State Office of Early Childhood Welcomes Bye with $8.5 Million from Feds
/The Connecticut Office of Early Childhood (OEC) has announced what amounts to a welcome gift for its incoming leader, former State Senator Beth Bye, named by Gov. Lamont two weeks ago to head the state agency. Just days ahead of Lamont’s inauguration, OEC said it had been awarded an $8,591,087 federal grant - funds intended to enable the state to design and launch better, more cost-effective systems serving families with young children.
The most anticipated federal early childhood initiative in years, according to OEC officials, the new Preschool Development Grant program was highly competitive. Connecticut is a national leader among states in both grant size and per capita funding, officials indicated. 
“This new grant will allow Connecticut to build on our nation-leading efforts, giving OEC new resources to work across agencies and increase impact for children and families,” former Gov. Dannel Malloy said as the grant was announced, in the final days of his administration. Connecticut was selected to receive one of the nation’s largest awards by the two federal agencies administering the grant, the Department of Health and Human Services and the Department of Education. Among the largest state recipients, no state received more funding per target family than Connecticut.
 Bye will begin serving as the Commissioner-designate later this month. Her nomination will be sent to the General Assembly for confirmation. Earlier in her career, Bye was director of the University of Saint Joseph School for Young Children and Trinity College Community Child Center preschools, and was early childhood director at the Capitol Region Education Council (CREC), where she supervised the birth to three program for CREC, and also helped to open two early childhood magnet schools. She was later elected to the Board of Education in West Hartford, then to the State House and State Senate. Reelected last fall, she did not take the oath of office last week in order to accept Lamont’s offer to lead the agency.
Bye will begin serving as the Commissioner-designate later this month. Her nomination will be sent to the General Assembly for confirmation. Earlier in her career, Bye was director of the University of Saint Joseph School for Young Children and Trinity College Community Child Center preschools, and was early childhood director at the Capitol Region Education Council (CREC), where she supervised the birth to three program for CREC, and also helped to open two early childhood magnet schools. She was later elected to the Board of Education in West Hartford, then to the State House and State Senate. Reelected last fall, she did not take the oath of office last week in order to accept Lamont’s offer to lead the agency.
“Beth Bye has devoted her entire professional career to helping to build a more progressive and equitable early childhood system in which all children, regardless of their parent’s socioeconomic status, can grow, learn and develop,” said Lamont. “It’s clear that the formative early childhood years are key to providing children a solid educational base and platform, and I know Beth is the best person to take helm of this critical agency.”
Her soon-to-be-predecessor, David Wilkinson, said “Connecticut punched well above its weight on this grant. That’s because its goals are in our DNA. OEC’s enabling legislation calls on us to be data driven, to be outcomes accountable, and to support the whole family by working across government silos. We’ve been delivering on that mission, but no agency can do those things alone. What’s exciting here is that these resources will allow the next administration to build a smart, collaborative infrastructure across agencies – one that better supports young children and families, reducing redundancies and focusing on shared goals for family success.”
 Unlike a previous iteration of this federal grant program – which focused on expanding preschool for four year-olds – the new grant focuses on child success from to zero to five, with an emphasis on infants and toddlers. Further, officials said, it calls on states to look beyond the classroom to broader measures of child and family success, including mental and physical health, family stability, and parental employment. Because such considerations involve multiple agencies, it calls on states to advance a cross-system data and performance infrastructure, asking them to cost-effectively implement new solutions with an emphasis on measurable outcomes.
Unlike a previous iteration of this federal grant program – which focused on expanding preschool for four year-olds – the new grant focuses on child success from to zero to five, with an emphasis on infants and toddlers. Further, officials said, it calls on states to look beyond the classroom to broader measures of child and family success, including mental and physical health, family stability, and parental employment. Because such considerations involve multiple agencies, it calls on states to advance a cross-system data and performance infrastructure, asking them to cost-effectively implement new solutions with an emphasis on measurable outcomes.
With this new grant, federal authorities call on states to improve measurable outcomes for children and families and to more efficiently use federal and state resources. The grant program asks states to do this by planning and building more coordinated systems, deploying resources to:
- Better link families to the full range of services they need, aligning and improving coordination among existing agencies and programs while blending and braiding funds for better efficiencies
- Advance an infrastructure for data sharing across the silos of government to better support families
- Design and implement a performance management approach focused on measurable child and family outcomes
- Develop and implement evidence-based practices to cost effectively improve child and family outcomes
- Investing in the cross agency, digital infrastructure to support all of the above
Established in 2014 with bi-partisan support and at the urging of Gov. Malloy, Sen. Bye and colleagues, the Connecticut Office of Early Childhood advances a family-centered approach to support young children and families. Integrating early childhood programming formerly administered by five separate state agencies, OEC serves children each year through programs including child care, preschool, home visiting, health and safety assurance, early intervention and parenting supports.
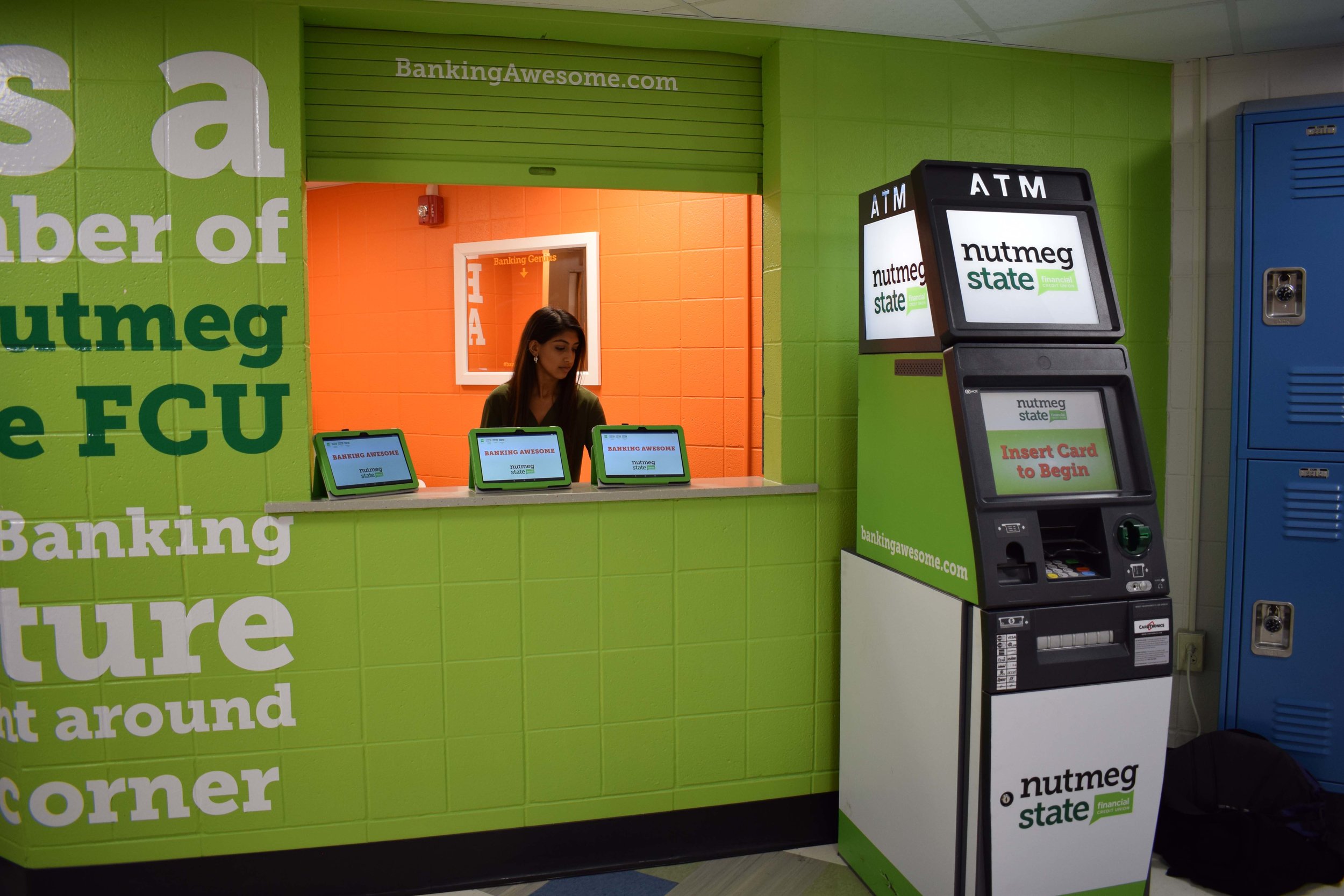



