Longstanding Coverage of State Government to End; Drastic Reduction in Funding, Imposition of Content Limitations Cited
/CT-N, which has provided coverage of State Senate and House sessions and all three branches of state government for nearly two decades, will cease operations on Friday, November 3, due to severe budget cuts and limitations on coverage being imposed by the legislature on the network’s operator, the Connecticut Public Affairs Network (CPAN).
CPAN has operated the network, under a series of contracts with the legislature’s Joint Committee on Legislative Management (OLM), since March, 1999, and was among the first in the nation to provide comprehensive coverage of state government.
“CPAN was created with a nonpartisan, educational mission to run CT-N as a three- branches network, at arm’s length from the government,” CPAN Executive Director Paul Giguere wrote in a letter notifying the non-partisan OLM that CPAN would be ending coverage. “It was a mission and purpose once supported by the Leadership of the General Assembly. Even the state statute governing CT-N’s revenue intercept refers broadly to coverage of ‘state government deliberations and public policy events.’ The thinking has clearly changed.”
At least one of those contracts, covering November 2003 - October 2006, clearly delineates that CPAN’s operation of CT-N would provide coverage of “the legislature, events of public interest in the Executive and Judicial Branches and other events of statewide interest.” That contract also indicates that “many of the executive branch events to be covered will be taking place at locations away from the Capitol Complex.” A subsequent contract, which ran through last year, also stated that “CPAN retains full editorial discretion regarding day-to-day programming.” CT-N broadcasts seven days a week, 24 hours a day.
 CPAN’s most recent contact expired in September, was extended through October, and was on a day-by-day basis this week. The 33-person staff worked with an annual operating budget that was unexpectedly reduced by 65 percent in the budget approved by the legislature this week for the current fiscal year. At the same time, the legislature sought reductions in coverage of state government outside the State Capitol, limitations on editorial content decisions, and cutbacks on public affairs programming. Those changes, which were revealed in the RFP for a new five-year in April, drew sharp criticism at that time, which were renewed this week.
CPAN’s most recent contact expired in September, was extended through October, and was on a day-by-day basis this week. The 33-person staff worked with an annual operating budget that was unexpectedly reduced by 65 percent in the budget approved by the legislature this week for the current fiscal year. At the same time, the legislature sought reductions in coverage of state government outside the State Capitol, limitations on editorial content decisions, and cutbacks on public affairs programming. Those changes, which were revealed in the RFP for a new five-year in April, drew sharp criticism at that time, which were renewed this week.
“For some time now, we have contended with encroachments on our editorial independence, despite our best efforts to be responsive to concerns while continually working to improve the CT-N service and over-delivering on every contract we have ever signed,” Giguere wrote.
The National Alliance of Public Affairs Networks (NAPAN), points out that while many variations exist in programming and operating models among state public affairs networks, a series of “Best Practices” can be drawn from “the most effective strategies used by highly regarded networks across the country.”
NAPAN points out that “citizens’ trust in all three branches of government is at all-time lows,” and “while the judicial, executive and legislative branches actively operate in states daily, the understanding of what and how decisions are being made at the highest levels go largely unreported and consequently unnoticed by the general public.” CT-N coverage was available on television and on-line, both live and in archives that are easily accessible to the public. CPAN also has provided educational materials for classroom teachers and the general public.
In his letter, Giguere, who brought the concept for such a network to the Connecticut legislature in the 1990’s and led its launch and development, said “the scope at which we would be obliged to operate CT-N would cease to provide any meaningful level of transparency: even less so, if the few coverage decisions we would have the opportunity to make were controlled by the CGA (Connecticut General Assembly) to the extent that recent events convince us they would be.” He continued: “at best, CT-N would provide the façade of transparency, cloaked – at least temporarily – in the credibility and reputation that CPAN has spent 18 years building. We will not abet that course of action by the CGA by participating in it.”
In recent days, CT-N has provided coverage of Gov. Malloy’s news conference announcing he had signed the state budget into law, a news briefing on state infrastructure and resiliency improvements since Super Storm Sandy, meetings of the Connecticut Board of Firearms Permit Examiners and the Governor’s Nonprofit Health & Human Services Cabinet, and a hearing by the legislature’s Judiciary Committee considering nominations of individuals to serve on the State Supreme Court and Appellate Court.
Earlier this year, Danbury State Rep. Bob Godfrey cited the role of CT-N in providing the public with access to government, noting that "The General Assembly itself has provided more public access to lawmaking through both our web site (www.cga.ct.gov) and the Connecticut Television Network (CT-N, at www.ct-n.com)."
-----
Five best practices for state public affairs networks are described on the NAPAN website:
1. Accessible to All: 24/7 programs on a dedicated channel across multiple platforms
A state public affairs network is most effective in connecting citizens to state government when it is available full-time to the maximum number of citizens possible, including a robust online presence with strong searchable streaming and on-demand content, accessibility enhancements such as closed captioning for the hearing impaired and a permanent archive of programming produced.
2. All Three Branches of State Government
A state public affairs network is most effective in connecting citizens to state government when it provides a nonpartisan, unbiased and unfiltered window on all official state business.
3. Operating at Arm’s Length
A state public affairs network is most effective in connecting citizens to state government when it is structured with an independent governing body using a set of agreed-upon operating guidelines to make programming and operational decisions free from political influence.
4. Citizen Engagement
A state public affairs network is most effective in connecting citizens to state government when it seeks to demystify the process of governing by providing additional information and context through on-screen graphics, online reference materials and links to other resources.
5. Programming Breadth
A state public affairs network is most effective in connecting citizens to state government when it provides a broad range of high-quality public affairs programming beyond gavel to gavel coverage of government proceedings, as well as official emergency information from appropriate state public safety agencies.


