CT Ranks 10th in Percentage of Structurally Deficient, Functionally Obsolete Bridges
/Of Connecticut’s 4,225 bridges, 357 are structurally deficient (8.4%) and another 1,087 are functionally obsolete. That’s 34 percent of the state’s bridges deemed deficient by experts – and it ranks Connecticut as the 10th worst state in the nation, by percentage.
Worse than Connecticut? Only Rhode Island, Massachusetts, Hawaii, Pennsylvania, Alaska, New York, West Virginia, New Jersey and Maine. The data, compiled by the Federal Highway Administration of the U.S. Department of Transportation, reflects information and analysis through December 31, 2015. 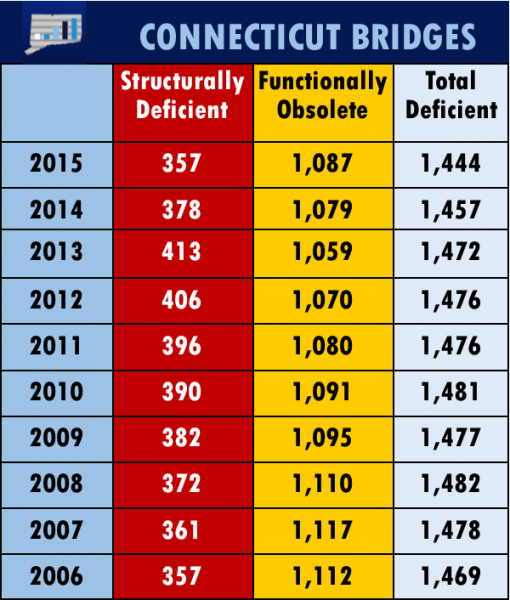
While the number of structurally deficient bridges in Connecticut is the lowest since 2006, the number of functionally obsolete structures has climbed in recent years, and is now the highest since 2010. The total number of bridges in the two categories has dropped in each of the past three years, but remains at about one-third of the state’s bridges. Connecticut ranks 26th in the percentage of structurally deficient bridges.
According to the Nation Bridge Inventory Database website, Structurally Deficient is a status used to describe a bridge that has one or more structural defects that require attention. This status does not indicate the severity of the defect but rather that a defect is present. Conditions driving the designation could include the bridge deck, the superstructure or the substructure of the bridge.
The sufficiency rating is calculated per a formula defined by the Federal Highway Administration, which places 55 percent value on the structural condition of the bridge, 30 percent on its serviceability and obsolescence, and 15 percent on its essentiality to public use. According to the Iowa Department of Transportation, “a structurally deficient bridge, when left open to traffic, typically requires significant maintenance and repair to remain in service and eventual rehabilitation or replacement to address deficiencies.”
The category Functionally Obsolete is a status used to describe a bridge that is no longer by design functionally adequate for its task. Reasons for this status include that the bridge doesn't have enough lanes to accommodate the traffic flow, it may be a drawbridge on a congested highway, or it may not have space for emergency shoulders, according to the National Bridge Inven tory Database. Functionally Obsolete does not communicate anything of a structural nature – it may be perfectly safe and structurally sound, but may be the source of traffic jams or may not have a high enough clearance to allow an oversized vehicle.
tory Database. Functionally Obsolete does not communicate anything of a structural nature – it may be perfectly safe and structurally sound, but may be the source of traffic jams or may not have a high enough clearance to allow an oversized vehicle.
A year ago, Connecticut has 378 structurally deficient bridges and 1,079 considered functionally obsolete. Two years ago, 413 bridges were defined as structurally deficient and 1,059 were listed as functionally obsolete.
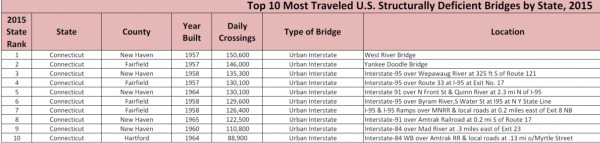
A January 2016 report by the American Road & Transportation Builders Association compiled the most traveled U.S. Structurally Deficient Bridges, and identified the West River Bridge in New Haven, built in 1957, ranked as the 98th most travelled structurally deficient in the nation. At number 110 on the list was the Yankee Doodle Bridge in Fairfield, also constructed in 1957. At number 148 was the I-95 bridge over the Wepawaug River, south of Route 121 in New Haven, built in 1958.
Also ranking in the nation’s top 200 most travelled structurally deficient bridges were the I-95 bridge in Fairfield over Route 33 at Exit 17 (ranked number 159), the I-91 Bridge over North Front Street and Quinn River in New Haven just north of I-95 (number 160), and the I-95 bridge over Byram River in Fairfield (number 161). Those bridges were built in 1957, 1964 and 1958, respectively.