 Because the technology is intuitive for most students, their transaction time can be used to talk about subjects they may be less familiar with – such as balancing a checkbook, how debit cards and account balances relate to each other, loans and interest rates, and what a credit score is all about. Not the typical teen conversation, but Holt indicates that students have been quite interested in learning more.
Because the technology is intuitive for most students, their transaction time can be used to talk about subjects they may be less familiar with – such as balancing a checkbook, how debit cards and account balances relate to each other, loans and interest rates, and what a credit score is all about. Not the typical teen conversation, but Holt indicates that students have been quite interested in learning more.

 “Girl Scouts is one of our nation’s most powerful leadership training grounds for young women,” said Openshaw. “We’re thrilled to support Girl Scouts as it seeks to modernize and remain relevant for young women in the new global economy.”
“Girl Scouts is one of our nation’s most powerful leadership training grounds for young women,” said Openshaw. “We’re thrilled to support Girl Scouts as it seeks to modernize and remain relevant for young women in the new global economy.” t have increased as much in comparison to other states, but isn’t the real question, ‘Why is it increasing at all?’” Luis Perez, president and CEO of
t have increased as much in comparison to other states, but isn’t the real question, ‘Why is it increasing at all?’” Luis Perez, president and CEO of  The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.”
The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.” “Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.
“Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.

 Among the 10 largest state agencies in Connecticut, OEC’s goal is to keep the state’s children safe, healthy, learning and thriving. Through its innovative feedback efforts, the agency is acting on evidence that engaging providers and parents in policymaking yields better results. Officials said that the agency combined data from 1,700 family surveys, another survey shared with all providers in the state, and 400 community and provider meetings in order to build a draft plan to transform the ECE system in the state, which serves 200,000 children.
Among the 10 largest state agencies in Connecticut, OEC’s goal is to keep the state’s children safe, healthy, learning and thriving. Through its innovative feedback efforts, the agency is acting on evidence that engaging providers and parents in policymaking yields better results. Officials said that the agency combined data from 1,700 family surveys, another survey shared with all providers in the state, and 400 community and provider meetings in order to build a draft plan to transform the ECE system in the state, which serves 200,000 children.



 Among the report’s other key findings:
Among the report’s other key findings:


























