Report Provides Guidance for School Districts and State Policymakers to Address Students’ Trauma & Mental Health Needs
/It is described as a “framework to advance policy and strategic school district planning to more effectively address the mental health and trauma needs of students and promote student success.” A new report, driven by research highlighting the connection between mental health and educational outcomes, is aimed at school districts looking to increase integration of student mental health services and supports. The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.”
The 40-page report, developed by The Child Health and Development Institute of Connecticut (CHDI), a subsidiary of the Children’s Fund of Connecticut, in partnership with the national Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland, provides a framework for policymakers and school districts interested in improving outcomes by addressing the mental health and trauma needs of students. The report indicates that “in a typical classroom of 25 students, approximately five will meet criteria for a mental health disorder but most of them are not receiving appropriate mental health treatment or support. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools.”
Connecticut is cited as an example of how states can promote collaborations within and across the behavioral health, education, and juvenile justice systems to provide an array of trauma-informed, evidence-based, and tiered services for students. It notes that school principals indicate that mental health is one of the most challenging unmet needs among their students and schools are increasingly seen as a critical setting for the delivery of mental health services.
The report provides “a blueprint and resources to guide state policymakers and school district leaders," including:
- an overview of core components of the Comprehensive School Mental Health
- Systems (CSMHS) model structured around family-school-community partnerships and the delivery of evidence-based mental health services within a multi-tiered system of supports;
- examples of best practice strategies to develop, implement, and sustain CSMHS;
- a model for a trauma-informed multi-tiered system of supports for school mental health;
- creative approaches to advance policy and funding structures to sustain CSMHS; and
- recommendations for state-level policymakers, districts, and schools to advance a comprehensive statewide system of school mental health to improve outcomes for all students.
 “Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.
“Approaching student mental health with a comprehensive lens that integrates health promotion, prevention, early intervention, and more intensive treatments leads to better school, student and community outcomes," said Dr. Sharon Hoover, Co-Director of the Center for School Mental Health at the University of Maryland and lead author of the report.
National prevalence rates indicate that approximately 20 percent of children meet criteria for a mental health disorder; however, many children’s mental health needs are not identified and the majority of children with identified challenges do not receive services, the report explained. Among those who do access care, approximately 70 percent receive services through their schools. Linking children to services through their schools reduces many traditional barriers to care. School mental health services are also associated with higher completion rates than treatment delivered in traditional outpatient community-based settings.
The report uses Stamford Public Schools (SPS) as a” local model for improving outcomes by adopting a trauma informed approach to school mental health.” CHDI began working with SPS in 2014 to conduct a review of the district’s mental health system and to develop a plan to enhance trauma-informed mental health services district-wide. That plan was subsequently implemented, and “lessons learned in Stamford are being used to engage other Connecticut districts to … integrate school and community-based mental health services, and promote quality and sustainability of these enhancements.”
“Schools are well positioned to promote wellness and social emotional competence for all students, as well as identify and address mental health concerns for students in need,” said Dr. Jeana Bracey, Director of School and Community Initiatives at CHDI and report co-author. “However, the responsibility is not on schools alone to integrate or fund these supports. This framework helps districts connect to and collaborate with Connecticut’s robust network of trauma-informed state and community-based services and programs so all students can be successful.”
The report concludes that a “systematic and streamlined partnership between families, schools, and communities to support a continuum of mental health supports in schools can lead to better behavioral health for all students, as well as increased access, earlier identification and intervention, and ultimately better outcomes for students with mental health challenges.”
[Visit wwws.chdi.org to download the IMPACT report or to read more about CHDI’s work related to school mental health.]




 Lewis’ commitment and dedication impressed the judging panel.
Lewis’ commitment and dedication impressed the judging panel.