 With the gun debate center-stage in the presidential primaries and in Washington, D.C., the website WalletHub analyzed which states depend most on the arms and ammunitions industry both directly for jobs and political contributions and indirectly through firearm ownership. WalletHub’s analysts compared the 50 states and the District of Columbia across three key dimensions: 1) Firearms Industry, 2) Gun Prevalence and 3) Gun Politics and eight metrics.
With the gun debate center-stage in the presidential primaries and in Washington, D.C., the website WalletHub analyzed which states depend most on the arms and ammunitions industry both directly for jobs and political contributions and indirectly through firearm ownership. WalletHub’s analysts compared the 50 states and the District of Columbia across three key dimensions: 1) Firearms Industry, 2) Gun Prevalence and 3) Gun Politics and eight metrics.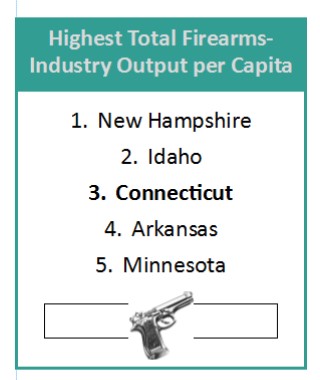


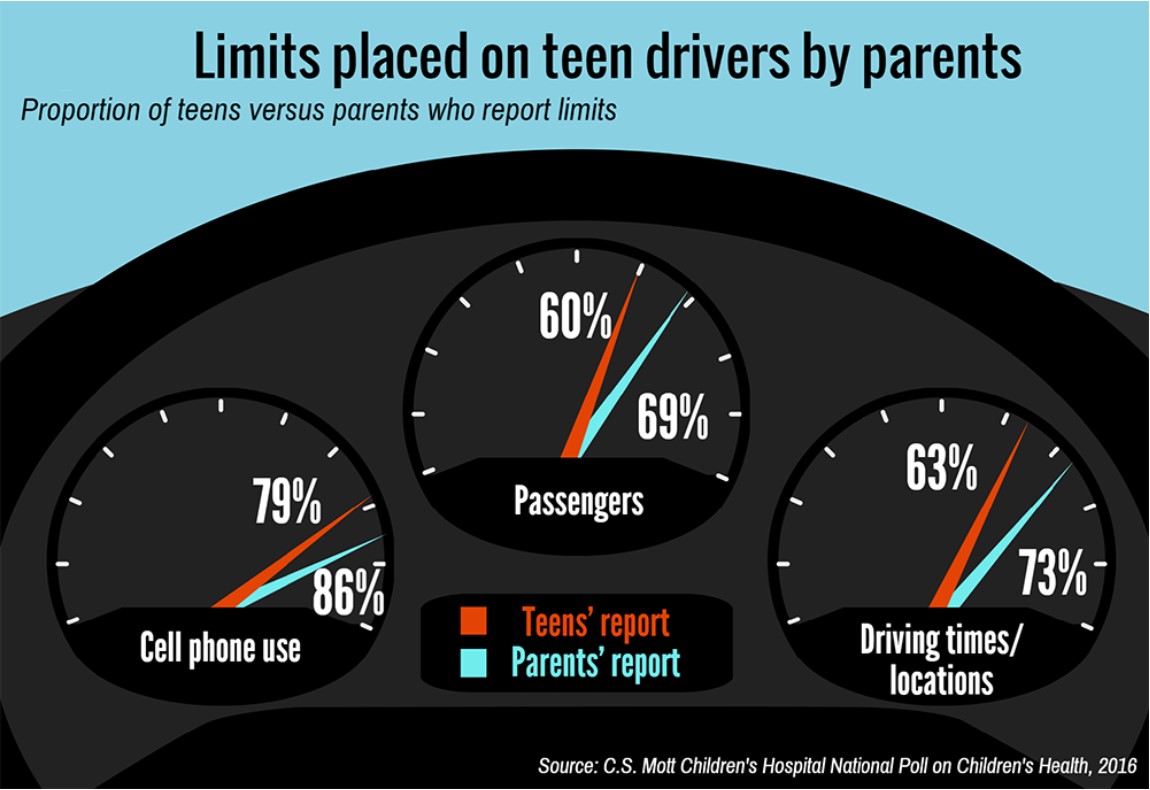
 hat their children will struggle with anxiety or depression.
hat their children will struggle with anxiety or depression.

