Health Risks of Flame-Retardant Chemicals Require Policy Changes in CT, Nation, Report Says
/
The 2014 session of the Connecticut General Assembly is expected to include consideration of legislation designed to protect the public from potential health risks of flame retardant chemicals that are present in many consumer products. Such a proposal, currently being developed, comes following a report from North Haven-based Environment and Human Health Inc. (EHHI), an organization of physicians and public health professionals, that calls on state and federal governments to institute new policies to protect the public from flame-retardant exposures that the researchers say “pose health risks to fetuses, infants, children and the human population as a whole.”
The comprehensive 107-page report, “Flame Retardants: The Case for Policy Change,” closely examines the health risks that flame-retardants pose to the general population and recommends sweeping policy changes to protect the public.
"It has become clear that flame-retardants are proving to be a health risk to both the human population and the environment,” said Nancy Alderma n, president of Environment and Human health, Inc. “It is time for flame-retardants to be removed from all low fire-risk situations and products. As well, a certification program should be established where manufacturers certify the absence of flame-retardants, just as organic food programs certify the absence of pesticides.”
n, president of Environment and Human health, Inc. “It is time for flame-retardants to be removed from all low fire-risk situations and products. As well, a certification program should be established where manufacturers certify the absence of flame-retardants, just as organic food programs certify the absence of pesticides.”
The report examines the history of flame-retardants and demonstrates the enormous scope of the problem, noting that flame-retardants “are now ubiquitous in our environment.” The history of flame-retardant use in the United States is a story of substituting one dangerous flame-retardant for another, the report outlines. The country lived through decades when asbestos was used as a fire-retardant. Then when asbestos was proven too dangerous to be used, the country moved over to PCBs, and five decades later, when PCBs were deemed too dangerous for use, the country moved on to chlorinated and brominated flame-retardants.
The report points out that “the labeling of flame-retardant chemicals in consumer products is NOT required by Congress, EPA, FDA or the Consumer Product Safety Commission. It is therefore impossible for consumers to avoid flame-retardants in their purchases.” Sources of exposure cited in the report include carpets, mattresses, children’s and baby products, furniture, and electronics. 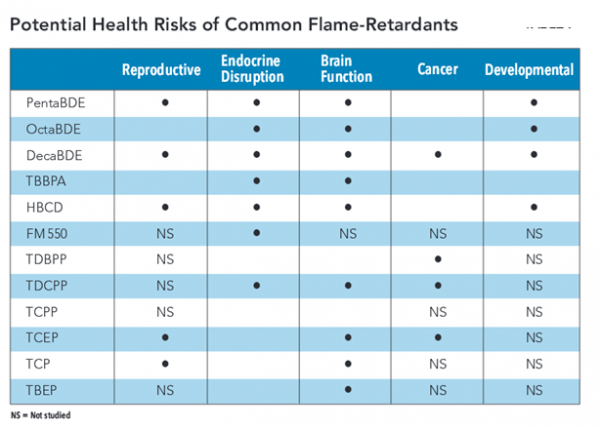
In the 1970s, a flame-retardant called "Tris" was added to children's sleepwear. Tris was later found not only to be carcinogenic but also capable of being absorbed through the skin. Tris was finally banned in children's sleepwear in 1977, according to the report. Tris is still used in many other infant products, such as crib mattresses, changing tables, nap mats, and infant car seats, the report indicated.
"Tris was, and remains, carcinogenic," said Dr. D. Barry Boyd, oncologist at Greenwich Hospital and Affiliate Member of the Yale Cancer Center. There is ample evidence concerning the health risks from Tris to conclude that it should be removed from all infant products."
John Wargo, Ph.D., first author of the report and the Tweedy-Ordway Professor of Environmental Health and Political Science at Yale University, said, "Flame-retardants are not required to undergo health and environmental testing, and they are not required to be labeled on the products that contain them. Because exposures to flame-retardants carry health risks, they should only be used when the risk of fire outweighs the risk from flame-retardant exposures. When risk from fire is high, such as in airplanes, then the use of flame-retardants is warranted; when the risk from fire is low, flame-retardants should not be used."
Recent toxicological studies demonstrate that flame-retardants pose the greatest risk to the normal growth and development of fetuses, infants and children. "Manufacturers should start labeling their products so that consumers can understand when flame-retardants have been added," said Dr. Andrea Asnes, associate professor of pediatrics at the Yale School of Medicine.
Environment and Human Health, Inc. (EHHI) is a non-profit organization composed of physicians, public health professionals and policy experts, dedicated to protectin g human health from environmental harms. EHHI does not receive any funds from businesses or corporations. The organization’s mission is “to conduct research to identify environmental harms affecting human populations, promote public education concerning the relationships between the environment and human health, and promote policies in all sectors that ensure the protection of human and environmental health with fairness and timeliness.
g human health from environmental harms. EHHI does not receive any funds from businesses or corporations. The organization’s mission is “to conduct research to identify environmental harms affecting human populations, promote public education concerning the relationships between the environment and human health, and promote policies in all sectors that ensure the protection of human and environmental health with fairness and timeliness.
By promoting effective communication of environmental health risks to those exposed and to responsible public and private officials, EHHI hopes to empower individuals and groups to take control over the quality of their environment and be more protective of themselves and their families. The report was issued in November 2013. Among the recommendations :
- States should pass laws that protect their citizens from flame-retardant exposures. Industry will always work to pre-empt states’ legal authority to set safety standards that are more stringent than those adopted by the federal government. States should have the right to protect their citizens when the federal government fails to do so.
- States should restrict flame-retardants in infant and toddler products. Recent toxicological studies show that flame-retardants pose the greatest risk to the normal growth and development of fetuses, infants and children. Infants and small children’s body weight is so low that their exposures to flame retardants, in relation to their body weight, is simply too great. The health risks that all infants and children are experiencing, due to the federal law mandating that flame retardants be in many of their products, far outweigh the risk of fire.
- States should require that products containing flame-retardants be labeled. Any product containing a flame-retardant should be labeled as such. Labels should include which flame-retardant has been used.
- States should promote fire-prevention programs. States should invigorate their fire prevention programs. Promotion of fire prevention is the most effective, least expensive, least environmentally damaging priority our nation could pursue to reduce loss of health, life and property from fires. States should promote low-cost and highly effective early warning technologies. Smoke alarms save lives. They should be available to all, regardless of income status.
- States should offer opportunities to recycle electronic products. Foam that contains flame-retardants remains a problem for landfills. State and local governments have primary responsibility for managing the disposal of solid and hazardous wastes. Most solid wastes in Connecticut are disposed of via incineration, but some are still placed in landfills. The broad failure to effectively recycle electronics, building materials, auto plastics and foam means that most products containing flame-retardants are released to the environment at the end of their life-cycle.