 Here are a few examples:
Here are a few examples:





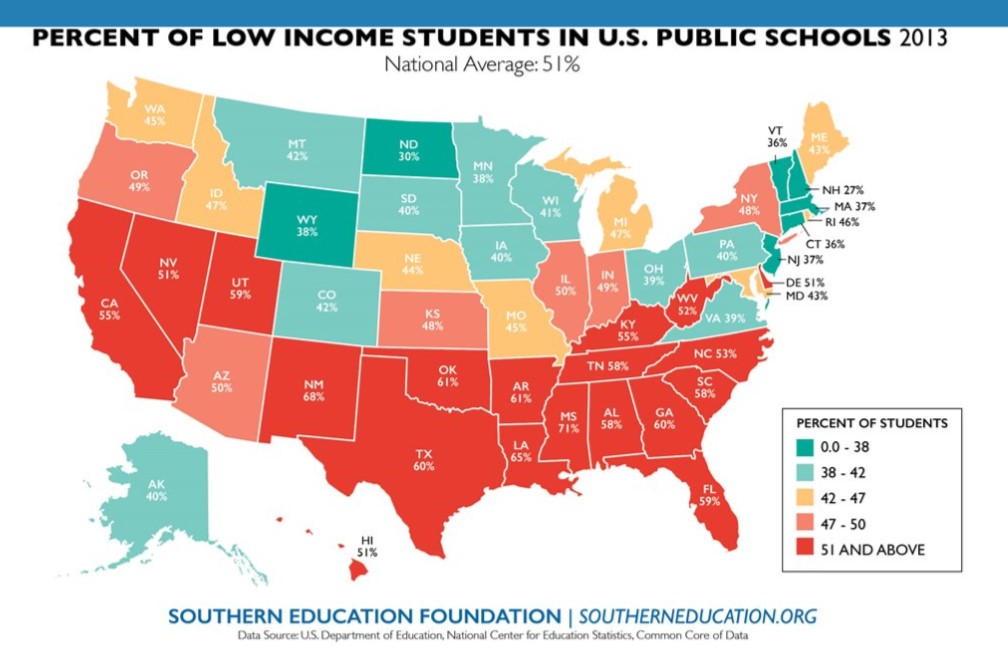
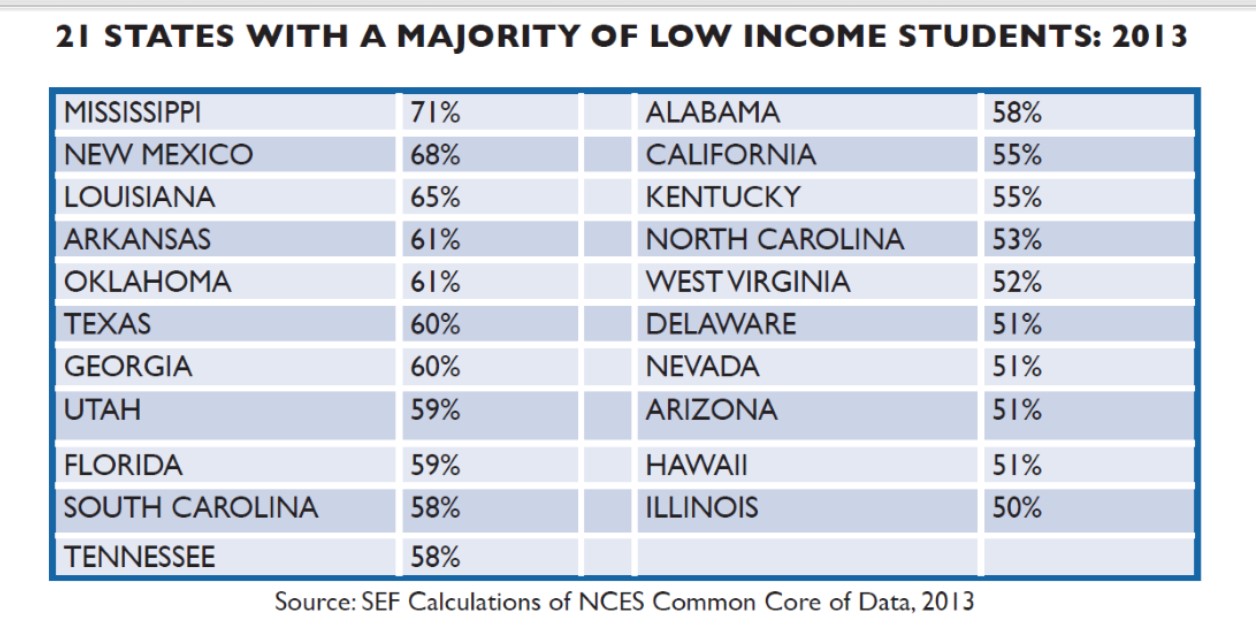 hat “The trends of the last decade strongly suggest that little or nothing will change for the better if schools and communities continue to postpone addressing the primary question of education in America today: what does it take and what will be done to provide low income students with a good chance to succeed in public schools? It is a question of how, not where, to improve the education of a new majority of students.”
hat “The trends of the last decade strongly suggest that little or nothing will change for the better if schools and communities continue to postpone addressing the primary question of education in America today: what does it take and what will be done to provide low income students with a good chance to succeed in public schools? It is a question of how, not where, to improve the education of a new majority of students.”