 dgun or revolver, and $25 gift card for a shotgun or rifle. Although held in Hartford and focused on the capital region, the buyback is open to all state residents.
dgun or revolver, and $25 gift card for a shotgun or rifle. Although held in Hartford and focused on the capital region, the buyback is open to all state residents. Hartford police also conducted a gun buyback program in
Hartford police also conducted a gun buyback program in 



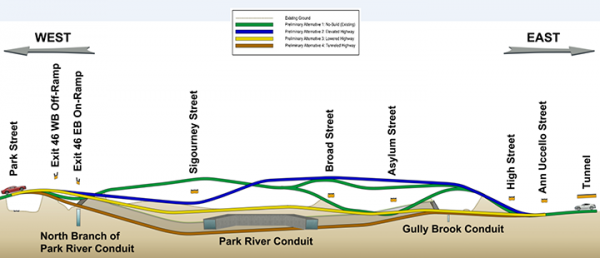 The work, which has yet to be funded, is likely to include moving or eliminating some exits and entrances – and possibly adding others in new locations - to improve traffic flow. Cost estimates range from $4 billion to $12 billion, depending on the option selected. Upcoming public meetings are to be held in East Hartford on Dec. 2 and Hartford on Dec. 10.
The work, which has yet to be funded, is likely to include moving or eliminating some exits and entrances – and possibly adding others in new locations - to improve traffic flow. Cost estimates range from $4 billion to $12 billion, depending on the option selected. Upcoming public meetings are to be held in East Hartford on Dec. 2 and Hartford on Dec. 10.


 Instead,
Instead,  l bus injuries in the U.S. every year — two to three times National Highway Traffic Safety Administration estimates, which use only a sampling of data and exclude field trips like the one on which Vikas Parikh died. Seat belts work best in rollover and side-impact collisions in which students are thrown out of their seats, as Vikas was. The American Academy of Pediatrics supports restraints on buses.”
l bus injuries in the U.S. every year — two to three times National Highway Traffic Safety Administration estimates, which use only a sampling of data and exclude field trips like the one on which Vikas Parikh died. Seat belts work best in rollover and side-impact collisions in which students are thrown out of their seats, as Vikas was. The American Academy of Pediatrics supports restraints on buses.” Marking the launch of the new Share the Road campaign, this year's featured speaker is Colleen Kelly Alexander. Bike Walk Connecticut officials describe her remarkable story: After undergoing brain surgery in 2007 for a chiari malformation, Colleen overcame a lupus and cryoglobulinemia diagnosis in 2009, pushing forward to become a successful, competitive triathlete. In 2011, while on a routine bike ride, she was run over by a freight truck. Crushed, ripped apart and bleeding out, she flatlined twice, spent five weeks in a coma and has since endured over twenty surgeries. Defying diagnoses, dire predictions and death, Colleen stunned doctors by bucking the odds and coming back to run more than 50 races and complete 15 triathlons, including 4 half Ironman events since her trauma. Colleen and husband Sean Alexander were elected to the Bike Walk Connecticut board of directors in 2015.
Marking the launch of the new Share the Road campaign, this year's featured speaker is Colleen Kelly Alexander. Bike Walk Connecticut officials describe her remarkable story: After undergoing brain surgery in 2007 for a chiari malformation, Colleen overcame a lupus and cryoglobulinemia diagnosis in 2009, pushing forward to become a successful, competitive triathlete. In 2011, while on a routine bike ride, she was run over by a freight truck. Crushed, ripped apart and bleeding out, she flatlined twice, spent five weeks in a coma and has since endured over twenty surgeries. Defying diagnoses, dire predictions and death, Colleen stunned doctors by bucking the odds and coming back to run more than 50 races and complete 15 triathlons, including 4 half Ironman events since her trauma. Colleen and husband Sean Alexander were elected to the Bike Walk Connecticut board of directors in 2015. 
 lnerable User Law Mandates $1000 Fine. Connecticut requires a fine of up to $1000 on drivers who cause the death or serious injury of a pedestrian, cyclist or other vulnerable road user who used reasonable care.
lnerable User Law Mandates $1000 Fine. Connecticut requires a fine of up to $1000 on drivers who cause the death or serious injury of a pedestrian, cyclist or other vulnerable road user who used reasonable care. For Pedestrians:
For Pedestrians:


























