Women’s Economic Status in Connecticut Among Best in Nation, But Still Insufficient
/Women are faring better in Connecticut than in most states in the nation, according to a new analysis that focused on data in two central areas of everyday life – Employment & Earnings and Poverty & Opportunity.
Connecticut ranked 4th in the Employment and Earnings category, earning a B+, and 4th in the Poverty and Opportunity category, with a B- grade.
Status of Women in the States is a project of the Institute for Women’s Policy Research, a comprehensive project that presents and analyzes data for all 50 states and the District of Columbia. The Institute suggests that the data can be used “to raise awareness, improve policies, and promote women’s equality.”
Connecticut’s grade for women’s Employment & Earnings, B+, has improved since the 2004 Status of Women in the States report. Its grade for women’s Poverty & Opportunity, B-, has dropped since 2004.
In the subcategories of Employment and Earnings, Connecticut ranked Connecticut ranked 2nd in median annual earnings for women employed full-time, 5th in the percent of all employed women in managerial or professional occupations, 13th in the percent of women in the labor force, and 38th in the earnings ratio between women and men employed full-time, year-round.
The Employment & Earnings Index measures states on women’s earnings, the gender wage gap, women’s labor force participation, and women’s representation in professional and managerial occupations. The top states were District of Columbia, Maryland, Massachusetts, Connecticut and New York.
 Women working full-time, year-round have the highest earnings in the District of Columbia, where women’s median annual earnings are $65,000. Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and New Jersey are tied for second, with women in those states earning $50,000 at the median.
Women working full-time, year-round have the highest earnings in the District of Columbia, where women’s median annual earnings are $65,000. Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, and New Jersey are tied for second, with women in those states earning $50,000 at the median.
In the Poverty and Opportunity subcategories, Connecticut ranked 2nd in the percent of women age 18 and older above poverty, 5th in the percent of women age 25 and older with a Bachelor’s degree or higher, 10th in the percent of women age 18-64 with health insurance, and 29th in the percent of businesses owned by women.
New Hampshire, Connecticut, Maryland, and New Jersey have the highest rates of women living above poverty in the country at 89.2 percent, 88.4 percent, 88.1 percent, and 88.1 percent, respectively.
