audience to his homegrown pedigree. Whether his youth in the Naugatuck Valley, college years (five of them) at UConn, or graduate work at Yale contributed to Harvard Pilgrim’s more-than-solid inaugural years doing business in Connecticut isn’t certain, but the above-expectations numbers are indisputable. And Schmitt made clear that his nonprofit health insurance company is looking for even greater achievements in his home state. Since entering the Connecticut market in the summer of 2014, the company has been aggressively growing its customer base in a competitive market while working diligently to grow and expand its network of doctors. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care announced recently that its Connecticut membership has grown to more than 24,000, exceeding expectations for 2015. It now serves more than 800 Connecticut businesses. Twenty-nine of the state’s 30 hospitals are now in-network.
Since entering the Connecticut market in the summer of 2014, the company has been aggressively growing its customer base in a competitive market while working diligently to grow and expand its network of doctors. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care announced recently that its Connecticut membership has grown to more than 24,000, exceeding expectations for 2015. It now serves more than 800 Connecticut businesses. Twenty-nine of the state’s 30 hospitals are now in-network.
 With more than 500 business leaders in attendance at an annual Economic Summit & Outlook last week, brought together by the Connecticut Business and Industry Association and MetroHartford Alliance, Schmitt spent some time touting a new model launched in the state of New Hampshire that he believes may be a glimpse into the direction the industry is moving. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care’s footprint in New England now covers “where 90 percent of New Englanders live,” in Massachusetts, Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire.
With more than 500 business leaders in attendance at an annual Economic Summit & Outlook last week, brought together by the Connecticut Business and Industry Association and MetroHartford Alliance, Schmitt spent some time touting a new model launched in the state of New Hampshire that he believes may be a glimpse into the direction the industry is moving. Harvard Pilgrim Health Care’s footprint in New England now covers “where 90 percent of New Englanders live,” in Massachusetts, Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire. 
Schultz, who succeeded now-Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker in leading the organization five years ago, pointed to what he described as “a practical example of how an insurance company and groups of providers can work together to get control of medical cost trends and to help improve medical outcomes and help create better experiences for physicians and their patients.”
The goals, Shultz explained, are to reduce insurance premium trends by 10 to 15 percent, to improve clinical outcomes, to create a better “practice environment” for medical staff and to grow business. The partnership is driven to “produce something that’s better than what we have today, because we know the financing of health care is largely broken in the U.S.”
 Launched in October 2015 and in business as of January 1, Benevera Health, a joint venture led by senior leadership at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care and Dartmouth-Hitchcock, is a population health company, centered around “clinical and medical informatics.” Dartmouth-Hitchcock, a nonprofit academic health system that serves a patient population of 1.2 million in New Hampshire and Vermont, is led by Dr. James Weinstein, recently named as one of “100 Physician Leaders to Know” by a national health care trade publication.
Launched in October 2015 and in business as of January 1, Benevera Health, a joint venture led by senior leadership at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care and Dartmouth-Hitchcock, is a population health company, centered around “clinical and medical informatics.” Dartmouth-Hitchcock, a nonprofit academic health system that serves a patient population of 1.2 million in New Hampshire and Vermont, is led by Dr. James Weinstein, recently named as one of “100 Physician Leaders to Know” by a national health care trade publication.
“We are combining insurance data with clinical data,” Schultz said, “from their electronic medical records and our claims system, and creating a very powerful source of information.” That information, he stressed, could be used to better understand what’s happening in regards to patient care, and it can help to redesign and improve clinical care. This has the potential to be especially important in chronically ill patients, noting that 10 percent of patients drive 50 percent of health care costs. “It is a great financial opportunity and a great clinical opportunity.”
“The magic,” Shultz noted, is in having the provider and the payer sit down together and figure out” what should be done. Too often in the past, he said, providers and insurers haven’t gotten together – a lack of cooperation and collaboration that contributes to higher costs and to disconnects regarding patient care. His expectation is the Benevera will “reduce headaches” that insurance companies often cause providers, reduce duplication and costs, and improve patient care. 
