Back to the Future: Permanent Commission on Status of Women Resurrected as Nonprofit
/When the state legislature surprisingly eliminated the landmark Connecticut Permanent Commission on the Status of Women (PCSW) on the heels of one of the agency’s most successful advocacy efforts on an array of pivotal issues, the dismay from an array of organizations across the state was strident and unified, but ultimately unsuccessful. The 2016 Legislative Session, which ended in June, had seen four of the largest gains for women’s rights. Bills to protect women from human trafficking, intimate partner homicide, campus sexual assault, and being forced to parent with a rapist all passed with bi-partisan support, with PCSW among the organizations leading the fight.
The agency, active and effective for 43 years, was no longer “permanent.” It was history. Unfazed, the legislature, pressed to find budgetary savings, merged it into a new structure, combined with former commissions on children and the elderly. For those involved with, and committed to, the work of the former PCSW, the legislature's approach fell short. So they took matters into their own hands. 
The tone was considerably more upbeat this week as it was announced that PCSW was back in business, new and improved, with an educational nonprofit and a companion advocacy organization formed to continue the work on issues that remain on the front burner – or ought to.
A group of former State Commissioners and former key employees of the previous PCSW, dismantled at the start of the new fiscal year on July 1, announced the formation of a new non-profit initiative to advance the work of the former state agency, which was among the oldest and largest women’s commissions left in the United States.
The Commission’s legacy of developing landmark legislation and research in the areas of sexual harassment, domestic violence, family medical leave protections, pay equity, and human trafficking will continue, advocates stressed, only now emanating from outside of state government.
“We will partner with leaders in Hartford, CWCS, and organizations around the state to ensure that the public policy agenda for women and girls addressed by the former PCSW continues to move forward. We will provide expertise, research, resources, and advocacy to improve the lives of women and girls in this state,” said Mary Lee Kiernan, former Chair of the PCSW and President of the newly formed Permanent Commission on the Status of Women in Connecticut Education Fund, Inc. (PCSW Education Fund, Inc.). PCSW Education Fund, Inc. is applying for 501(c)(3) tax status with the IRS.
A new website, www.ctpcsw.org, was launched along with the new organizations. The new initiatives were announced at a State Capitol news conference, alongside the statue of Prudence Crandall, Connecticut’s state heroine. 
“Our new initiative will advocate in the same key policy areas addressed by the former PCSW, including economic security; health and safety for women of all ages; discrimination in all forms; education; and women’s leadership,” explained Carolyn Treiss, Executive Director of the former PCSW and President of the newly formed Permanent Commission on the Status of Women in Connecticut, Inc. (PCSW, Inc.). PCSW, Inc. is applying for 501(c)(4) tax status with the IRS and intends to advocate for an annual legislative agenda in these key policy areas. 501(c)(4) tax status allows for unlimited advocacy on legislation.
The board members of these two entities currently consist of eleven of the sixteen former PCSW commissioners, the former PCSW Executive Director and the former PCSW Policy Director. These individuals provide expertise on a wide variety of issues affecting women and girls, and they represent all regions of the state.
“I am impressed with the expertise that our board members bring, particularly around the intersection of gender with issues of race, ethnicity, age, religion, and socio-economic status,” explained Catherine Ernsky, President of the Ernsky Group and Vice President of the PCSW Education Fund, Inc. Board members also bring experience in the areas of law, finance, medicine, insurance, communications, philanthropy, health equity, criminal justice, state and local government, legislation, education, environmental justice, organized labor, and non-profit leadership.
An advisory board to the PCSW Education Fund, Inc. has been established that includes Senator Richard Blumenthal; Congresswoman Rosa DeLauro; former PCSW Executive Director and current President of the Ms. Foundation, Teresa Younger; former PCSW Honorary Commissioner and Executive Director of the Women’s Campaign School at Yale, Patricia Russo; former PCSW Honorary Commissioner Patricia Hendel; and former PCSW Honorary Commissioner Barbara DeBaptiste. Pro-Bono legal services are being provided by Wiggin & Dana, LLP. PFK O’Conner Davies, LLP will serve as auditors.
PCSW Education Fund, Inc. and PCSW Inc. intend to collaborate with non-profit partners from around the state, the new CWCS, and state leaders to “continue the long legacy of progress for women and girls” that characterized the former state agency.
“Collaboration in this space is key,” explained Fran Pastore, President of the Women’s Business Development Council, a frequent collaborator with the former PCSW. “The board members of these entities are well-known for building effective coalitions. I hope to work with them to improve financing for women-owned businesses and workplace practices impacting women. Ultimately, these issues spur economic growth and improve the lives of everyone in the state.”
In 1973, the CT General Assembly passed, and Governor Thomas Meskill signed into law, Public Act 73-559, establishing the Permanent Commission on the Status of Women. The PCSW was charged with providing research and analysis on issues related to gender discrimination, women’s health and safety, and economic security. “In its 43 year history, the PCSW has informed many important public policies that make Connecticut a desirable place for women to live and work today,” the Commission explained in its final legislative report, issued in June. The list of highlight legislative victories runs six pages, single spaced, in small type.
