UConn Adds Major in Arabic and Islamic Civilizations; Southern Expands Drone Applications to Academic Minor
/If you’re wondering about the degree to which Connecticut universities are keeping up with world trends, the University of Connecticut and Southern Connecticut State University seem to indicate the answer is yes. UConn has approved a new major in Arabic and Islamic civilizations, developed to equip students with a working knowledge of the Arabic language, and allow them to explore classical Islamic civilizations, as well as the literature, culture, heritage, and intellectual life of the modern Arab world.
The program, housed in the Department of Literatures, Cultures, and Languages in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, stresses the many different aspects of the Arab world, and the different linguistic, cultural, and religious traditions that shaped it.
At Southern, a new interdisciplinary minor in Drone Applications has a decidedly journalistic flavor, but extends to provide a basis for careers utilizing the rapidly unfolding drone technology.
Approved by the UConn Board of Trustees this summer, the Arabic and Islamic civilizations major appeals to students who are studying in many other areas, including the sciences. Some students are native speakers of Arabic or have a Muslim background; others are not sure what it means to be “Arab” or to be “Muslim,” and so come to learn, according to program director and assistant professor of literatures, cultures, and languages Nicola Carpentieri, who spoke recently with UConn Today.
UConn is unusual in offering such a robust program in the language. “The program is unique in the U.S. in that we delve so much into Arabic literature, poetics, and other cultural aspects such as music, science, art, and architecture,” Carpentieri noted. “That’s what sets it apart.”
“Students in our classes come from all majors, but they are curious and motivated students,” Carpentieri said. “They may have seen bad press about the Arab world. But they’re open-minded, and aware that simplistic divisions are fabrications. We want to shatter the binaries of East and West.”
Students in the program take courses in both classical Arabic, or the formal version of the language used in education and literature, and other dialects, like Media Arabic and Levantine Arabic. It’s especially useful to learn these types of “street language,” Carpentieri points out.
Unlike most other languages, Arabic gives its speakers access to many different nations and cultures, including Egypt, Lebanon, Morocco, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, and others. In addition, students in the major will learn about the many influences that Muslim conquests had on the Europe we know today.
The Journalism Department at Southern now offers an interdisciplinary minor with the Geography Department in Drone Applications. Students study how drones (small unmanned aerial systems) are employed for geography, environmental sciences, journalism and other industries. This interdisciplinary minor prepares students with the fundamental knowledge, skills and experience in the technological, legal and ethical considerations and applications of drones in various fields.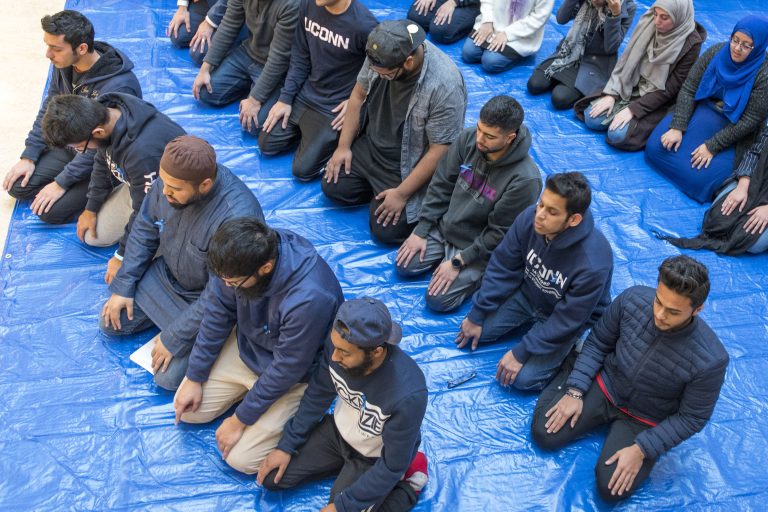
The minor is aimed at students who are interested in learning about emerging drone technologies and how they can be applied to professional settings. It complements environmental sciences, geography, journalism and communication programs.
The 18-credit minor requires courses such as Basic Drone Technology, Drone Journalism, Introduction to GIS and Remote Sensing or Advanced Drone Journalism.
The coursework focuses on flying drones for the purposes of news gathering in both image and data applications and includes the legal, ethical, and safety requirements for flying drones and reviewing necessary requirements for getting licensed by the FAA.
The drone courses are taught by Assistant Professor of Journalism Vern Williams, who has more than two decades in news photography and served as photo director of the New Haven Register for 15 years, where he supervised the photographic and video coverage of the news. His teaching experience includes work at Southeastern Associated Press Managing Editors Association, University of South Carolina, and Cornell University.