 Among the panelists will be former Senate President Pro Tempore Don Williams, former House Speaker James Amann, former Senate Minority Leader John McKinney, and former House Minority leader Lawrence Cafero. They will be joined by former House member Tim O’Brien, who served on the Government Administration and elections Committee, and Senate Co-Chair of that committee, Sen. Michael McLachlan.
Among the panelists will be former Senate President Pro Tempore Don Williams, former House Speaker James Amann, former Senate Minority Leader John McKinney, and former House Minority leader Lawrence Cafero. They will be joined by former House member Tim O’Brien, who served on the Government Administration and elections Committee, and Senate Co-Chair of that committee, Sen. Michael McLachlan. A week ago, in an op-ed
A week ago, in an op-ed  Flynn added that the law, passed in 2005, “allows candidates and officeholders to look out for the interests of all their constituents rather than being consumed with the needs of their major campaign contributors. It gives talented, motivated citizens who've never had the money or the connections traditionally required for success in politics a chance to seek and win public office with neither big money nor connections. Now, nearly 80 percent of all candidates for legislative and state offices use the program.” Qualifying candidates must raise $5,000 to $250,000 — depending whether they are seeking a statewide office or legislative seat — in $100 increments or less in order to receive a grant of public funds from the CEP.
Flynn added that the law, passed in 2005, “allows candidates and officeholders to look out for the interests of all their constituents rather than being consumed with the needs of their major campaign contributors. It gives talented, motivated citizens who've never had the money or the connections traditionally required for success in politics a chance to seek and win public office with neither big money nor connections. Now, nearly 80 percent of all candidates for legislative and state offices use the program.” Qualifying candidates must raise $5,000 to $250,000 — depending whether they are seeking a statewide office or legislative seat — in $100 increments or less in order to receive a grant of public funds from the CEP.

 t Hartford also looks forward to entering.
t Hartford also looks forward to entering.
 District teams identify one exemplary teacher from within their teaching populations. Each district nominee completes the state application in the ensuing months and submits it to the State Department of Education. Applications are distributed to members of a reading committee, and the results are tabulated to identify approximately fifteen semi-finalists.
District teams identify one exemplary teacher from within their teaching populations. Each district nominee completes the state application in the ensuing months and submits it to the State Department of Education. Applications are distributed to members of a reading committee, and the results are tabulated to identify approximately fifteen semi-finalists.



 The U.S. Census Bureau’s
The U.S. Census Bureau’s  ensus officials are necessary to obtain more accurate population and demographic counts. If those visits are reduced in order to cut costs, the accuracy of the census itself is likely to diminish, observers say. Connecticut, which does not have independent counts of its entire population, depends heavily on data derived from the U.S. Census for a host of policy and funding decisions.
ensus officials are necessary to obtain more accurate population and demographic counts. If those visits are reduced in order to cut costs, the accuracy of the census itself is likely to diminish, observers say. Connecticut, which does not have independent counts of its entire population, depends heavily on data derived from the U.S. Census for a host of policy and funding decisions.


 Orders. Most historians agree the Fundamental Orders are significant, but the state of Connecticut decided in 1959 to call itself the Constitution State based on the premise that the Fundamental Orders were the first constitution in North America.
Orders. Most historians agree the Fundamental Orders are significant, but the state of Connecticut decided in 1959 to call itself the Constitution State based on the premise that the Fundamental Orders were the first constitution in North America.




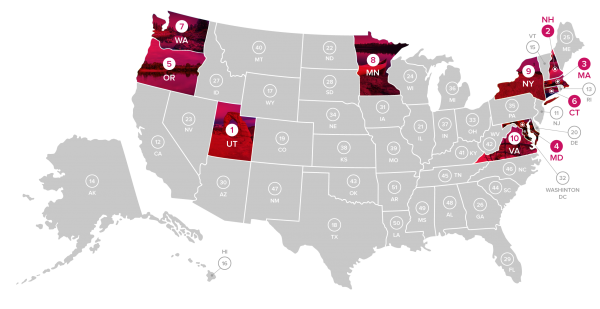
 The analysis points out that a main reason why people don’t have access to broadband internet is due to a lack of income. Cited is a Pew Research poll that found 23 percent of people making under $30,000 per year don’t use the internet, possibly because of the high price for something they don’t consider a basic need. Most rural schools across the country still lack access to fiber and pay more than twice as much for bandwidth.
The analysis points out that a main reason why people don’t have access to broadband internet is due to a lack of income. Cited is a Pew Research poll that found 23 percent of people making under $30,000 per year don’t use the internet, possibly because of the high price for something they don’t consider a basic need. Most rural schools across the country still lack access to fiber and pay more than twice as much for bandwidth.




























