Manufacturing Goes High Tech; Key Segment of CT Economy
/Factory jobs in Connecticut slumped from 477,000 in 1969 – accounting for about one-third of total employment in the state – to just 174,000, about 10 percent of jobs statewide, in 2011, according to U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis data. In the new issue of The Connecticut Economy however, UConn economist Steven Lanza issues a “report card” on manufacturing that presents the sector as among the most dynamic in the state’s economy, transformed by advanced technologies linked to research and development that are providing a catalyst for economic growth. The analysis notes that during the past two years, Connecticut manufacturing employment has remained steady at about 165,000 workers.
The manufacturing sector contributed 20 percent of the growth in the state’s economic output in the decade ending in 2010, Lanza estimates, while boosting productivity – the value of manufactured goods per worker – by more than 50 percent from 1990 to 2007, with 35 percent fewer workers.
“Expanding output and falling employment [over that timeframe] combined to raise productivity per worker from $57,900 to $135,800, an impressive 134 percent increase,” Lanza says. Enhanced productivity, in turn, also led to higher wages: in 2011, Connecticut factory workers – who are now more likely to have a graduate degree and wear a suit or lab coat to work – earned an average salary of $76,900, or 26 percent above the state’s all-industry average of $61,100.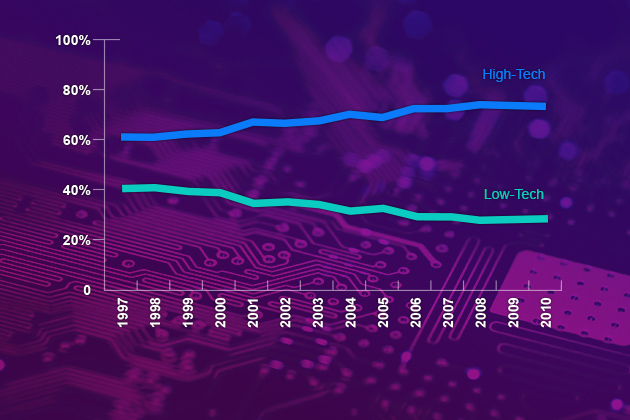
Connecticut’s manufacturing profile has also changed drastically; high-tech firms now produce more than 70 percent of the state’s output with computer/electronic products and chemicals accounting for more than 13 percent and 30 percent, respectively, of the total output in 2010.
Lanza also details how the state is now a leader in the aerospace and defense-related transportation equipment field – largely in the production of aircraft engines, helicopters, and nuclear submarines – totaling 23 percent of the state’s manufacturing output in 2010, compared with 20 percent in 1997.
Lanza is executive editor of The Connecticut Economy, a quarterly journal published by the University of Connecticut’s Department of Economics that offers data, forecasts, and substantive, data-driven analyses of current events, longer-term trends, and public policies affecting Connecticut’s economy.