The report noted that women in Connecticut aged 16 and older who work full-time, year-round have median annual earnings of $50,000, which is 76.9 cents on the dollar compared with men who work full-time, year-round. Hispanic women earn just 47 cents for every dollar earned by White men, according to the report. According to the report’s analysis, if employed women in Connecticut were paid the same as comparable men, their poverty rate would be reduced by more than half and poverty among employed single mothers would be cut in half.
In Connecticut, 32.7 percent of businesses in 2012 were owned by women, up from 28.1 percent in 2007. The report also indicates that 94.2 percent of Connecticut’s women aged 18 to 64 have health insurance coverage, which is above the national average for women of 89.4 percent.
The report, published in March 2018, concludes that “Women in Connecticut have made considerable advances in recent years but still face inequities that often prevent them from reaching their full potential.”




 CERC is a nonprofit corporation and public‐private partnership that provides clients with objective research, marketing and economic development services. The organizations mission is to “provide services consistent with state strategies, leveraging Connecticut’s unique advantages as a premier business location.”
CERC is a nonprofit corporation and public‐private partnership that provides clients with objective research, marketing and economic development services. The organizations mission is to “provide services consistent with state strategies, leveraging Connecticut’s unique advantages as a premier business location.”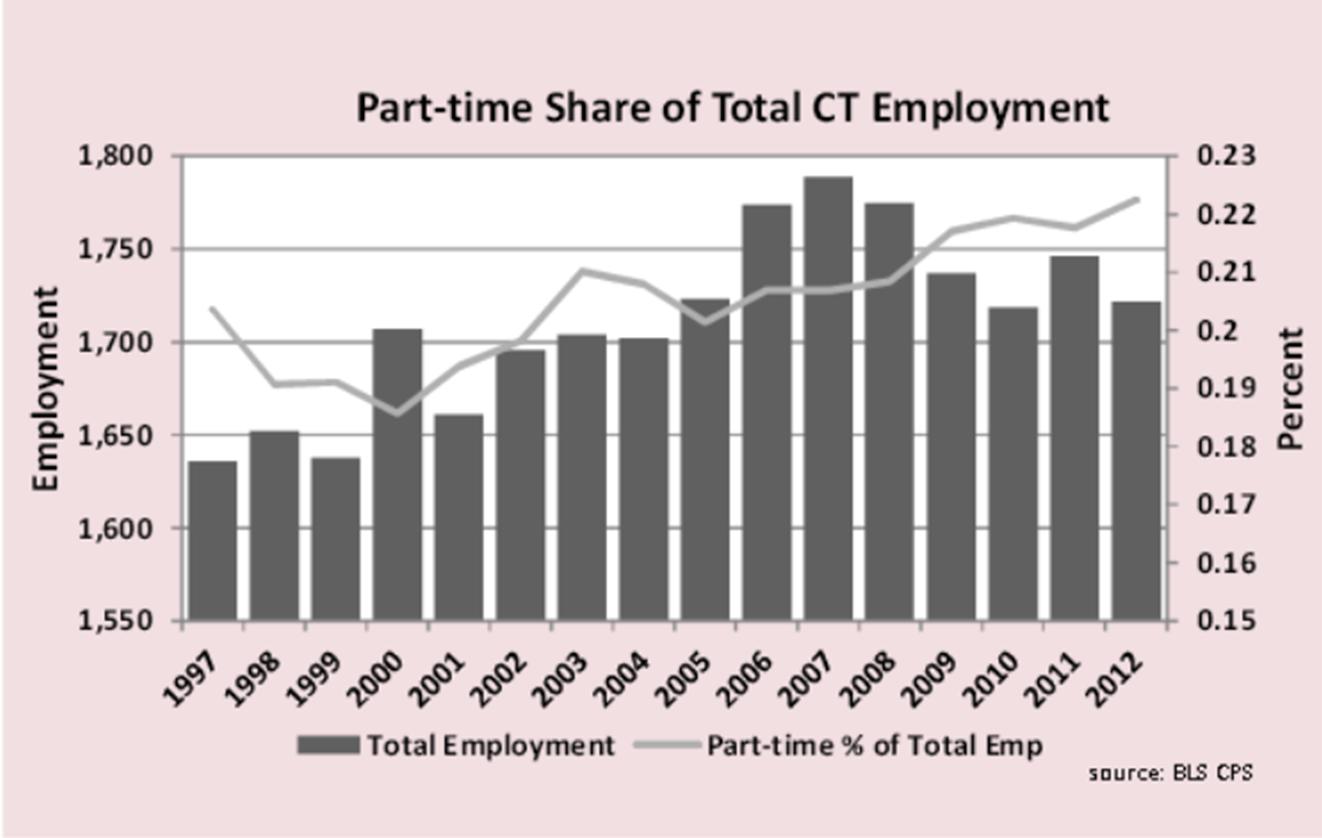
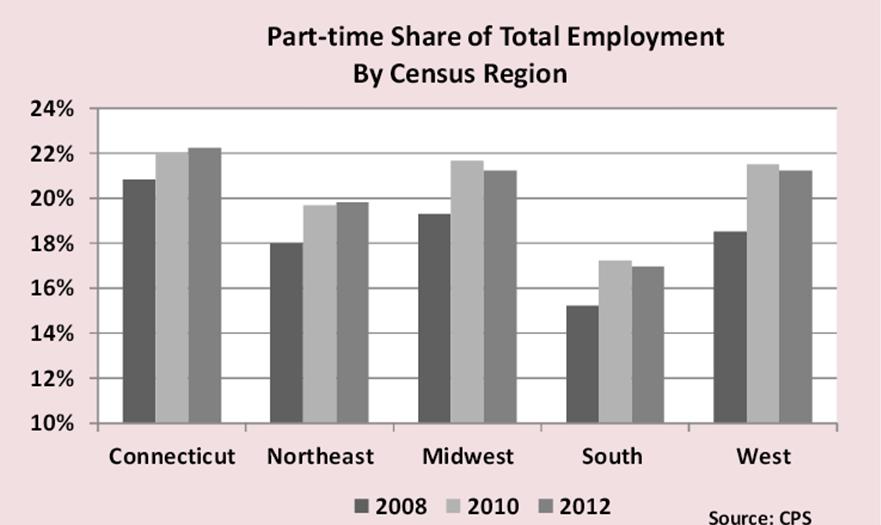
 a and the basis for the analysis. The breakdown of hours worked shows that Connecticut has less under 35 hours per week employment than other New England states but more than the Northeast region overall.
Part-time employment was 23.3% of all New England employment in 2012, higher than any other census division in the country. The other eight census divisions averaged 19.3% with the West- South Central division lowest at 16.4%.
a and the basis for the analysis. The breakdown of hours worked shows that Connecticut has less under 35 hours per week employment than other New England states but more than the Northeast region overall.
Part-time employment was 23.3% of all New England employment in 2012, higher than any other census division in the country. The other eight census divisions averaged 19.3% with the West- South Central division lowest at 16.4%.