No Chocolate Milk? Kids Get Used to Plain Milk, UConn Study Finds
/There’s good news and bad news for chocolate milk advocates, depending upon which University of Connecticut research study you come across. The studies don’t necessarily conflict, but provide differing points of view in the plain milk vs. chocolate milk debate. A new study by the Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity at the University of Connecticut has found that most students adjust to drinking plain milk after flavored milk is removed from school lunch menus.
Flavored milk served in the National School Lunch Program contains up to 10 grams of added sugar per serving, which is 40 percent of a child’s daily allowance of added sugar. G iven the nation’s key public health target of limiting added sugars in children’s diets, flavored milk has come under scrutiny in the context of school nutrition, UConn Today recently reported.
iven the nation’s key public health target of limiting added sugars in children’s diets, flavored milk has come under scrutiny in the context of school nutrition, UConn Today recently reported.
The study, published in July in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, measured plain milk selection and consumption in the years after flavored milk was removed in two schools. Key findings include:
- The first school year after flavored milk was removed, 51.5 percent of students selected milk and drank 4 ounces per carton, indicating school-wide per-student consumption of 2.1 ounces.
- Two years later, 72 percent of students selected milk and drank 3.4 ounces per carton, significantly increasing the school-wide per-student consumption to 2.5 ounces.
- Older students and boys consumed significantly more milk.
- The availability of 100 percent fruit juice at lunch was associated with a significant decrease in students selecting milk and lower milk consumption per carton throughout the years of the study. Both years, student selection and consumption of plain milk dropped significantly on days when 100 percent fruit juice was also available.
The study could have implications for school nutrition policy and efforts to reduce added sugars in children’s diets. The study was conducted in two elementary (K-8) schools in an urban New England school district during the 2010-2011 and 2012-2013 school years. Researchers assessed the selection and consumption of milk immediately after flavored milk was removed in the 2010-2011 school year, and two years later in the 2012-2013 school year.
“The decision to remove flavored milk has both nutritional benefits and potential costs. It is clearly an effective way to lower student intake of added sugars at lunch, and over time, the majority of students will switch to plain milk,” said Marlene Schwartz, professor of human development and family studies, director of the UConn Rudd Center, and lead author of the study. “However, there will always be some students who don’t like plain milk. The challenge is finding a way to meet their dietary needs by providing other nutrient-rich options at lunch.”
The study was funded by the Cornell Center for Behavioral Economics in Child Nutrition Programs and the Rudd Foundation. In the conclusion to the study, the researchers note that “A school policy to remove flavored milk has potential public health benefits and costs—it is likely to decrease consumption of added sugars at lunch for all children, but it is also likely to decrease consumption of milk for some children and increase their risk of missing key nutrients.”
Seven years ago, another UConn researcher was touting the virtues of chocolate milk. That study, centered in Professor Nancy R. Rodriguez’s lab, found that drinking a 16-ounce glass of fat-free chocolate milk after exercise gives the body essential proteins and carbohydrates that help refuel weary muscles better than a beverage containing carbohydrates alone.
Rodriguez, with joint appointments in the departments of kinesiology and allied health – and who serves, then and now, as UConn’s director of sports nutrition – advocated for the benefits of milk in relation to athletic performance since the late 1990’s. But the 2010 study believed to be the first study of its kind showing a direct correlation between consuming chocolate milk and improved muscle recovery after prolonged exercise.
Results showed that chocolate milk was as effective as the carbohydrate drink in replenishing the body’s stores of glycogen, a form of carbohydrate the body uses as fuel during intense or prolonged exercise. Rodriguez said at the time that the sugar from the chocolate syrup in the milk helps athletes replace depleted glycogen in their muscles to prepare them for their next workout.
Rodriguez subsequently served on the President’s Council on Fitness, Sports, and Nutrition (PCFSN), 2014-2017. She has been a Sports Nutritionist for the NFL’s Indianapolis Colts and has provided services to the NBA’s Chicago Bulls and Charlotte Bobcats, and the AHL’s Hartford Wolfpack.
The 2010 study was funded by the National Dairy Council and the National Fluid Milk Processor Promotion Board.


 Among adults who admit to not always using safety belts in the back seat, 4 out of 5 surveyed say short trips or traveling by taxi or ride-hailing service are times they don't bother to use the belt. Nearly 40 percent of people surveyed said they sometimes don't buckle up in the rear seat because there is no law requiring it. If there were such a law, 60 percent of respondents said it would convince them to use belts in the back seat. A greater percentage said they would be more likely to buckle up if the driver could get pulled over because someone in the back wasn't buckled.