In fact, when the new venture was launched last fall, officials from the two companies stressed that the groundbreaking entity, “will take health care coordination to a new level by bringing together clinical, financial and operational data from across partner institutions to provide actionable analytics for clinicians to further improve the quality and efficiency of patient care.” They added that “at the center of this approach will be locally-based care advocates who will identify early opportunities to engage patients – especially those with chronic, complex or emerging conditions - and provide them with one-on-one support.”
Schultz noted that insurance companies tend to resist providers suggesting how insurance plans ought to be designed. He disagrees with that resistance. “If more insurers took more input from providers on plan design, we’d be a lot better off.”
Harvard Pilgrim is the only not-for-profit, regional health plan operating in four contiguous New England states. Harvard Pilgrim’s flagship health plans in New England provide health coverage to 1.3 million members, while another 1.4 million individuals are served through Health Plans, Inc., a subsidiary that provides integrated care management, health coaching and plan administration solutions to self-funded employers nationwide. Schultz holds an MBA in Health Care Leadership from Yale University’s School of Management, as well as a bachelor of science degree in biology and a bachelor of arts degree in economics from the University of Connecticut.
“We’re about change and driving change,” Schultz told those attending the Hartford summit, “and I believe we need to do more of that.” He’s hoping to build a similar structure in Connecticut, and in other states around the country, because “it’s exactly what we need to do.”
Link to CT-N video of Economic Summit & Outlook.



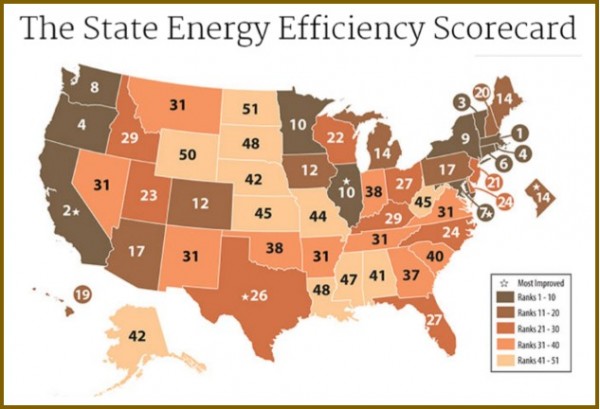 nd compliance efforts, earned 3 points out of 4 for its combined heat and power policies and programs, 5.5 out of 7 points for state-led energy efficiency initiatives, and 1 point out of 2 for appliance standards.
nd compliance efforts, earned 3 points out of 4 for its combined heat and power policies and programs, 5.5 out of 7 points for state-led energy efficiency initiatives, and 1 point out of 2 for appliance standards.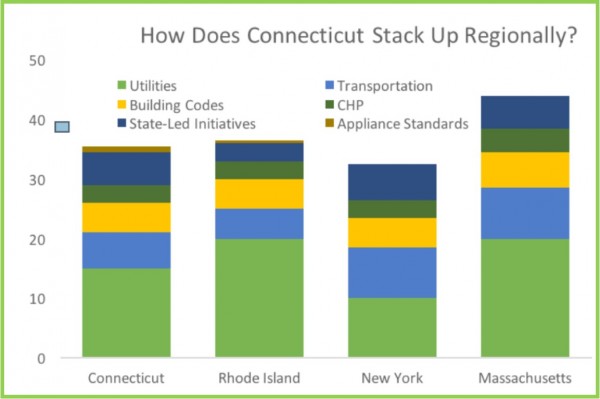 olar power in Connecticut has grown 221 percent per Capita since 2012, ranking the state 13th in the nation, the report points out. The top solar growth states in the nation, like Connecticut, have adopted renewable energy requirements, strong laws allowing solar customers to sell their excess power to the electric grid, and other policies encouraging growth of the industry, the report indicates. The industry is also adding jobs much faster than the overall economy, employing 1,600 people in Connecticut last year, according to
olar power in Connecticut has grown 221 percent per Capita since 2012, ranking the state 13th in the nation, the report points out. The top solar growth states in the nation, like Connecticut, have adopted renewable energy requirements, strong laws allowing solar customers to sell their excess power to the electric grid, and other policies encouraging growth of the industry, the report indicates. The industry is also adding jobs much faster than the overall economy, employing 1,600 people in Connecticut last year, according to  ."
."
