Hartford, New Haven Rank 73, 74 Among Best U.S. Cities to Retire
/Even as Hartford and New Haven spend considerable time and attention directed at attracting millennials, a new national survey finds that the two Connecticut cities are ranked in the nation’s top 100 best places to retire. Hartford ranked 73rd on the list with an overall score of 6.35. New Haven came in 74th with a score of 6.33. Among New England cities, only Boston and Springfield scored higher.
U.S. News evaluated the country's 100 largest metropolitan areas based on how well they meet Americans' retirement expectations. Perhaps not surprisingly, three Florida cities placed in the top 10. It was Lancaster, Pennsylvania, that earned the No. 1 on the 2019 list. According to U.S. News, Lancaster moved to the No. 1 spot after placing No. 2 last year thanks to increases in housing affordability and overall happiness of its residents.
Fort Myers, Florida, moved from No. 15 to No. 2, driven by "increases in desirability and happiness scores." Last year's top place to retire — Sarasota, Florida — fell to No. 3 because of a decline in overall happiness and desirability, U.S. News reported.
Of Hartford, U.S. News said “Don't let the historic architecture fool you – even as one of the oldest metro areas in America, Hartford, Connecticut, has a lot to offer, both old and new.” The Capitol City scored 5.3 in Housing Affordability and 8.5 in Healthcare, the two  components of the overall score.
components of the overall score.
New Haven is described as “home to one of the most walkable city centers between New York City and Boston,” with “centuries-old architecture” which “houses the galleries, concert venues and coffee shops that help make New Haven the cultural capital of Connecticut.” New Haven earned a 5.2 in Housing Affordability and 8.8 in Healthcare.
The top ranked New England city was Boston at #25. Springfield, MA ranked #69, Worcester was #77, and Providence was #85. New York’s state capitol, Albany, ranked #61.
The top 10 places to retire, according to U.S. News, are: Lancaster; Fort Myers; Sarasota; Austin; Pittsburgh; Grand Rapids; Nashville; San Antonio; Dallas-Fort Worth; and Lakeland, Florida.