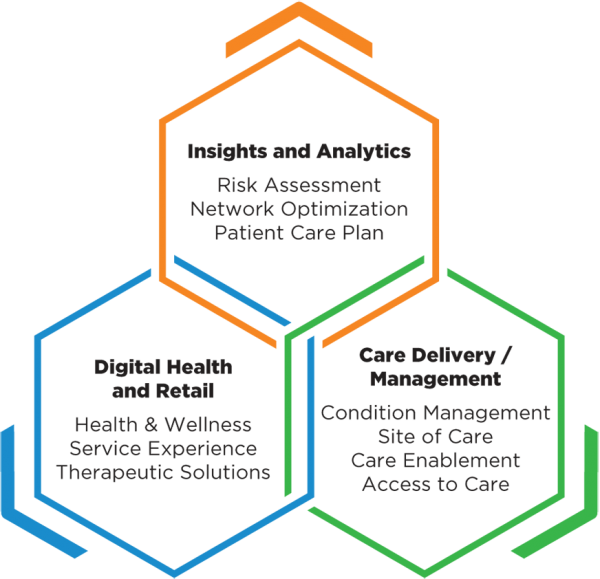 Companies in the portfolio, according to published reports, include Omada Health, a digital therapeutics company treating chronic diseases; Prognos, a predictive analytics company for healthcare; Contessa Health, a home-patient care service; Mdlive, which provides remote health consultations; and Cricket Health, a special kidney care provider.
Companies in the portfolio, according to published reports, include Omada Health, a digital therapeutics company treating chronic diseases; Prognos, a predictive analytics company for healthcare; Contessa Health, a home-patient care service; Mdlive, which provides remote health consultations; and Cricket Health, a special kidney care provider.



 Timex
Timex

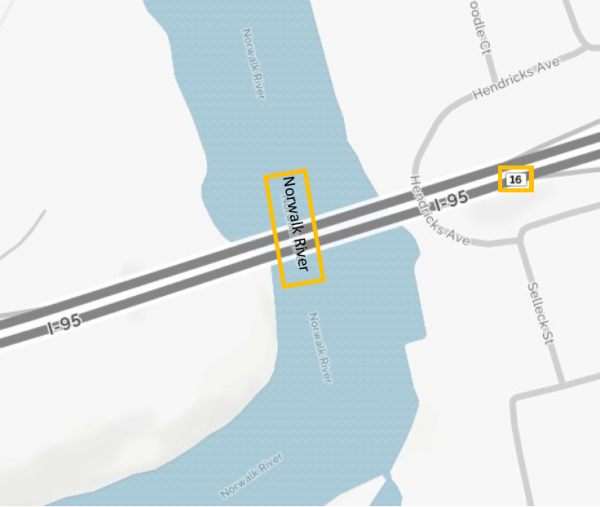
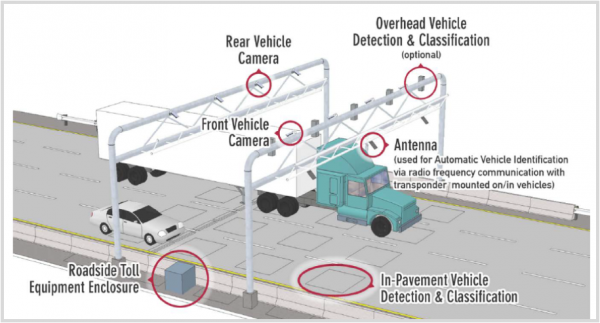
 The Indianapolis Star reported earlier this summer that the state signed a $9.6 million contract with HNTB Indiana Inc. to study the impact of tolling and provide project planning if the state chooses to move forward with tolling. The administration of Gov. Eric Holcomb is required to study tolling under a road-funding plan lawmakers passed in 2017, but a decision has not been made on whether the state will go forward with authorizing a tolling plan, according to published reports.
The Indianapolis Star reported earlier this summer that the state signed a $9.6 million contract with HNTB Indiana Inc. to study the impact of tolling and provide project planning if the state chooses to move forward with tolling. The administration of Gov. Eric Holcomb is required to study tolling under a road-funding plan lawmakers passed in 2017, but a decision has not been made on whether the state will go forward with authorizing a tolling plan, according to published reports.

