Increased Municipal Burden, Disproportionate Impact on Low-Income Drivers Among Possible Effects of Highway Tolls, Report Finds
/If Connecticut opts to introduce a system of tolls on the state’s roads to help fund a significant expansion of transportation infrastructure projects in the years ahead, the toll system instituted could run the risk of causing an increased use of local roadways that “could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities,” and lower income residents in the state could be faced with “a higher burden relative to their incomes than wealthier Connecticut residents.”
Those warnings to policy makers are included in an Issue Brief by Inform CT that reviews the various tolling options and respective challenges posed. Connecticut eliminated tolls more than 30 years ago in the aftermath of a horrific accident at the Stratford toll plaza, and state leaders have been in a “perpetual debate about whether to reinstate them ever since,” the paper points out.
With overhauling the state’s transportation system is a leading element in Governor Malloy’s agenda to boost the state’s economy, renewed attention is being paid to methods of generating sufficient revenue to support those initiatives, and to issues raised in the 2015 policy brief. Spurred by advances in technology, the possibility of imposing a system of electronic tolls, such as those in use in other states, are among the considerations, with border tolling, distance tolling and congestion pricing among the options.
 The issue brief indicated that a disadvantage of a distance toll system on all limited access highways in Connecticut would be that it “could create an incentive for people to use alternative roadways. The increased use of these roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.” The advantage would be that distance tolls “could help to more efficiently allocate the cost of these roadways to drivers who use them the most.”
The issue brief indicated that a disadvantage of a distance toll system on all limited access highways in Connecticut would be that it “could create an incentive for people to use alternative roadways. The increased use of these roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.” The advantage would be that distance tolls “could help to more efficiently allocate the cost of these roadways to drivers who use them the most.”
In analyzing the potential impact of tolls placed at Connecticut’s borders, the policy paper notes that while such an approach would “help to ensure that out-of-state residents driving through Connecticut pay for their use of Connecticut’s roadways,” border tolls “place a disproportionate burden on residents of Connecticut who commute out-of-state to work. This burden is further amplified if we believe that, on average, these out-of-state commuters use a smaller share of the roadways than their in-state commuting counterparts.”
 Congestion pricing, which provides for higher toll charges at peak traffic times, “helps to limit traffic on major roadways and create an incentive for people to use more environmentally friendly forms of public transportation,” the policy paper indicates. However, a congestion pricing system “could polarize roadway use by displacing low income commuters during peak driving hours. Congestion pricing could also create displacement effects whereby the increased use of local roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.”
Congestion pricing, which provides for higher toll charges at peak traffic times, “helps to limit traffic on major roadways and create an incentive for people to use more environmentally friendly forms of public transportation,” the policy paper indicates. However, a congestion pricing system “could polarize roadway use by displacing low income commuters during peak driving hours. Congestion pricing could also create displacement effects whereby the increased use of local roadways could shift the burden of maintenance and congestion to municipalities.”
The report suggests that “congestion pricing and distance tolls could become more affordable for low income residents if electronic payment systems were implemented that allow for income-based rate reductions.”
Earlier this year, a study panel recommended installing tolls and raising taxes in order to pay for Malloy's 30-year, $100 billion transportation program. Legislators have said that any decision on the imposition of tolls is at least a year away, as attention focuses during the current session on establishing a method to assure that money allocated to transportation is not redirected to other areas of government.
The issue brief also stress that “a key consideration when trying to outweigh the benefits and costs of implementing tolling in Connecticut is how the revenue from the tax will be redistributed to the residents of the state.” It goes on to highlight that “as the bill stands, the monies raised would go into the Special Transportation Fund but allocation of the monies from there is not specified. The allocation of these funds is an important discussion that needs to take place before the impact of the legislation can be considered in earnest.”
InformCT is a public-private partnership that currently includes staff from the Connecticut Economic Resource Center and the Connecticut Data Collaborative. The mission of InformCT is to provide independent, non-partisan research, analysis, and public outreach focused on issues in Connecticut, and to act as the convener for fact-based dialogue and action.


