Building Police-Community Connections As Diversity Lags in Hartford
/When Governing magazine examined the diversity within local police departments, compared with the communities they serve, Hartford was among the ten cities with the largest disparity. But two recent programs that have also received national attention underscore the city’s efforts to strengthen relationships between police and the community. The data indicated that Hartford’s police department was 35.3 percent minority, in a city where the population is 84.1 percent minority. That was the 7th largest gap in the nation, after Fontana, CA; Edison, NJ; Irving, TX; Grand Prairie TX; Daly City, CA; and Allentown, PA. Using 2013 data, Governing reviewed 269 local police agencies across the country.
The article points out that “although no national standards regarding diversity levels exist, the Commission on Accreditation for Law Enforcement Agencies does require accredited agencies to adopt steps to ensure their workforce mirrors their communities.” It also indicates that “law enforcement experts emphasize that mending fractured relationships with communities takes much more than merely a diverse force.”
Two locally developed programs, one at the Hartford Public Library (HPL) and the other at the Charter Oak Cultural Center, are working at building police-community relationships.
HPL is one of 10 public libraries in the U.S. that have been participating in the American Library Association’s Libraries Transforming Communities (LTC) initiative since April 2014. The initiative, in collaboration with the nonprofit Harwood Institute for Public Innovation, is an 18-month community engagement training program where libraries learn how to address challenges facing their community.
Hartford’s work was recently featured on the national website of the American Library Association.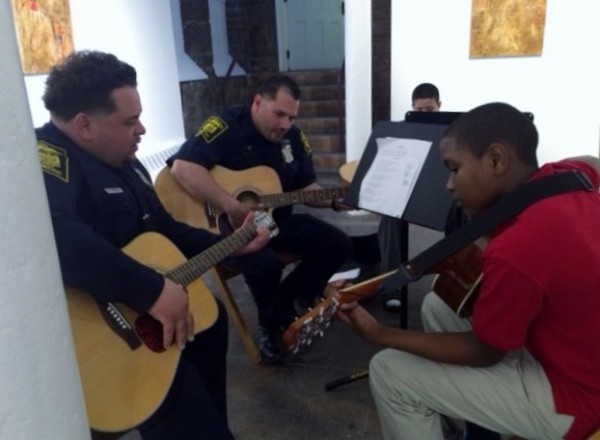
Through eight community conversations in Hartford’s North End neighborhood, HPL found that residents’ main concerns were public safety, community violence, and their relationship with the police. In response, a three-session community dialogue on public safety with police and community members was held, led by HPL community engagement director Richard Frieder. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 87.
During the three sessions, according to published reports, the groups got to know each other; talked about what makes a good neighborhood and what they liked about theirs, what they would like to change, how safe community members feel, and what they believed the residents’ and police officers’ roles were in making the community safe; and figured out how to take action and solve the problems.
Some of the ideas generated include having the police and the community members participate in more activities and learning experiences together, such as block parties and community theater, where they address these issues. Even though the 18-month project officially ends this month, HPL’s staff hopes to sustain the values and goals they developed.
 At the same time, another initiative in the city was taking root – one which soon reached the pages of The New York Times and the attention of the White House.
At the same time, another initiative in the city was taking root – one which soon reached the pages of The New York Times and the attention of the White House.
The Charter Oak Cultural Center’s Good Vibrations program began with a conversation between Hartford’s police chief, James Rovella, and the Center’s director, Rabbi Donna Berman. The innovative program, which began earlier this year, sought to pair middle school age students who were at a crossroads in their lives with Hartford police officers to inspire and inform the youths involved as well as helping to change the community's negative perception of police officers. Nearly two dozen students – and police officers – collaborate on musical instruments, and in composing rap lyrics. The relationships built, and music made, has been described as transformative. Good Vibrations includes two free courses; a Rap Poetry/CD production class, and a guitar class. All the materials are free, including the guitars, which students get to keep.
 Last month, a Hartford police officer and a seventh-grader who participate in the program were honored at the White House as "Champions of Change" for their role in helping to build "bridges between youth and law enforcement, while improving public safety," according to the White House. "During the three-and-a-half month program, officers and youth helped to lift the negative stigma between police and youth through open discussions about racism, crime, government, and family."
Last month, a Hartford police officer and a seventh-grader who participate in the program were honored at the White House as "Champions of Change" for their role in helping to build "bridges between youth and law enforcement, while improving public safety," according to the White House. "During the three-and-a-half month program, officers and youth helped to lift the negative stigma between police and youth through open discussions about racism, crime, government, and family."
One participating middle-schooler told the Times: “I thought police officers were just to catch bad guys and be in a bad tone. But these guys are awesome. They’re always in a good tone with us. They play with us. They tag along in our jokes. They do stuff with us. They help us. They give us advice and everything.”




 Women in Science and Technology
Women in Science and Technology Last year, Kievman delivered a keynote speech at the CT Invention Convention, and issued a challenge to the inventors: to develop and commercialize their products and to give back to the community. She has committed a percentage of the profits from Hiccupops to support programs like the CIC that encourage youth entrepreneurship and innovation.
Last year, Kievman delivered a keynote speech at the CT Invention Convention, and issued a challenge to the inventors: to develop and commercialize their products and to give back to the community. She has committed a percentage of the profits from Hiccupops to support programs like the CIC that encourage youth entrepreneurship and innovation. nt and work closely with stakeholders in developing the conference, viewed as “an opportunity to look ahead to the issues that will help shape the landscape for older Americans for the next decade.”
nt and work closely with stakeholders in developing the conference, viewed as “an opportunity to look ahead to the issues that will help shape the landscape for older Americans for the next decade.”
 rnment with the mission to create strong libraries and museums that connect people with information and ideas, is celebrating its 20th year of saluting institutions that make a difference for individuals, families and communities.
rnment with the mission to create strong libraries and museums that connect people with information and ideas, is celebrating its 20th year of saluting institutions that make a difference for individuals, families and communities.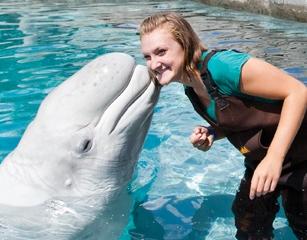
 0 animals, including such species as beluga whales and the endangered African Penguin.
0 animals, including such species as beluga whales and the endangered African Penguin. n in UConn’s commitment to diversity. Officials pointed out that the jump in UConn applications runs counter to national and regional trends in which declines in the number of high school graduates have caused many universities to see their applications and enrollments level off or decrease.
n in UConn’s commitment to diversity. Officials pointed out that the jump in UConn applications runs counter to national and regional trends in which declines in the number of high school graduates have caused many universities to see their applications and enrollments level off or decrease. ment at the community colleges fell 2.1 percent to 56,977, reflecting losses in both full and part time students.
ment at the community colleges fell 2.1 percent to 56,977, reflecting losses in both full and part time students.
 ll be hosting two upcoming events focusing on the remediation issue, the White House report indicated:
ll be hosting two upcoming events focusing on the remediation issue, the White House report indicated: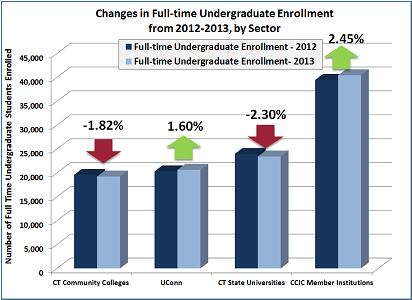 nd math) curricula.
nd math) curricula.