 The state currently operates advanced manufacturing programs at Asnuntuck, Housatonic, Manchester, Middlesex, Naugatuck Valley, Quinnebaug Valley and Three Rivers community colleges.
The state currently operates advanced manufacturing programs at Asnuntuck, Housatonic, Manchester, Middlesex, Naugatuck Valley, Quinnebaug Valley and Three Rivers community colleges.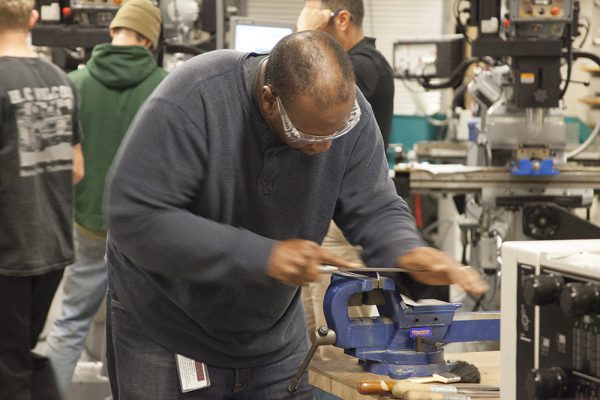

 The three institutions will work during the next few months to develop the curriculum, establish an advisory board, create a virtual inter-institutional platform, and plan to start recruiting for the first cohort of students. All three institutions have a lengthy pedigree in engineering, and effective programs to advance entrepreneurship at the undergraduate level. UNH
The three institutions will work during the next few months to develop the curriculum, establish an advisory board, create a virtual inter-institutional platform, and plan to start recruiting for the first cohort of students. All three institutions have a lengthy pedigree in engineering, and effective programs to advance entrepreneurship at the undergraduate level. UNH  The purpose of the pilot program, according to OPM, is to encourage and allow for the testing of fully autonomous vehicles (FAV) on local highways in Connecticut. The goal for the pilot program is to allow a variety of FAV testing to occur in four municipalities throughout the state, bringing Connecticut to the forefront of the innovative and burgeoning autonomous vehicle industry.
The purpose of the pilot program, according to OPM, is to encourage and allow for the testing of fully autonomous vehicles (FAV) on local highways in Connecticut. The goal for the pilot program is to allow a variety of FAV testing to occur in four municipalities throughout the state, bringing Connecticut to the forefront of the innovative and burgeoning autonomous vehicle industry.
 The state law outlines a framework of the minimum requirements to be included in agreements between municipalities and autonomous vehicle testers approved for participating in the Fully Autonomous Vehicle Testing Pilot Program (FAVTPP). The Connecticut law, according to the
The state law outlines a framework of the minimum requirements to be included in agreements between municipalities and autonomous vehicle testers approved for participating in the Fully Autonomous Vehicle Testing Pilot Program (FAVTPP). The Connecticut law, according to the  3 Seconds Behind the Wheel, which debuts on Connecticut Public on Thursday evening, is a new
3 Seconds Behind the Wheel, which debuts on Connecticut Public on Thursday evening, is a new  The film also gives audiences a firsthand look at emerging technologies that could one day offer solutions to rising crash statistics. The documentary follows researchers at Google who are using driving simulators to develop next-generation in-car infotainment systems, and explores how one Swedish company is experimenting with technology that could one day allow cars to understand human feelings and make driving decisions based on individual needs.
The film also gives audiences a firsthand look at emerging technologies that could one day offer solutions to rising crash statistics. The documentary follows researchers at Google who are using driving simulators to develop next-generation in-car infotainment systems, and explores how one Swedish company is experimenting with technology that could one day allow cars to understand human feelings and make driving decisions based on individual needs.



