Among adults who admit to not always using safety belts in the back seat, 4 out of 5 surveyed say short trips or traveling by taxi or ride-hailing service are times they don't bother to use the belt. Nearly 40 percent of people surveyed said they sometimes don't buckle up in the rear seat because there is no law requiring it. If there were such a law, 60 percent of respondents said it would convince them to use belts in the back seat. A greater percentage said they would be more likely to buckle up if the driver could get pulled over because someone in the back wasn't buckled.
 The Governors Highway Safety Association issued a report in 2015, "Unbuckled In Back," analyzing the difference in highway fatalities between states that require rear seat passengers to buckle up and those that do not, the Hartford Courant reported. At a Connecticut legislative hearing that year, the paper noted, state Transportation Commissioner James Redeker said that everyone in a passenger vehicle should buckle up, saying statistics show "people become projectiles because they're not strapped in a safety device."
The Governors Highway Safety Association issued a report in 2015, "Unbuckled In Back," analyzing the difference in highway fatalities between states that require rear seat passengers to buckle up and those that do not, the Hartford Courant reported. At a Connecticut legislative hearing that year, the paper noted, state Transportation Commissioner James Redeker said that everyone in a passenger vehicle should buckle up, saying statistics show "people become projectiles because they're not strapped in a safety device." A pilot partnership between the AGP and CCSU establishes a new base of operations for the
A pilot partnership between the AGP and CCSU establishes a new base of operations for the 
 Márquez-Greene will also work with the School of Education & Professional Studies to establish a Center for Social & Emotional Learning to provide education, training, and research to the campus, community, and state. Other expected collaborations include the training of CCSU undergraduate and graduate students in the Marriage & Family Therapy, Psychology, and Counseling programs in the use of social-emotional curriculum in the classroom.
Márquez-Greene will also work with the School of Education & Professional Studies to establish a Center for Social & Emotional Learning to provide education, training, and research to the campus, community, and state. Other expected collaborations include the training of CCSU undergraduate and graduate students in the Marriage & Family Therapy, Psychology, and Counseling programs in the use of social-emotional curriculum in the classroom.


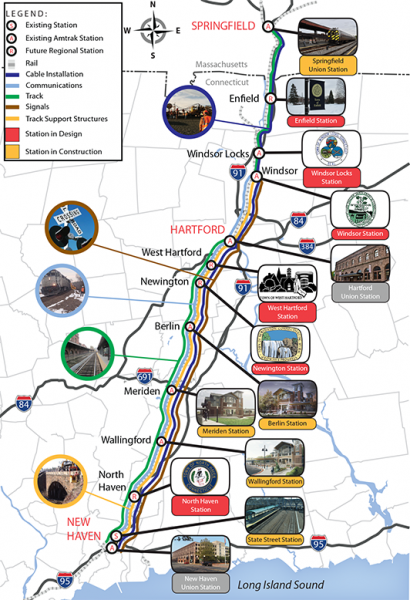 The Hartford Line will act as a regional link with connections to existing rail services, including Metro-North, Shoreline East, and Amtrak Acela high-speed rail services on both the New Haven Line to New York and on the Northeast Corridor to New London and Boston. There will also be direct bus connections to the Bradley Airport Flyer and to CTfastrak. With a heightened level of direct and connecting service linking the region, the hope is that towns along the future Hartford Line will become magnets for growth – ideal places to live and to relocate businesses that depend on regional markets and travel.