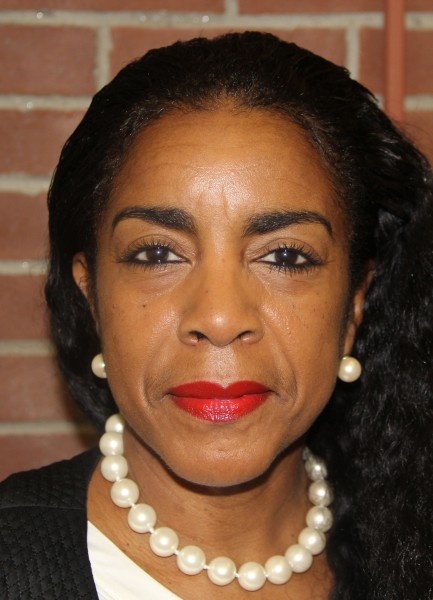 Diane Brown is branch manager of the New Haven Free Public Library’s Stetson Branch. Known as the “urban librarian” to her patrons, Brown develops valuable programs and services to meet the needs of the underserved residents in a community with high rates of poverty, crime and low literacy levels. Under Brown’s leadership, the library has been transformed into a true community center. She brings residents together by hosting cultural and educational events such as an international “pop up” festival, art exhibits, lectures and health fairs, according to officials. She has been praised for facilitating an afterschool tutoring program for K-8 students and providing opportunities for children and their families to spend time together by establishing history and game nights.
Diane Brown is branch manager of the New Haven Free Public Library’s Stetson Branch. Known as the “urban librarian” to her patrons, Brown develops valuable programs and services to meet the needs of the underserved residents in a community with high rates of poverty, crime and low literacy levels. Under Brown’s leadership, the library has been transformed into a true community center. She brings residents together by hosting cultural and educational events such as an international “pop up” festival, art exhibits, lectures and health fairs, according to officials. She has been praised for facilitating an afterschool tutoring program for K-8 students and providing opportunities for children and their families to spend time together by establishing history and game nights. Elizabeth G. Rumery, library director for the Avery Point Campus Library at the University of Connecticut in Groton, has “transformed the library into a welcoming and dynamic place for students by modernizing the facility to meet the needs of 21st century learners.” Officials indicate that she worked with contractors and school administrators on renovating the library, with improvements including new media rooms and collaborative study spaces for students and faculty.
Elizabeth G. Rumery, library director for the Avery Point Campus Library at the University of Connecticut in Groton, has “transformed the library into a welcoming and dynamic place for students by modernizing the facility to meet the needs of 21st century learners.” Officials indicate that she worked with contractors and school administrators on renovating the library, with improvements including new media rooms and collaborative study spaces for students and faculty. The librarians join “an esteemed group of award recipients who are recognized as being catalysts for powerful individual and community change.” Only 80 librarians have received the national award since its inception in 2008, including six from Connecticut. In 2012, the recipients were Rachel Hyland, Tunxis Community College Library in Farmington, and Rae Anne Locke, Saugatuck Elementary "Secret Garden" Library in Westport. The 2011 winners included Jennifer O. Keohane, The Simsbury Public Library and Michelle Luhtala, New Canaan High School Library.
The librarians join “an esteemed group of award recipients who are recognized as being catalysts for powerful individual and community change.” Only 80 librarians have received the national award since its inception in 2008, including six from Connecticut. In 2012, the recipients were Rachel Hyland, Tunxis Community College Library in Farmington, and Rae Anne Locke, Saugatuck Elementary "Secret Garden" Library in Westport. The 2011 winners included Jennifer O. Keohane, The Simsbury Public Library and Michelle Luhtala, New Canaan High School Library.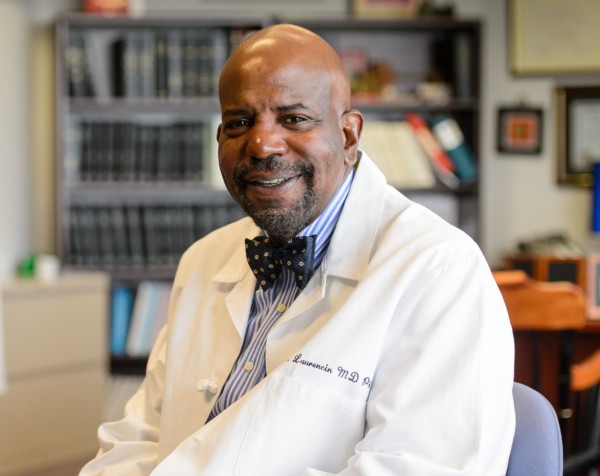 The news came just weeks after it was announced that Laurencin is the recipient of the 2016 Founders Award, the highest honor of The Society For Biomaterials. He will be honored at the 2016 World Biomaterials Congress in Montreal, Canada on May 18, 2016.