The rankings, according to U.S. News, “offer a comprehensive evaluation of the country's 100 largest metropolitan areas based on how well they meet Americans' expectations for retirement, with measures including housing affordability, desirability, health care and overall happiness.” Data sources include the U.S. Census Bureau and the Bureau of Labor Statistics, as well as U.S. News rankings of the Best Hospitals.



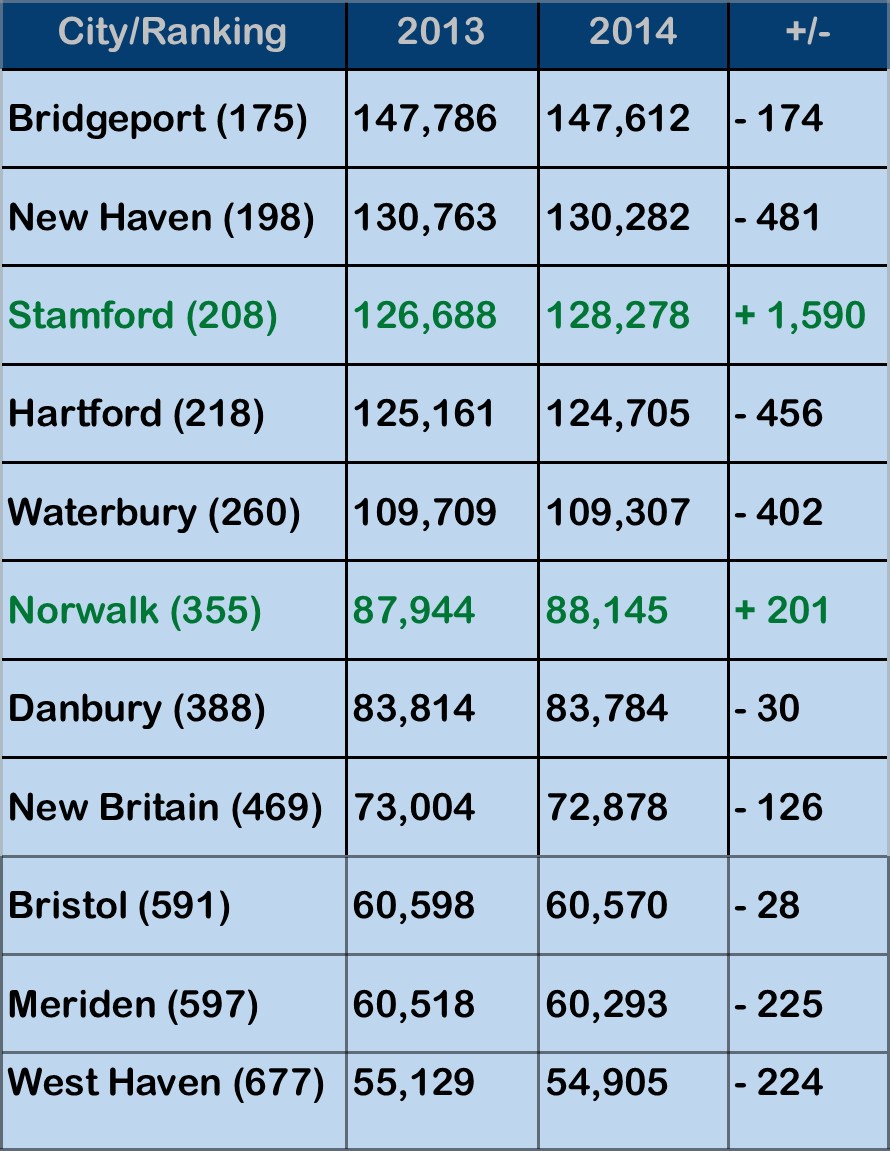 Over the past four years, population also grew in Hartford, New Haven, Stamford, Danbury and Norwalk, but declined in some of the state’s other large municipalities, including Waterbury, New Britain, Meriden and West Haven.
Over the past four years, population also grew in Hartford, New Haven, Stamford, Danbury and Norwalk, but declined in some of the state’s other large municipalities, including Waterbury, New Britain, Meriden and West Haven. wed the gap between the two cities to 2,004. Just four years ago, the population differential was 7,075. Stamford passed Hartford to rank as the state’s third largest city three years ago.
wed the gap between the two cities to 2,004. Just four years ago, the population differential was 7,075. Stamford passed Hartford to rank as the state’s third largest city three years ago.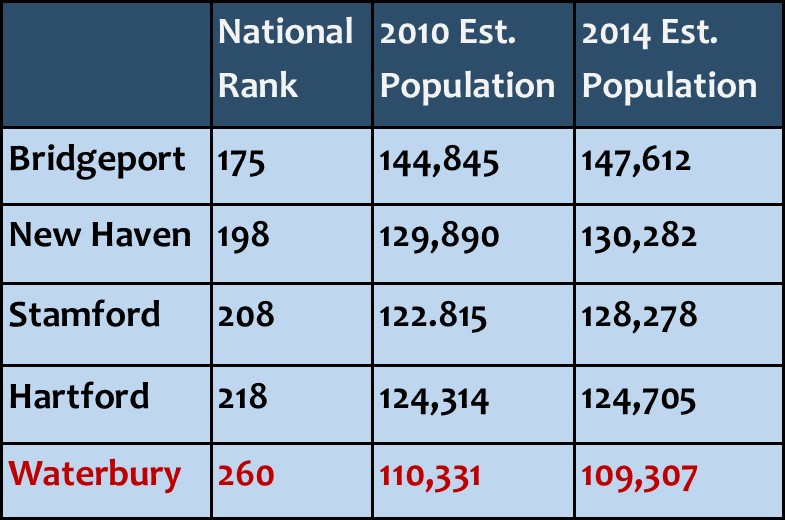 according to the census data, while Bristol (number 591) saw a slight uptick of just under 100 residents, from 60,477 to a 60,570. Meriden (number 597) saw population slip from 60,868 to 60,293. West Haven, the 677th most populous city in the nation, also experienced a drop in populations, from 55,565 to 54,905.
according to the census data, while Bristol (number 591) saw a slight uptick of just under 100 residents, from 60,477 to a 60,570. Meriden (number 597) saw population slip from 60,868 to 60,293. West Haven, the 677th most populous city in the nation, also experienced a drop in populations, from 55,565 to 54,905. sbury in 2013 and 2011, and Cheshire in 2013 and 2011. Single appearances were made by Norwalk, Stamford, Portland, Tolland, Greenwich, South Windsor, Fairfield, and most recently, Brookfield.
sbury in 2013 and 2011, and Cheshire in 2013 and 2011. Single appearances were made by Norwalk, Stamford, Portland, Tolland, Greenwich, South Windsor, Fairfield, and most recently, Brookfield. Hartford at #55. The town was joined by Stamford at #78, Hamden at #87, and Norwalk at #90.
Hartford at #55. The town was joined by Stamford at #78, Hamden at #87, and Norwalk at #90.