The Hartford Line will act as a regional link with connections to existing rail services, including Metro-North, Shoreline East, and Amtrak Acela high-speed rail services on both the New Haven Line to New York and on the Northeast Corridor to New London and Boston. There will also be direct bus connections to the Bradley Airport Flyer and to CTfastrak. With a heightened level of direct and connecting service linking the region, the hope is that towns along the future Hartford Line will become magnets for growth – ideal places to live and to relocate businesses that depend on regional markets and travel. Also, very much a part of the strengthening transportation options with the potential to spur economic development is
Also, very much a part of the strengthening transportation options with the potential to spur economic development is 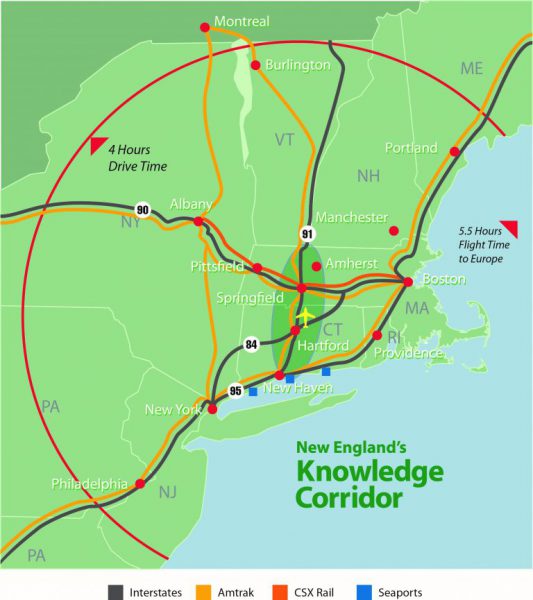
 Program organizers point out that “young children are naturally curious and full of life. Provided a supportive environment, they will joyfully splash, build and smash, pretend, sing, and dance.” While they are having a ton of fun, they are also making sense of the world and learning through exploration, experimentation and social interaction.
Program organizers point out that “young children are naturally curious and full of life. Provided a supportive environment, they will joyfully splash, build and smash, pretend, sing, and dance.” While they are having a ton of fun, they are also making sense of the world and learning through exploration, experimentation and social interaction.

 Manchester’s Supervisor of Student Development, Karen Gray, says it became “obvious how developmentally appropriate it is for children to play, and to have fun, and to smile and to laugh.” As they did, teachers would “see them develop cognitively," although "they are not necessarily aware of the skills that they are actually developing.”
Manchester’s Supervisor of Student Development, Karen Gray, says it became “obvious how developmentally appropriate it is for children to play, and to have fun, and to smile and to laugh.” As they did, teachers would “see them develop cognitively," although "they are not necessarily aware of the skills that they are actually developing.”


 A sweeping mandate for these manufacturers to cover all labor and replacement costs associated with warranty claims would have led to higher prices, they explain, along with weakened consumer protections, and fewer products available to consumers. The legislation would have also required manufacturers to address warranty claims within 30 days’ receipt of a claim – which industry officials say would have been “an unreasonable timeframe” to comply with.
A sweeping mandate for these manufacturers to cover all labor and replacement costs associated with warranty claims would have led to higher prices, they explain, along with weakened consumer protections, and fewer products available to consumers. The legislation would have also required manufacturers to address warranty claims within 30 days’ receipt of a claim – which industry officials say would have been “an unreasonable timeframe” to comply with.
 In Connecticut, April 5, 2017, was the Connecticut SAT School Day administration. SAT scores are used by the Connecticut State Department of Education (CSDE) for school and district accountability purposes, state Education Commissioner Diana Wentzell explained in a
In Connecticut, April 5, 2017, was the Connecticut SAT School Day administration. SAT scores are used by the Connecticut State Department of Education (CSDE) for school and district accountability purposes, state Education Commissioner Diana Wentzell explained in a  Hyman found that, prior to the policy, a substantial number of Michigan’s low-income students didn’t take the ACT even though they would have scored at or above the standard for college readiness. That might been due to financial or logistical barriers, like the cost of the test (between $30 and $50) or difficulties traveling to an exam center on a Saturday. (Both the SAT and ACT offer fee waivers to low-income students, but the study notes that the waivers are underused.)
Hyman found that, prior to the policy, a substantial number of Michigan’s low-income students didn’t take the ACT even though they would have scored at or above the standard for college readiness. That might been due to financial or logistical barriers, like the cost of the test (between $30 and $50) or difficulties traveling to an exam center on a Saturday. (Both the SAT and ACT offer fee waivers to low-income students, but the study notes that the waivers are underused.) search has helped establish the field of quantum computation with solid-state devices. The Connecticut Medal of Science is the state’s highest honor for scientific achievement in fields crucial to Connecticut’s economic competiveness and social well-being.
search has helped establish the field of quantum computation with solid-state devices. The Connecticut Medal of Science is the state’s highest honor for scientific achievement in fields crucial to Connecticut’s economic competiveness and social well-being.




