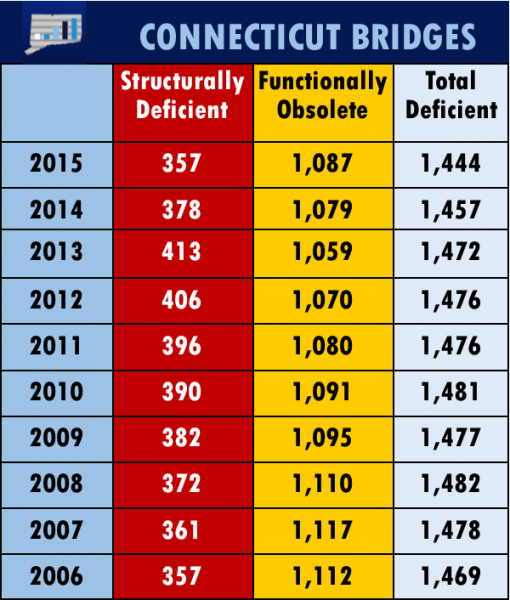
 tory Database. Functionally Obsolete does not communicate anything of a structural nature – it may be perfectly safe and structurally sound, but may be the source of traffic jams or may not have a high enough clearance to allow an oversized vehicle.
tory Database. Functionally Obsolete does not communicate anything of a structural nature – it may be perfectly safe and structurally sound, but may be the source of traffic jams or may not have a high enough clearance to allow an oversized vehicle.
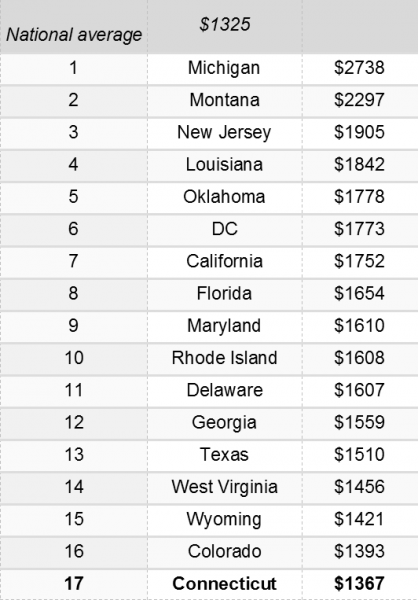
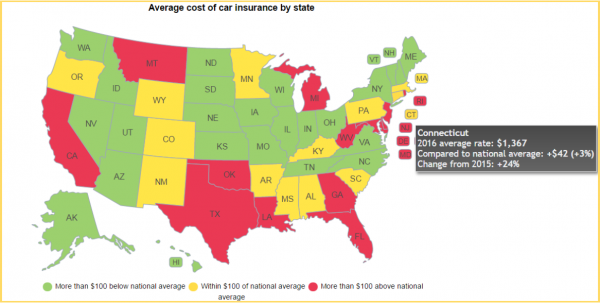 The national average for a full-coverage policy as featured in the Insure.com report came in at $1,325 this year – a slight increase from last year’s average of $1,311. Rates varied from a low of $808 a year in Maine to a budget-busting $2,738 in Michigan. Insurance rates in Michigan are more than double (107 percent) the national average.
The national average for a full-coverage policy as featured in the Insure.com report came in at $1,325 this year – a slight increase from last year’s average of $1,311. Rates varied from a low of $808 a year in Maine to a budget-busting $2,738 in Michigan. Insurance rates in Michigan are more than double (107 percent) the national average.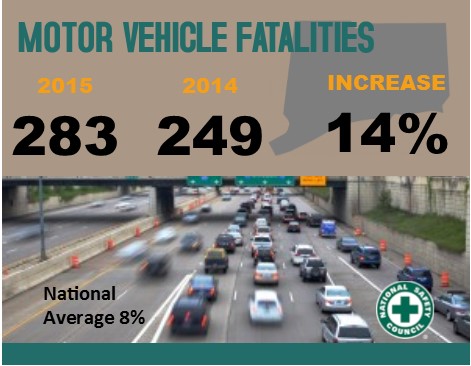 Nationally, 2015 saw the largest single-year percent increase in motor vehicle deaths since 1966. Estimates from the National Safety Council (NSC) show an 8 percent increase in 2015 compared with 2014 – with substantial changes in some states, including Connecticut. There were 283 motor-vehicle related deaths in Connecticut last year, compared with 249 in 2014 and 276 in 2013.
Nationally, 2015 saw the largest single-year percent increase in motor vehicle deaths since 1966. Estimates from the National Safety Council (NSC) show an 8 percent increase in 2015 compared with 2014 – with substantial changes in some states, including Connecticut. There were 283 motor-vehicle related deaths in Connecticut last year, compared with 249 in 2014 and 276 in 2013.
 safety, the National Safety Council recommends drivers:
safety, the National Safety Council recommends drivers:
 The OLR report also indicates that a Federal Highway Administration pilot program permits up to three states to toll existing Interstate highways that they could not otherwise adequately maintain or improve, and increase funding available for public transportation initiatives. In addition, $2.6 billion is provided to Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor (and $5.4 billion to other Amtrak lines) over five years. It separates the Northeast Corridor, from Boston to Washington, D.C, from other Amtrak accounts to ensure that the amounts assigned to that Corridor are used there, OLR reports.