The news came just weeks after it was announced that Laurencin is the recipient of the 2016 Founders Award, the highest honor of The Society For Biomaterials. He will be honored at the 2016 World Biomaterials Congress in Montreal, Canada on May 18, 2016.


 This summer, Shemitz was among those appointed to serve on the state’s Commission on Economic Competitiveness, created by the legislature amidst concerns in the state’s business community about the perceived lack of competitiveness. The Commission is considering steps to improve Connecticut’s employment and business climate including measures to support workforce development and family and economic security. Recommendations are anticipated for legislative action next year.
This summer, Shemitz was among those appointed to serve on the state’s Commission on Economic Competitiveness, created by the legislature amidst concerns in the state’s business community about the perceived lack of competitiveness. The Commission is considering steps to improve Connecticut’s employment and business climate including measures to support workforce development and family and economic security. Recommendations are anticipated for legislative action next year.


 The action plan is spurred by clear concerns: “When young people are not attending school or working, they cannot attain necessary education or work experience, support themselves, save for their future, or contribute to the economy. What future do they face? What future does Fairfield County face?”
The action plan is spurred by clear concerns: “When young people are not attending school or working, they cannot attain necessary education or work experience, support themselves, save for their future, or contribute to the economy. What future do they face? What future does Fairfield County face?”



 According to the
According to the 
 In addition, the Great Recession encouraged many young adults to ride out the difficult job market by continuing their education.
In addition, the Great Recession encouraged many young adults to ride out the difficult job market by continuing their education.
 ort called for an increase of 36,000 students system-wide without adding additional faculty or space. The 17 institutions currently have a total of 92,000 students. The report recommended experimentation with price reductions for out-of-state-students, changing the name of the state system, asserting a new brand position, developing a new logo and color palette, maintaining low tuition increases, centralizing and outsourcing administrative services such as call centers and marketing, and developing goals for students success and metrics to track progress.
ort called for an increase of 36,000 students system-wide without adding additional faculty or space. The 17 institutions currently have a total of 92,000 students. The report recommended experimentation with price reductions for out-of-state-students, changing the name of the state system, asserting a new brand position, developing a new logo and color palette, maintaining low tuition increases, centralizing and outsourcing administrative services such as call centers and marketing, and developing goals for students success and metrics to track progress.
 in 1997. At that time, the college had approximately 2,700 students enrolled and immediately experienced a significant enrollment increase, according to the college. But the peak years now appear to be in the rear view mirror.
in 1997. At that time, the college had approximately 2,700 students enrolled and immediately experienced a significant enrollment increase, according to the college. But the peak years now appear to be in the rear view mirror.
 The APNA Annual Conference delivers more than 100 varied educational sessions and invaluable networking opportunities to the more than a thousand psychiatric-mental health RNs and APRNs who attend each year. The organization has more than 10,000 members nationwide.
The APNA Annual Conference delivers more than 100 varied educational sessions and invaluable networking opportunities to the more than a thousand psychiatric-mental health RNs and APRNs who attend each year. The organization has more than 10,000 members nationwide.
 In Florida last month, more than 1,800 attendees were on hand for a program “packed with psychiatric-mental networking, updates, and continuing education targeted to psychiatric-mental health nurses.” Session recordings from the Annual Conferences are made available in the APNA eLearning Center in podcast form, along with up-to-date session slides and other relevant materials.
In Florida last month, more than 1,800 attendees were on hand for a program “packed with psychiatric-mental networking, updates, and continuing education targeted to psychiatric-mental health nurses.” Session recordings from the Annual Conferences are made available in the APNA eLearning Center in podcast form, along with up-to-date session slides and other relevant materials.




