Back in February, Kiernan testified at the legislature, explaining that "The empirical evidence on gender in Connecticut is very clear. Women still face widespread discrimination in the workplace and beyond. Women continue to face far greater barriers to educational success than men. Women face wage inequality, occupational segregation and barriers to credit in the business sector. Women still struggle for basic economic self-sufficiency and fail to build the assets needed for retirement at greater rates than their male counterparts. And women and girls face increasingly complex threats to their health and safety. All of these issues are compounded and complicated by race and ethnicity."
Now, a new chapter begins, with experienced hands at the helm.



 Republicans. The House Speaker, House Majority Leader, Senate President Pro Tempore Senate Majority Leader, and Senate Republican Leader for the 2015 session are men, as was true in the previous legislative session. Connecticut has seen a woman Speaker of t
Republicans. The House Speaker, House Majority Leader, Senate President Pro Tempore Senate Majority Leader, and Senate Republican Leader for the 2015 session are men, as was true in the previous legislative session. Connecticut has seen a woman Speaker of t he House, but there has not been a woman selected to serve as Senate President Pro Tempore or Majority Leader.
he House, but there has not been a woman selected to serve as Senate President Pro Tempore or Majority Leader.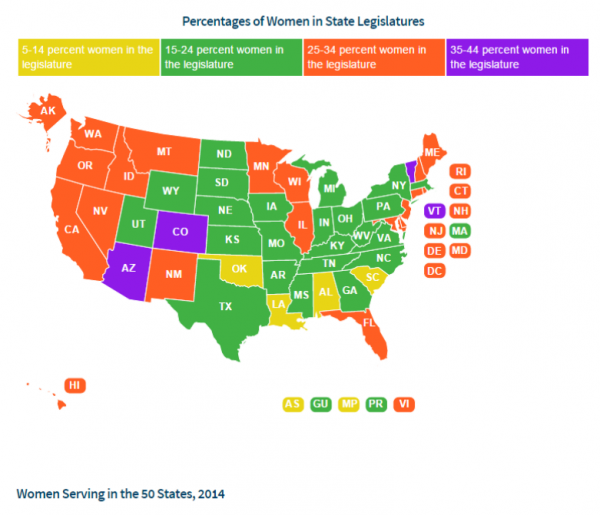
 e ombudsmen, protective service employees probate judges and court personnel.
e ombudsmen, protective service employees probate judges and court personnel.
 of a “train the trainer” dementia course based on the existing Alzheimer’s Association leaders’ training, and drawing on the model of the American Red Cross’ CPR training program to offer “accessible and affordable dementia education to caregivers.”
of a “train the trainer” dementia course based on the existing Alzheimer’s Association leaders’ training, and drawing on the model of the American Red Cross’ CPR training program to offer “accessible and affordable dementia education to caregivers.” Health for homemaker and companion agencies and collaborative initiatives with the Department of Social Services.
Health for homemaker and companion agencies and collaborative initiatives with the Department of Social Services. n, president of Environment and Human health, Inc. “It is time for flame-retardants to be removed from all low fire-risk situations and products. As well, a certification program should be established where manufacturers certify the absence of flame-retardants, just as organic food programs certify the absence of pesticides.”
n, president of Environment and Human health, Inc. “It is time for flame-retardants to be removed from all low fire-risk situations and products. As well, a certification program should be established where manufacturers certify the absence of flame-retardants, just as organic food programs certify the absence of pesticides.”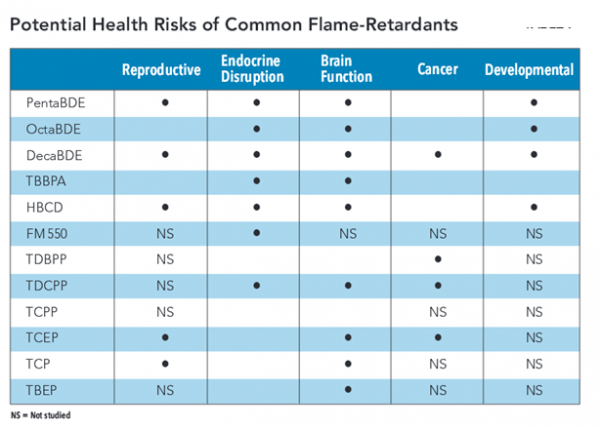
 g human health from environmental harms. EHHI does not receive any funds from businesses or corporations. The organization’s mission is “to conduct research to identify environmental harms affecting human populations, promote public education concerning the relationships between the environment and human health, and promote policies in all sectors that ensure the protection of human and environmental health with fairness and timeliness.
g human health from environmental harms. EHHI does not receive any funds from businesses or corporations. The organization’s mission is “to conduct research to identify environmental harms affecting human populations, promote public education concerning the relationships between the environment and human health, and promote policies in all sectors that ensure the protection of human and environmental health with fairness and timeliness. ,” the report indicated. Then, the shooting at Sandy Hook Elementary School in Newtown on December 14, 2012 provided “a major impetus for lawmakers to propose legislation which would impact children and adults living with mental illness,” the 63-page report indicated.
,” the report indicated. Then, the shooting at Sandy Hook Elementary School in Newtown on December 14, 2012 provided “a major impetus for lawmakers to propose legislation which would impact children and adults living with mental illness,” the 63-page report indicated.