The OLR report also indicates that a Federal Highway Administration pilot program permits up to three states to toll existing Interstate highways that they could not otherwise adequately maintain or improve, and increase funding available for public transportation initiatives. In addition, $2.6 billion is provided to Amtrak’s Northeast Corridor (and $5.4 billion to other Amtrak lines) over five years. It separates the Northeast Corridor, from Boston to Washington, D.C, from other Amtrak accounts to ensure that the amounts assigned to that Corridor are used there, OLR reports.






 locations in the United States to offer Aer Lingus flights to Ireland. The daily service will include one evening departure from Bradley and one afternoon departure from Dublin. Published
locations in the United States to offer Aer Lingus flights to Ireland. The daily service will include one evening departure from Bradley and one afternoon departure from Dublin. Published  The demolition of the half-century old Terminal B is
The demolition of the half-century old Terminal B is 

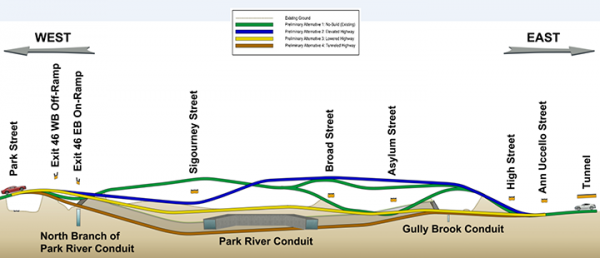 The work, which has yet to be funded, is likely to include moving or eliminating some exits and entrances – and possibly adding others in new locations - to improve traffic flow. Cost estimates range from $4 billion to $12 billion, depending on the option selected. Upcoming public meetings are to be held in East Hartford on Dec. 2 and Hartford on Dec. 10.
The work, which has yet to be funded, is likely to include moving or eliminating some exits and entrances – and possibly adding others in new locations - to improve traffic flow. Cost estimates range from $4 billion to $12 billion, depending on the option selected. Upcoming public meetings are to be held in East Hartford on Dec. 2 and Hartford on Dec. 10.
 Marking the launch of the new Share the Road campaign, this year's featured speaker is Colleen Kelly Alexander. Bike Walk Connecticut officials describe her remarkable story: After undergoing brain surgery in 2007 for a chiari malformation, Colleen overcame a lupus and cryoglobulinemia diagnosis in 2009, pushing forward to become a successful, competitive triathlete. In 2011, while on a routine bike ride, she was run over by a freight truck. Crushed, ripped apart and bleeding out, she flatlined twice, spent five weeks in a coma and has since endured over twenty surgeries. Defying diagnoses, dire predictions and death, Colleen stunned doctors by bucking the odds and coming back to run more than 50 races and complete 15 triathlons, including 4 half Ironman events since her trauma. Colleen and husband Sean Alexander were elected to the Bike Walk Connecticut board of directors in 2015.
Marking the launch of the new Share the Road campaign, this year's featured speaker is Colleen Kelly Alexander. Bike Walk Connecticut officials describe her remarkable story: After undergoing brain surgery in 2007 for a chiari malformation, Colleen overcame a lupus and cryoglobulinemia diagnosis in 2009, pushing forward to become a successful, competitive triathlete. In 2011, while on a routine bike ride, she was run over by a freight truck. Crushed, ripped apart and bleeding out, she flatlined twice, spent five weeks in a coma and has since endured over twenty surgeries. Defying diagnoses, dire predictions and death, Colleen stunned doctors by bucking the odds and coming back to run more than 50 races and complete 15 triathlons, including 4 half Ironman events since her trauma. Colleen and husband Sean Alexander were elected to the Bike Walk Connecticut board of directors in 2015. 
 lnerable User Law Mandates $1000 Fine. Connecticut requires a fine of up to $1000 on drivers who cause the death or serious injury of a pedestrian, cyclist or other vulnerable road user who used reasonable care.
lnerable User Law Mandates $1000 Fine. Connecticut requires a fine of up to $1000 on drivers who cause the death or serious injury of a pedestrian, cyclist or other vulnerable road user who used reasonable care. For Pedestrians:
For Pedestrians:


























